Chronic venous Congestion – Liver
Cause: Right heart failure.
Right heart failure occurs when the right side of the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This can lead to an increase in pressure in the veins upstream of the heart, causing systemic venous congestion. The liver, along with the spleen and kidneys, is one of the organs that can be affected by this condition.
The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s metabolic functions. The hepatic veins drain blood from the liver and empty into the vena cava just below the heart. However, if there is an increase in pressure in the central vein, as in the case of right heart failure it can lead to congestion of the liver.
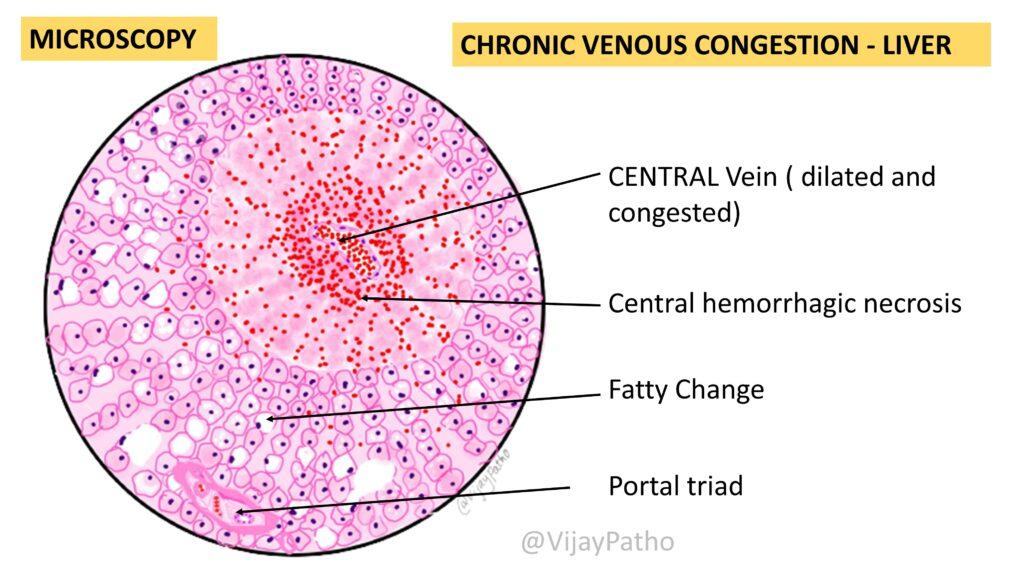
When there is an increase in pressure in the central vein, it is transmitted to the sinusoids, leading to the dilation of the sinusoids. This can result in pressure atrophy of the hepatocytes, especially in the centrilobular zone. there will be centrilobular hemorrhagic necrosis. Moreover, the mid-zone hepatocytes may also show fatty changes due to relative hypoxia. However, the peripheral zones of the lobule are relatively spared.
In long-standing cases of hepatic congestion, there can be thickening of the central vein, sinusoidal thrombosis, and strain that promotes fibrosis. Fibrosis is the buildup of excess fibrous tissue, leading to scarring and damage to the liver tissue.
In extreme cases, in conditions such as constrictive pericarditis or tricuspid stenosis, fibrosis becomes generalized and severe. This is referred to as cardiac cirrhosis, which is a condition where the liver is severely damaged due to heart disease.
Gross features:
the liver will be mildly enlarged and has dark and pale spots on the cut section. The dark spots are likely due to dilated and congested hepatic venules, while the paler areas indicate normal parenchyma. This pattern is similar to the appearance of a nutmeg when cut, hence the term “nutmeg liver.”
Microscopy:
The features are described in the illustration below.






Recent Comments