Helicobacter Pylori
Slender curved rods with polar flagella ( Rapidly motile due to the action of flagella )
Gram negative, Only human bacteria to persistently inhabit the gastric mucus.
Cannot colonize duodenum/esophagus unless they have undergone gastric metaplasia
Unique bacteriologic features of H Pylori
1. Flagella – Moves/swim to less acidic locale- beneath the gastric mucus
2. urease – Generates ammonia, Increases pH AND Allows organism to persist in low pH environment
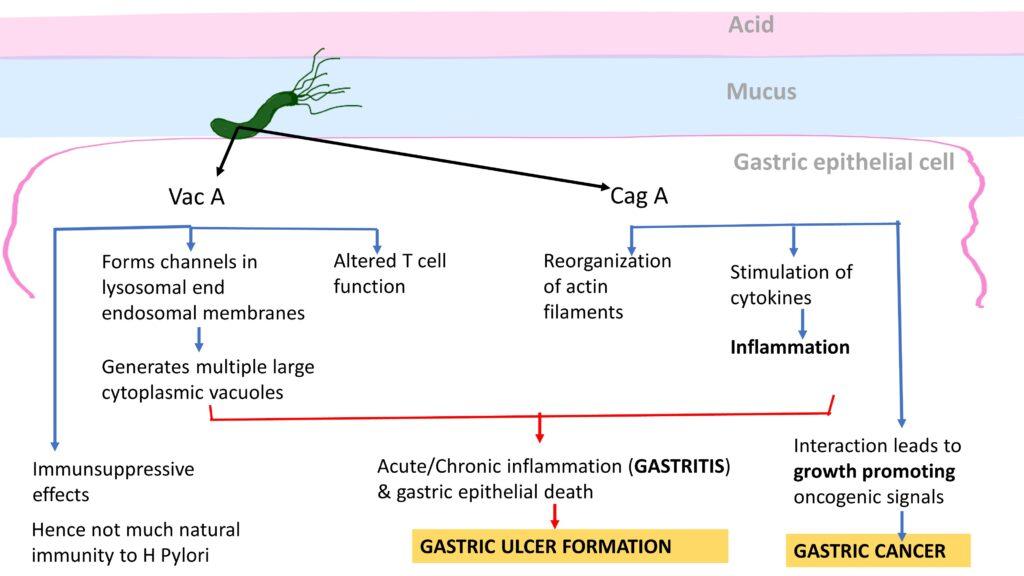
3. Vacuolating cytotoxin A ( VacA) – CYTOTOXIN
4. cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA) – Proinflammatory & Pro proliferative
Pathogenesis:
Not all individuals colonized by H Pylori develop disease , Only 15% develop disease
Pathogenesis depends on Virulence , Host genetic susceptibility & Environmental co factors.
pathogenesis is illustrated as below
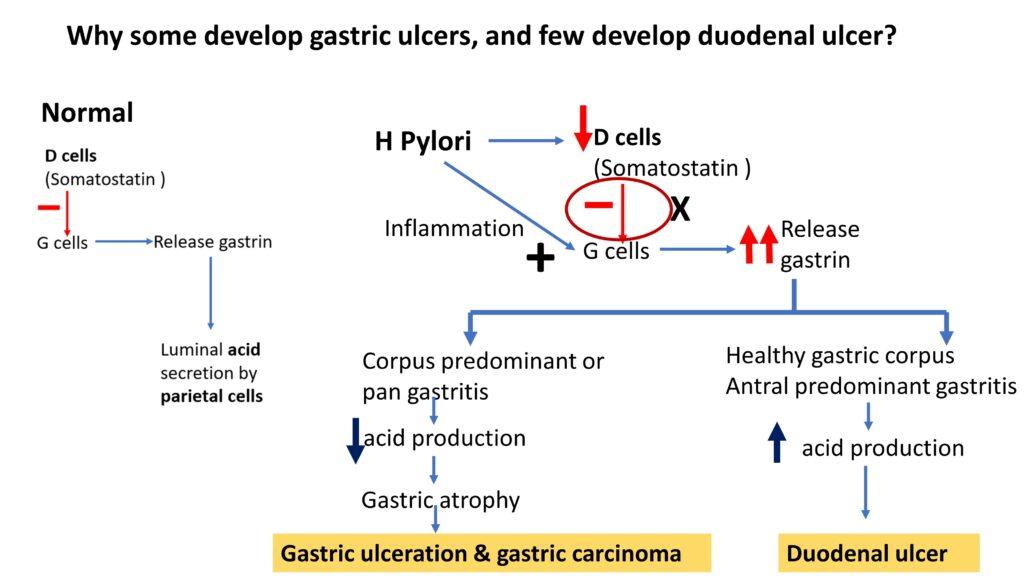
Why some develop gastric ulcers, and few develop duodenal ulcer?
H Pylori results in inflammationm and G cell hyperplasia, leading to increased release of gastrin. If the inflammation i scorpus predominant, there is decreased gasric acid production and atrophy which further leads to gastric atrophy and carcinoma. IF the corpus is healthy and teh gastritis is predominantly antral, then it leads to increased acid production which moves to duodenum and cause duodenal ulcer. the same is illustrated as below.
Note: H Pylori induces gastric atrophy , which progresses to adenocarcinoma even if H Pylori is treated!!!
How gastric atrophy is implicated in adenocarcinoma?
GASTRIC ATROPHY leads to Increased ROS ( due to inflammatory cells ) , Over growth of other bacteria and Loss of sonic hedgehog expression ( Expresses cell to mutagenic agents) all leading to increased risk of adenocarcinoma.
Clinical features
Nausea upper abdominal pain
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease leading to nausea, anorexia, omitting epigastric pain, belching etc..
Many can be asymptomatic for decades
Perforation can lead to extensive bleeding and peritonitis
Diagnosis
Most sensitive – endoscopy +biopsy & culture of gastric mucosa
Non invasive – Serology – Antibody detection IgG/IgA; Urea breath test – Ingestion of 13C/14C labelled urea – Labelled CO2 ( appears in breath)
Stool antigen detection test- sensitive indicator of colonization
Special stain- Giemsa, Diff- Quick, Warthin-Starry
IHC- in difficult cases, and specially after therapy
Molecular : by polymerase chain reaction
Sequalae
Peptic ulcer and Adenocarcinoma
Intense inflammation with lymphoid follicles and prominent germinal centers ( Represent Mucosa associated Lymphoid Tissue)
Has Potential to transform to Lymphoma
Thus, chronic H. pylori gastritis is associated with increased risk of both gastric adenocarcinoma and lymphoma.
Treatment
90% cure rate with quadruple regimen- 14 days ( Bismuth subsalicylate, PPI, tetracycline & metranidazole)
Triple therapy is less effective
Prophylactic treatment of ASYMPTOMATIC persons colonized by H Pylori is NOT recommended
CLICK below To view the video tutorial on the above topic








Recent Comments