Pathology of Endometrial Hyperplasia
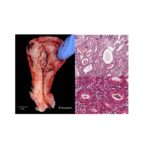
ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIA Definition: is defined as an abnormal proliferation of the endometrial glands relative to the stroma, resulting in an increased gland-to-stroma ratio Most common symptom:
Read MorePathology of Iron Deficiency Anemia
Define Anemia Anemia is defined as a reduction of total circulating red cell mass or hemoglobin concentration or oxygen carrying capacity of blood below normal limits that is expected for a healthy
Read MorePathology of Meningioma
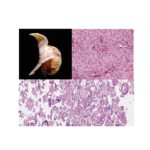
Meningioma: Meningioma is a predominantly benign tumour of meninges occuring in the adult population. It arises from the meningothelial cells of the arachnoid. These tumours are usually attached to
Read MoreGRANULOMATOUS INFLAMMATION
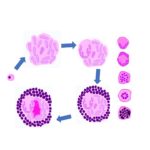
GRANULOMATOUS INFLAMMATION It is a form of chronic inflammation characterized by collections of “Activated” Macrophages, T lymphocytes and sometimes with necrosis. Before we understand granuloma, let
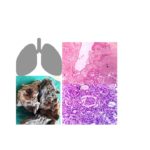
Read MorePathology of Bronchogenic carcinoma /squamous cell carcinoma-lung
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer related mortality globally. Lung cancer occurs mostly in the age-group of 40 to 70 years. Etiology of Lung cancer Tobacco smoking- Most important. The
Read MorePathology of PAROXYSMAL NOCTURNAL HEMOGLOBINURIA
Definition: Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a disease that results from acquired mutations in the phosphatidylinositol glycan complementation group A gene (PIGA), an enzyme that is
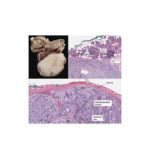
Read MorePathology of Pleomorphic Adenoma
Pleomorphic adenomas are benign ‘mixed’ tumors that consist of varying proportions of epithelial and mesenchymal elements. The word “Pleomorphism” denotes the architectural complexity. They represent
Read MorePathology of SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA
SKIN CANCER Three important types of skin cancer Basal Cell Carcinoma ( BCC): Most common, locally aggressive Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): Second most common, Aggressive MELANOMA: Most LETHAL! Risk
Read More