CRYSTALLURIA : Crystals in urine
This is a frequent finding in the routine examination of urine sediments.
COMMON REASONS for crystalluria
Transient supersaturation of the urine
Ingestion of certain foods
Changes of urine temperature and/or pH which occur upon standing after micturition
Eg: Precipitation of urates and phosphates when refrigerated.
Calcium phosphate precipitates when pH increases ( due to multiplication of bacteria )
Hence Urine should be handled as early as possible in normal temperature. No refrigerated sample for studying crystals
PATHOLOGICAL CONDITIONS associated with crystalluria
Urolithiasis
Nephropathy . Uric acid nephropathy
Poisoning ( ethylene glycol )
Various drugs
HOW TO IDENTIFY crystals??
By Proper approach! Knowledge of pH is an Important prerequisite
Crystals in acidic urine
Calcium oxalate
Uric acid
Urates –amorphous
Cystine
Tyrosine
Leucine
Cholesterol
Crystals in alkaline urine
Calcium phosphates
Triple phosphates
Phosphates- amorphous
Calcium carbonate
Ammonium biurate
PHASE CONTRAST microscopy is best to study crystals. HOWEVER, may not be available in most places and Bright field microscopy is good too!
Let us look into the common crystals in urine and their morphological appearance in bright field microscopy.
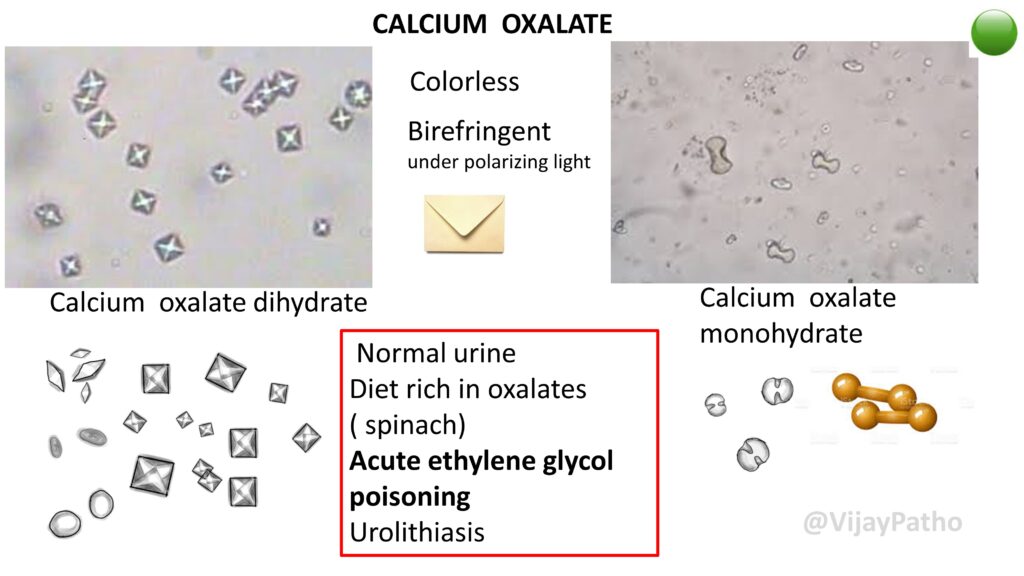
CALCIUM OXALATE
Colorless , Birefringent under polarizing light
Calcium oxalate dihydrate are envelope shaped crystals whereas Calcium oxalate monohydrate are hourglass or dumbell shaped.
Conditions associated :
Normal urine
Diet rich in oxalates
( spinach)
Acute ethylene glycol poisoning
Urolithiasis
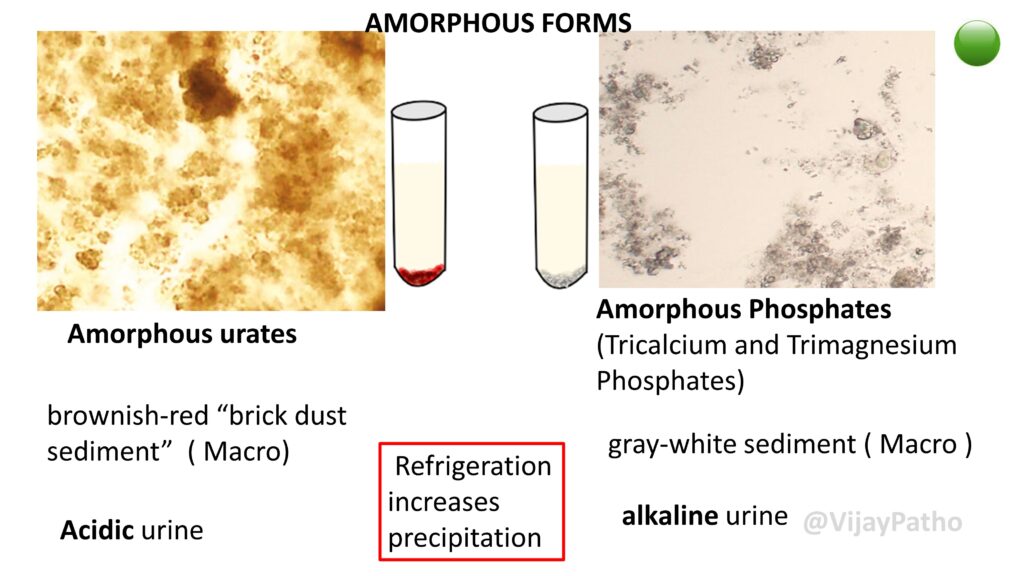
AMORPHOUS FORMS
Amorphous urates: brownish-red “brick dust sediment” ( Macro). Seen in acidic urine.
Amorphous Phosphates (Tricalcium and Trimagnesium Phosphates) , gray-white sediment ( Macro ) Seen in alkaline urine.
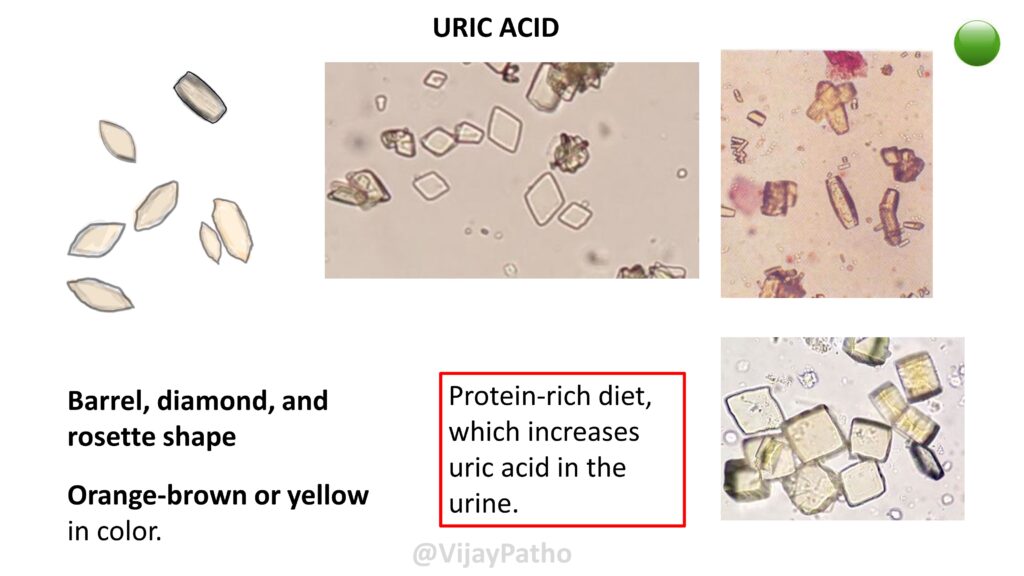
URIC ACID
Barrel, diamond, and rosette shape, Orange-brown or yellow in color.
seen in patients with Protein-rich diet, which increases uric acid in the urine.
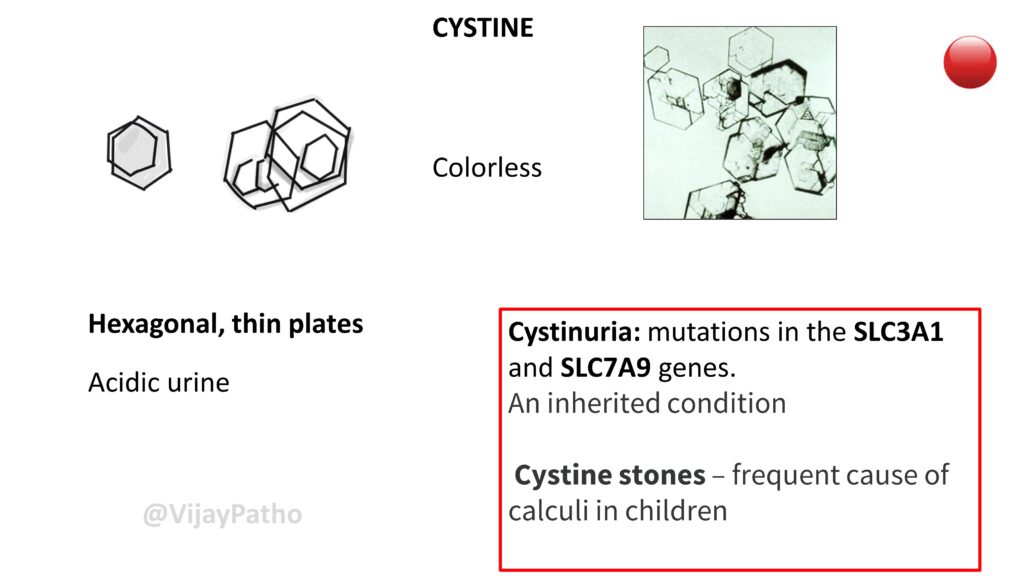
CYSTINE
Colorless, Hexagonal, thin plates seen in Acidic urine
condistions associated :
Cystinuria: mutations in the SLC3A1 and SLC7A9 genes.An inherited condition
Cystine stones – frequent cause of calculi in children
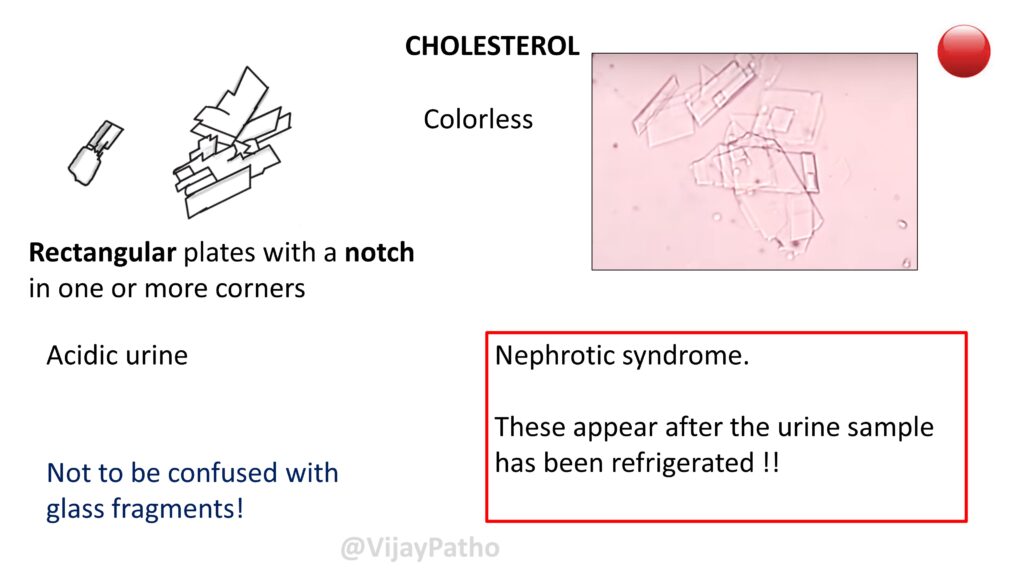
CHOLESTEROL
Colorless , Rectangular plates with a notch in one or more corners seen in Acidic urine
Not to be confused with glass fragments!
Conditions associated : Nephrotic syndrome.
These appear after the urine sample has been refrigerated !!
TYROSINE
Colorless to YELLOW BROWN Needles. Straight or bent! Arranged in sheaves or bundles, seen in acidic urine.
conditions associated :
Tyrosinemia
Liver diseases

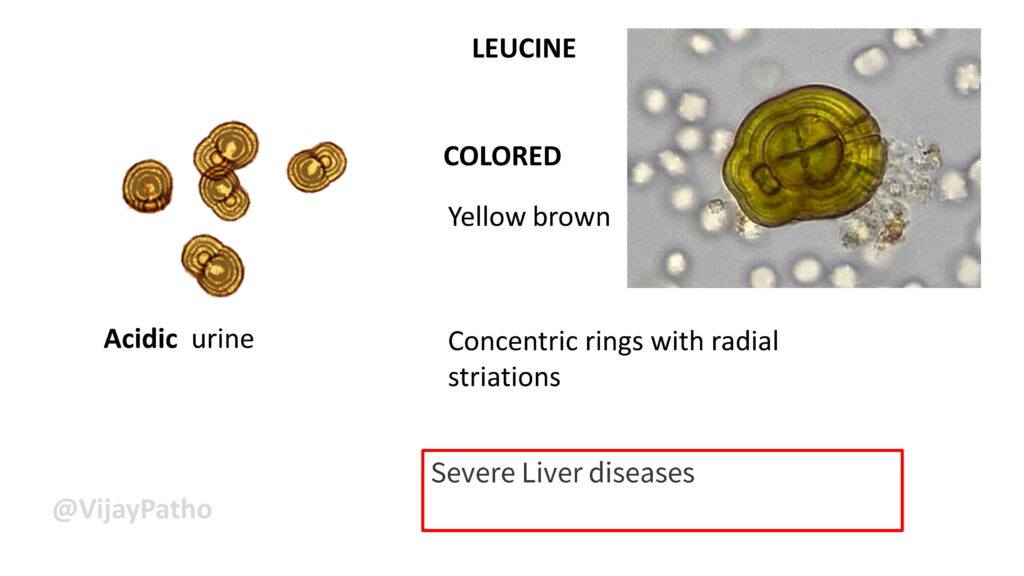
LEUCINE
COLORED , Yellow brown, Concentric rings with radial striations Seen in Acidic urine
Seen in patients with Severe Liver diseases
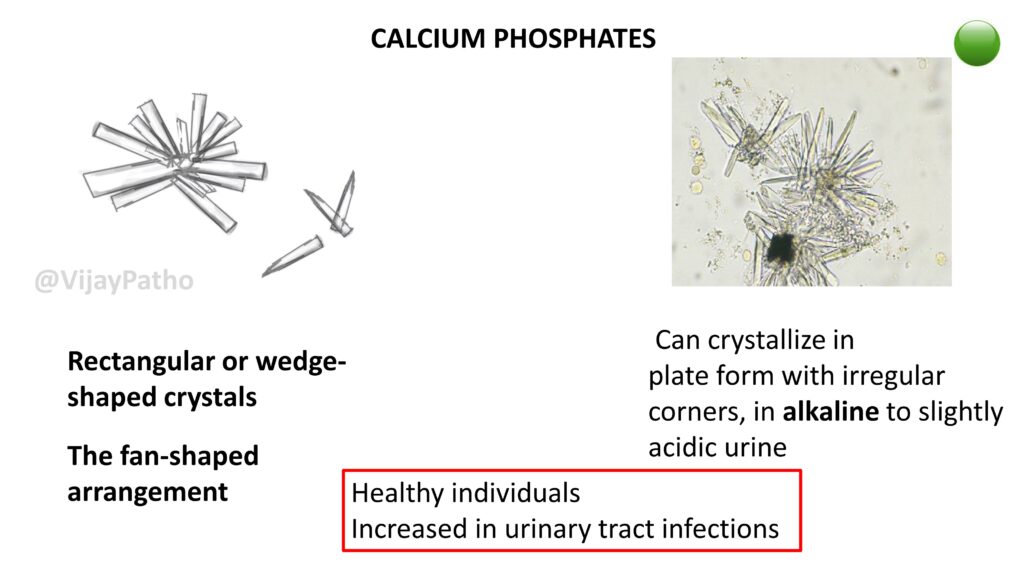
CALCIUM PHOSPHATES
Rectangular or wedge-shaped crystals, with the characteristic The fan-shaped arrangement
Can crystallize in plate form with irregular corners, in alkaline to slightly acidic urine.
Seen in Healthy individuals. Increased in urinary tract infections
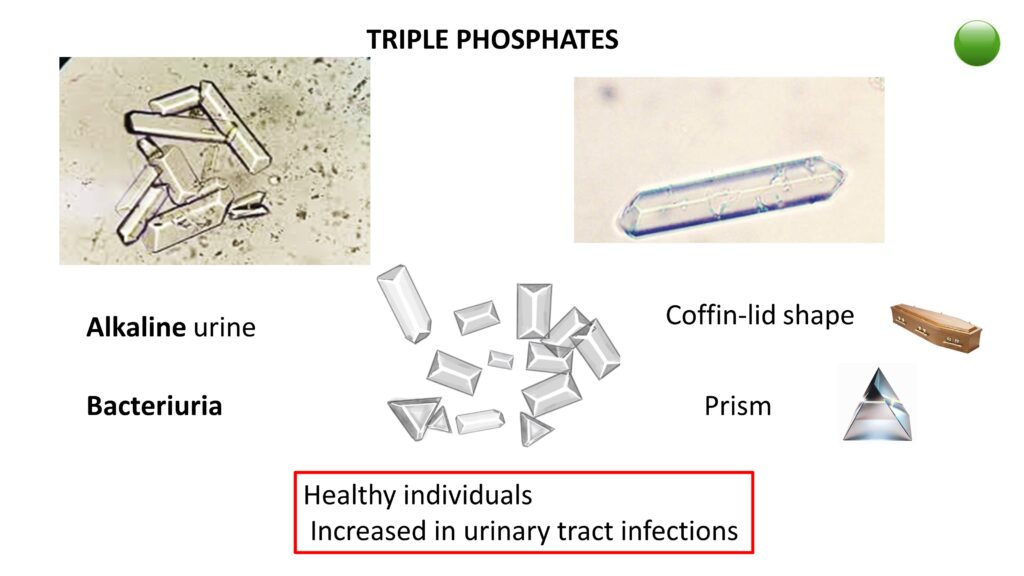
TRIPLE PHOSPHATES
Coffin-lid shape to prism shaped colorless crystals, seen in alakaline urine. Obsevrved Healthy individuals. Increased in urinary tract infections
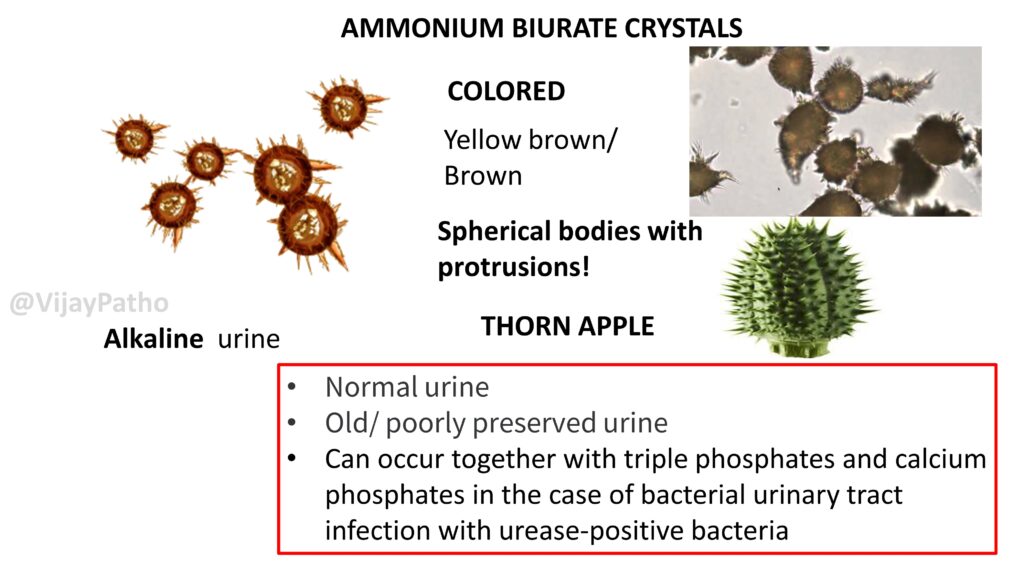
AMMONIUM BIURATE CRYSTALS
COLORED , Yellow brown/ Brown Spherical bodies with protrusions! hence named ” Thorn apple” appearance. seen in Alkaline urine
Conditions associated :
Normal urine
Old/ poorly preserved urine
Can occur together with triple phosphates and calcium phosphates in the case of bacterial urinary tract infection with urease-positive bacteria
Points to remember!
Identifying crystals under a microscope does not guarantee that they were present in the urinary system.
They can continue to form after micturition . Can precipitate due to variations in temperature and pH
Crystals are not always Pathological
Yet it is important to Know the Abnormal crystals!






Recent Comments