Alcoholic liver disease: Morphology, Clinical features & Complications
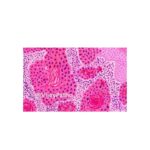
Alcoholic liver disease: Morphology, Clinical features & Complications ALCOHOLIC STEATOSIS- FATTY LIVER Gross: Size- enlarged Capsule: stretched Margins: round Color: yellowish gray The cut
Read MoreAlcoholic liver disease: Types & Pathogenesis
ALCOHOLIC LIVER DISEASE Excessive alcohol (ethanol) consumption is a major cause of liver disease, accounts for 5.9% of deaths globally - leads to death and disability earlier in life than other forms
Read MoreURINARY CRYSTALS
CRYSTALLURIA : Crystals in urine This is a frequent finding in the routine examination of urine sediments. COMMON REASONS for crystalluria Transient supersaturation of the urine Ingestion of certain
Read MoreBarr body / X- Chromatin / Sex Chromatin & Davidson body
Barr body Barr body is the small darkly stained structure, in the nucleus. In the majority of cases, it is found in the periphery of the nucleus, in minority of cases, it is seen in other parts ,
Read MoreCutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What is Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma? • Malignancy of epidermal keratinocytes with variable degrees of differentiation and cytological features Sites • Most often in sun exposed areas •
Read MoreIntradermal Nevus
Intradermal nevus Melanocytes: these are the pigment producing cells in the skin which are present in the dermoepidermal junction. They are also seen in hair follicles. Melanocytic nevi: benign
Read More