SKIN CANCER
Three important types of skin cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma ( BCC): Most common, locally aggressive
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): Second most common, Aggressive
MELANOMA: Most LETHAL!
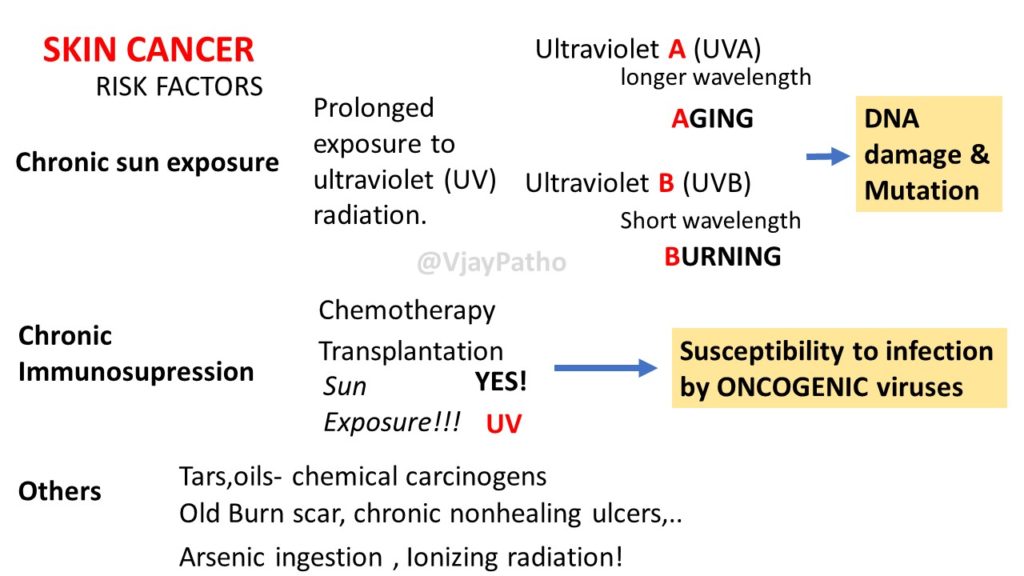
Risk factors
1. Chronic sun exposure: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation.Ultraviolet A ( longer wavelength) & (UVA)Ultraviolet B (UVB)( Short wavelength) leads to DNA damage and mutation.
2. Chronic Immunosupression: Eg, Chemotherapy, transplation and sun exposure leads to increased susceptibility to infections by oncogenic viruses.
3. Others: Tars,oils- chemical carcinogens
Old Burn scar, chronic nonhealing ulcers,..
Arsenic ingestion , Ionizing radiation!
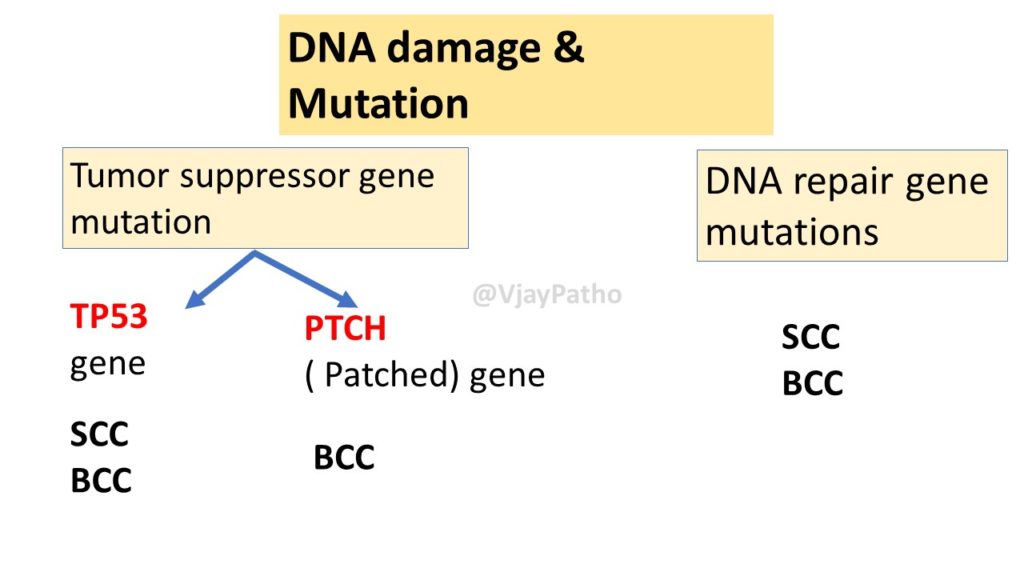
XERODERMA PIGMENTOSUM: Genetic disorder with Inherited mutation in DNA repair genes leads to Increased susceptibility to skin cancers
The illustration below show the common genes associated with skin cancers.
Precancerous/ premalignant Lesions – skin: These are morphologically altered lesions which can progress to cancer. Dysplasia of epidermal keratinocytes can involve the lower portion of the epidermis or the full thickness. These are usually UVR induced. These include ACTINIC KERATOSES and BOWENS DISEASE.
ACTINIC KERATOSES: single or multiple, discrete, dry, rough, adherent scaly lesions occur on the sun-exposed skin of adults.Microscopically Dysplasia of epidermal keratinocytes can involve the lower portion of the epidermis
BOWENS DISEASE/Squamous cell carcinoma in situ: usually a large, sharply demarcated, scaly, erythematous plaque which resembles a psoriatic lesion.Microscopically dysplasia of epidermal keratinocytes involve the full thickness.
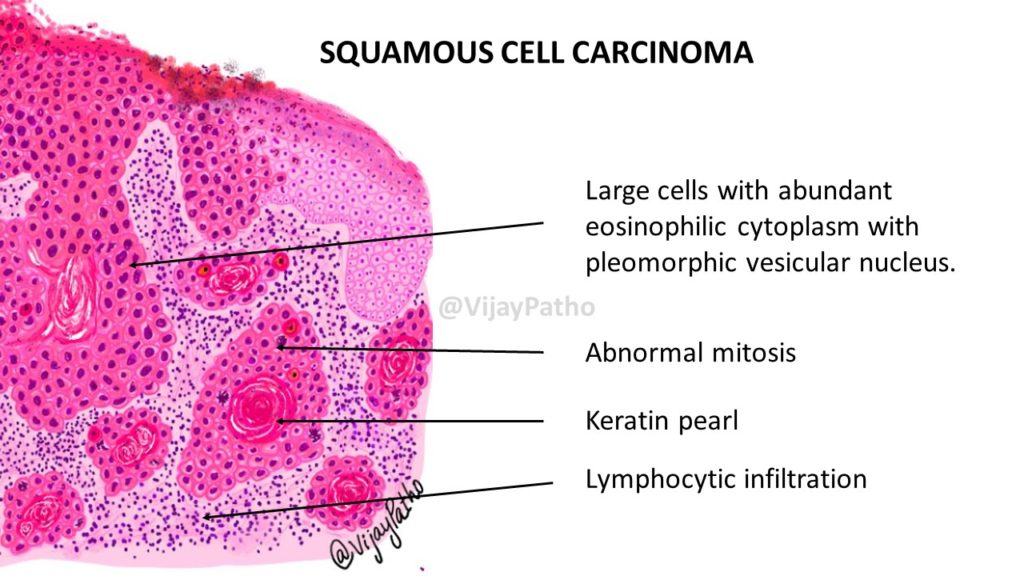
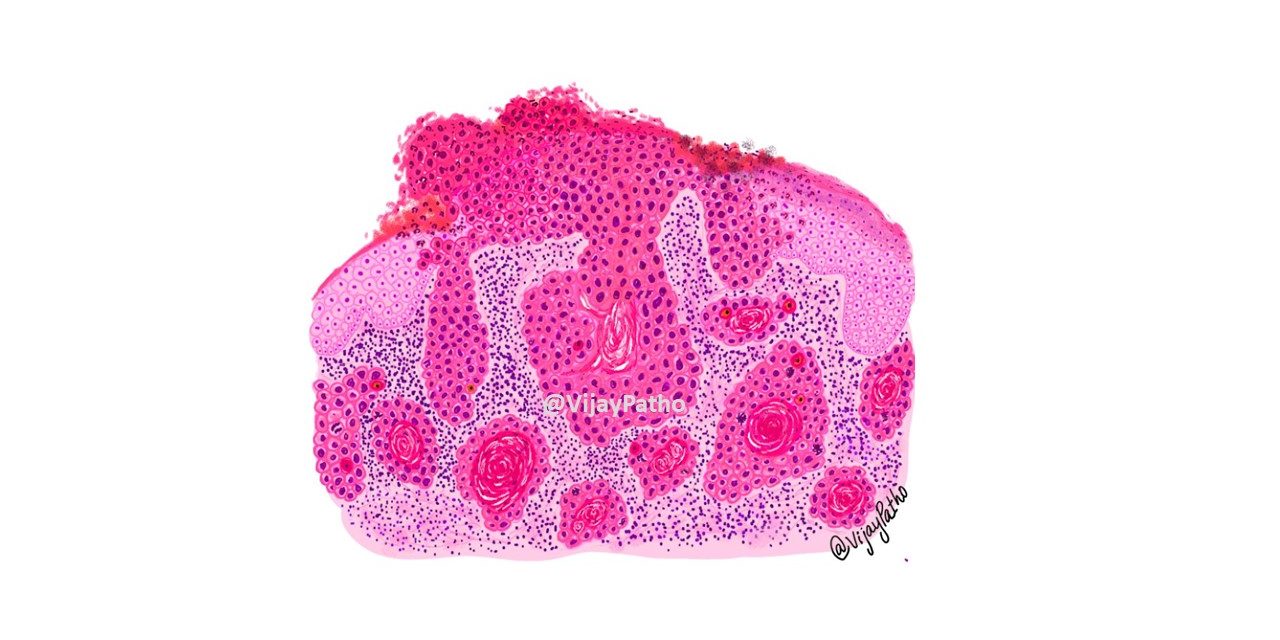
SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA(SCC)
Second most common tumor arising on the sun exposed sites.
Males have slightly higher preponderance than females.
Often White skin individuals where the etiology is almost always UVR induced.
Brown- or black-skinned persons can develop SCC from numerous etiologic agents other than UVR.
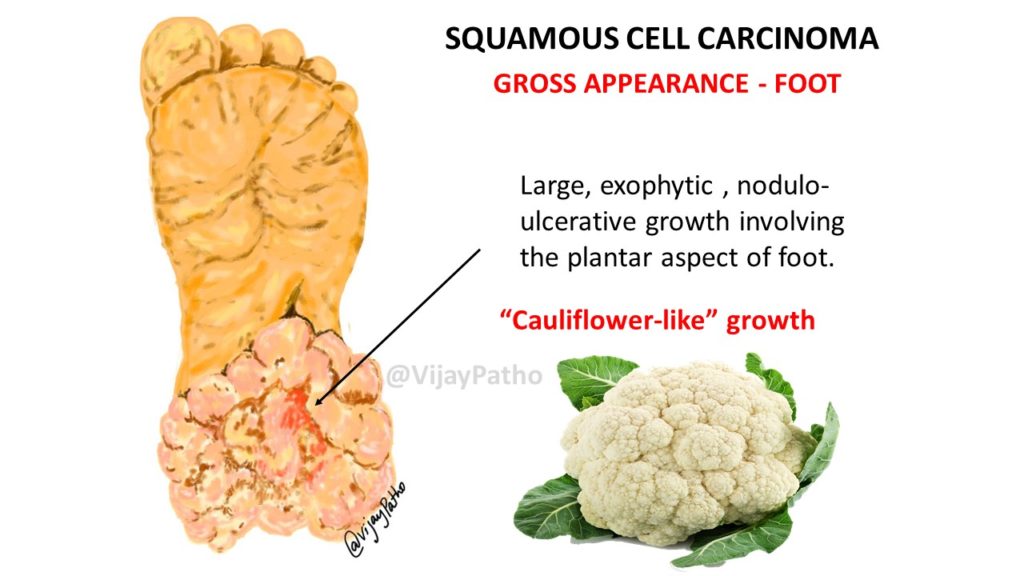
Clinically: Variable morphology depending on the age of the lesion. It can be aa large subtle nodule or round nodule with central hyperkeratosis which is firm and indolent. Rarely can be a large verrucuous/ cauliflower like lesion.
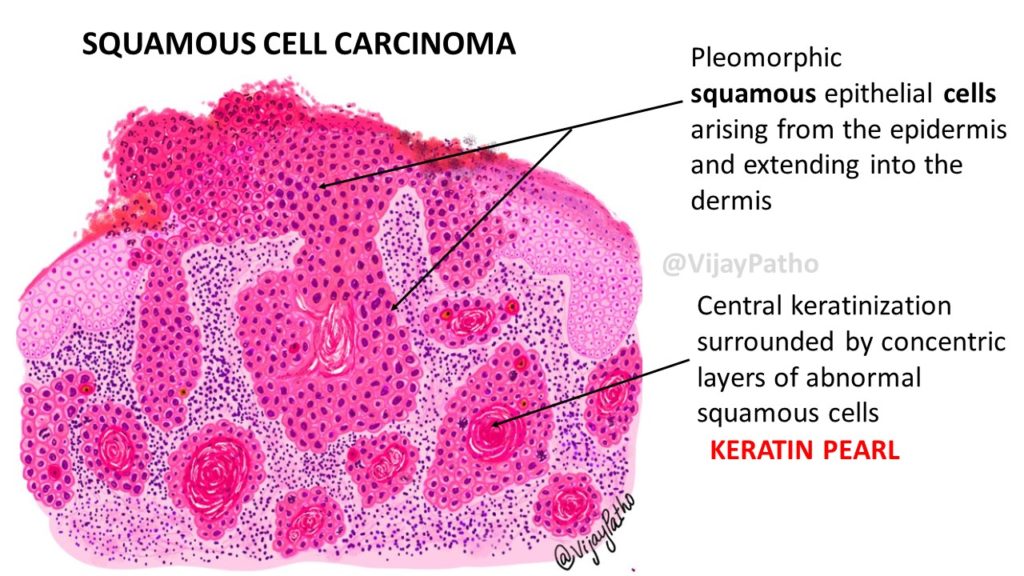
Microscopy:
Pleomorphic squamous epithelial cells arise from the epidermis and extend into the dermis.
Individual cells are Large cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm with pleomorphic vesicular nucleus.
Numerous keratin pearls will be noted which are areas of central keratinization surrounded by concentric layers of abnormal squamous cells






Recent Comments