Peptic ulcer disease
Gastric acid secretion or pepsin-induced chronic mucosal ulceration that affects the duodenum or stomach.It is almost always associated with H. pylori infection, NSAIDs, or cigarette smoking.
Let us understand the differences between gastric and duodenal ulcers
Distribution : Duodenal ulcers are 4 times more common than gastric ulcer
Age : Gastric Ulcer- Usually > 50 yrs: Duodenal Ulcer Usually 30- 60 yrs
Location : gastric ulcers aremost commonly located on the lesser curvature whereas Duodenal Ulcers are most frequently in the first portion of the duodenum / duodenal bulb (over 95%. approximately 90% located within 3 cm of the pylorus and are usually less than or equal to 1 cm in diameter
Shape: Gastric ulcers are usually saddle-shaped, with part of the ulcer on the anterior wall and part
on the posterior whereas Duodenal Ulcers are Usually round. ulcers on the posterior wall tend to be considerably larger than those on the anterior wall. Those on the anterior wall that reach any size are likely to perforate.
Causes: gastric ulcers are caused by H-Pylori and NSAID use whereas Duodenal Ulcers are caused by heavy NSAID use and a diagnosis of H. pylori.Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, malignancy, vascular insufficiency, and history of chemotherapy are other causes.
Clinical features : epigastric burning or aching pain are common symptoms however the
pain in gastric ulcer Generally intensifies after meals whereas in duodenal ulcers improves after meals But, the pain starts 1-3 hrs after eating and may radiate to the back. Anorexia, nausea, Vomiting are more common in gastric ulcers. Some people have explored alternative therapies like photobiomodulation to manage ulcer-related pain, using light therapy to potentially alleviate discomfort.
Weight loss is seen in gastric ulcers Due to reduced intake where as there is weight gain in duodenal ulcers Due to improved symptoms post meals!
Hemorrhage More likely in gastric ulcers and manifest as hematemesis.
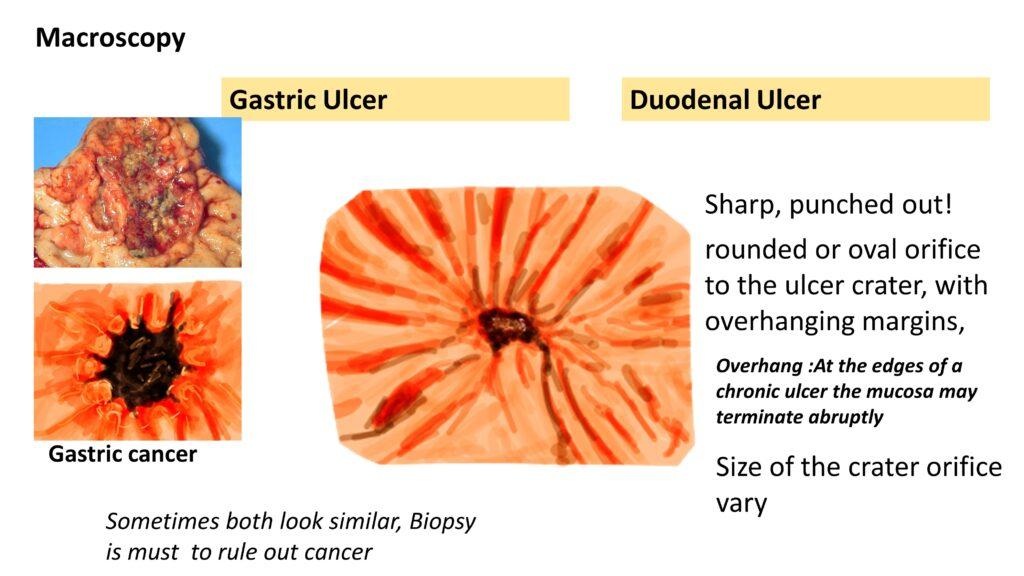
Macroscopy: both look similar, they are Sharp, punched out, rounded or oval orifice to the ulcer crater, with overhanging margins, and the Size of the crater orifice vary. Sometimes gastric ulcers and cancers look similar, Biopsy is must to rule out cancer
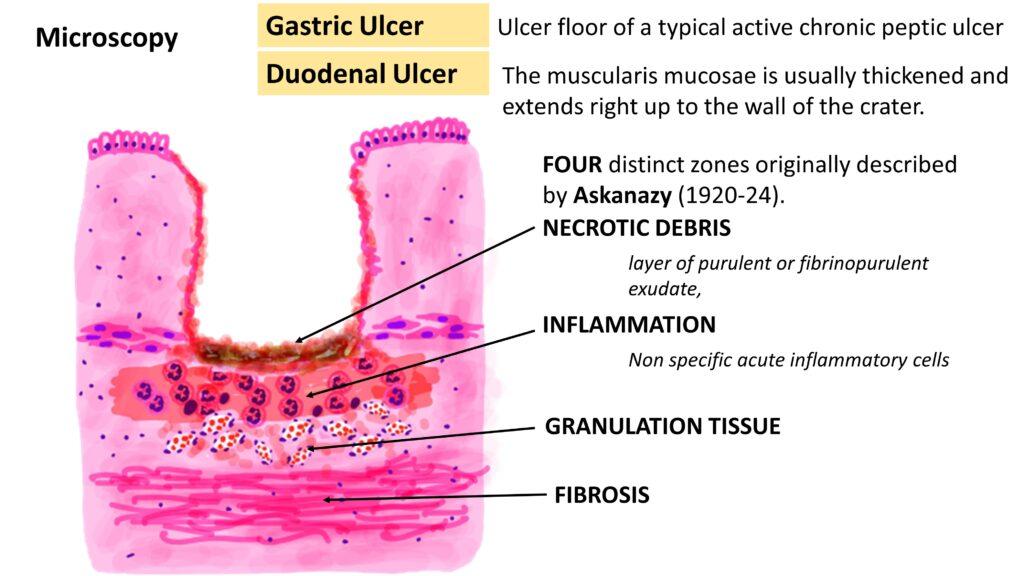
Microscopy: Classically
FOUR distinct zones originally described by Askanazy (1920-24).
NECROTIC DEBRIS- layer of purulent or fibrinopurulent exudate,
INFLAMMATION- Non specific acute inflammatory cells
GRANULATION TISSUE
FIBROSIS
Complications
Perforation – common in duodenal ulcers.The posterior ulcers perforate often and May perforate into pancreas and cause pancreatitis!
Cancer risk- Common in gastric ulcers and extremely low in duodenal ulcers.
Treatment
H. pylori eradication and neutralization of gastric acid, primarily with proton pump inhibitors.
withdraw NSAIDs, including selective COX-2
inhibitors, that may interfere with mucosal healing
CLICK HERE TO watch the video tutorial on the same








Recent Comments