Pathology of Medullary Carcinoma- Breast
New terminology: ” Invasive breast carcinoma- not special type(IBC-NST) with medullary pattern”
IBC-NST with medullary pattern (Medullary carcinoma) appears usually in younger patients than that affected by invasive ductal carcinoma. The mean age is 45-54 years. it is a rapidly growing, round or oval, well-circumscribed tumor.
IBC-NST with medullary pattern (Medullary carcinoma) breast accounts for less than 5% of all invasive breast cancers.
Occurs more frequently in patients with mutations BRCA-1 Gene ( Tumor suppressor gene)
Medullary: The term” medullary “ is used as an adjective here, which refers to or which resembles “medulla” or a ” centre of a tissue” like that of a marrow. It can also represent medullary oblongata. Well, it just tells us that the given lesion is “ soft” in consistency!
Gross Appearance : The tumor is well circumscribed and soft in consistency and hence the name “ medullary”. Often it is lobulated. The cut surface is fleshy and gray-tan.
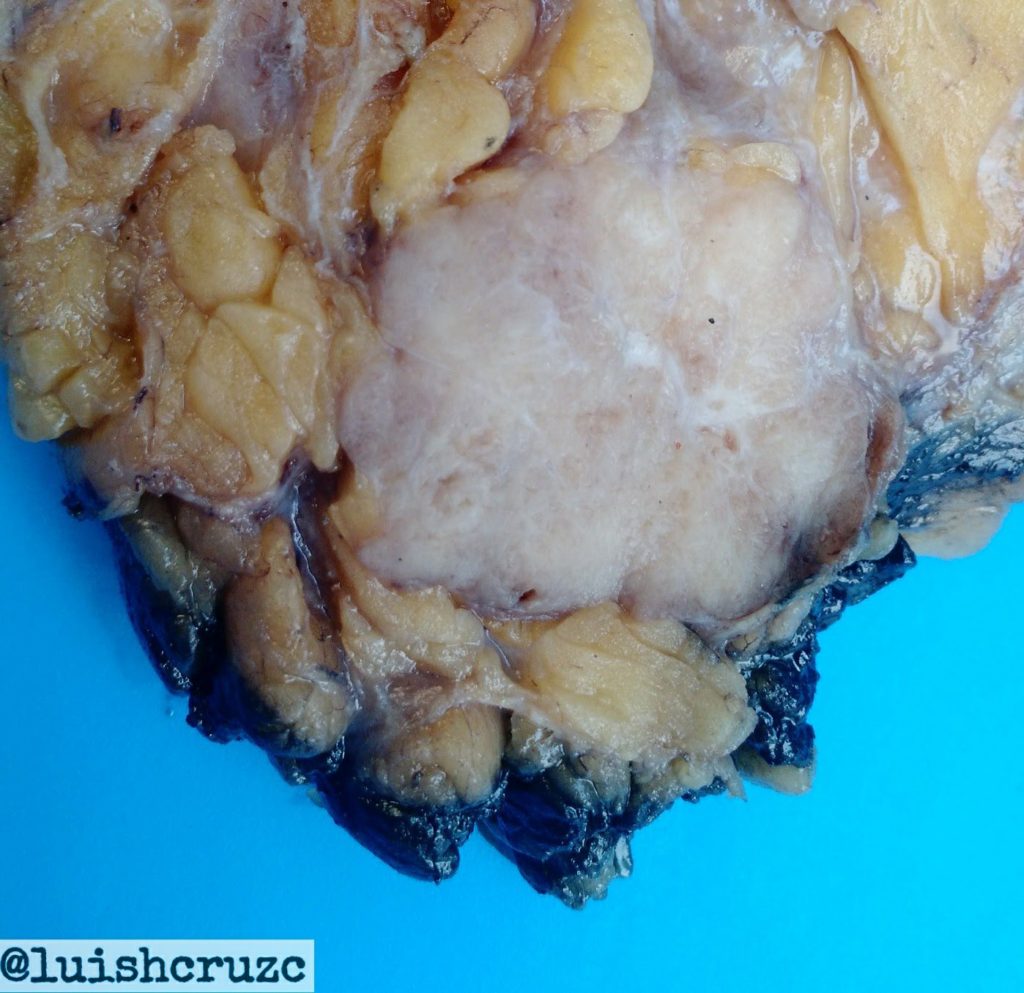 Photo credit: Dr Luis Humberto Cruz C
Photo credit: Dr Luis Humberto Cruz C
Microscopic appearance:
Diagnostic Criteria: these are the criteria which has to be strictly met
- Syncytial growth pattern in more than 75% of the tumor
- Intensive lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate in the stroma
- Noninfiltrating (“pushing”) tumor border /complete histologic circumscription
- Highly atypical tumor cells ( Moderate to marked nuclear pleomorphism)
- No glandular or tubular structures
Note: “syncytial” is an adjective which means constituting “syncytium”. Syncytium meaning mass of cytoplasm due to fusion of cells resulting in multinucleation. syn- ‘together/united’ + -cyte ‘cell’ + -ium.
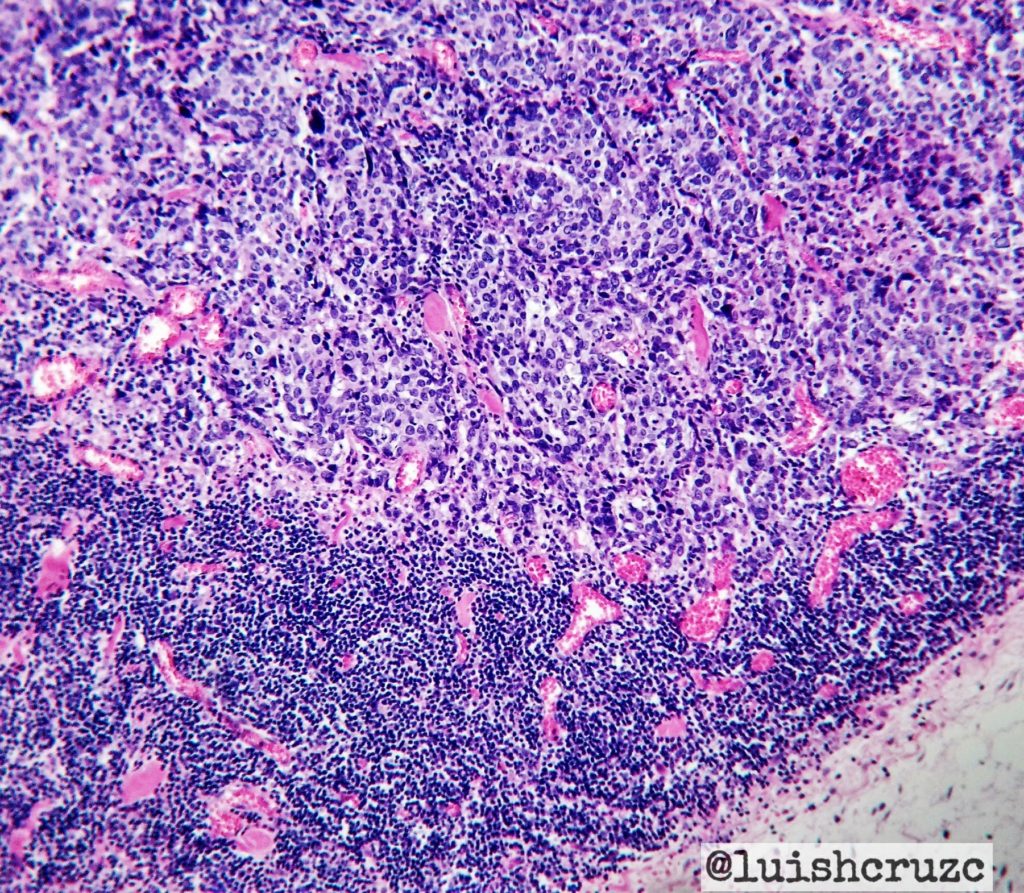 Syncitial growth pattern and dense lymphoplamacytic infiltrate. Photo credit: Dr Luis Humberto Cruz C
Syncitial growth pattern and dense lymphoplamacytic infiltrate. Photo credit: Dr Luis Humberto Cruz C
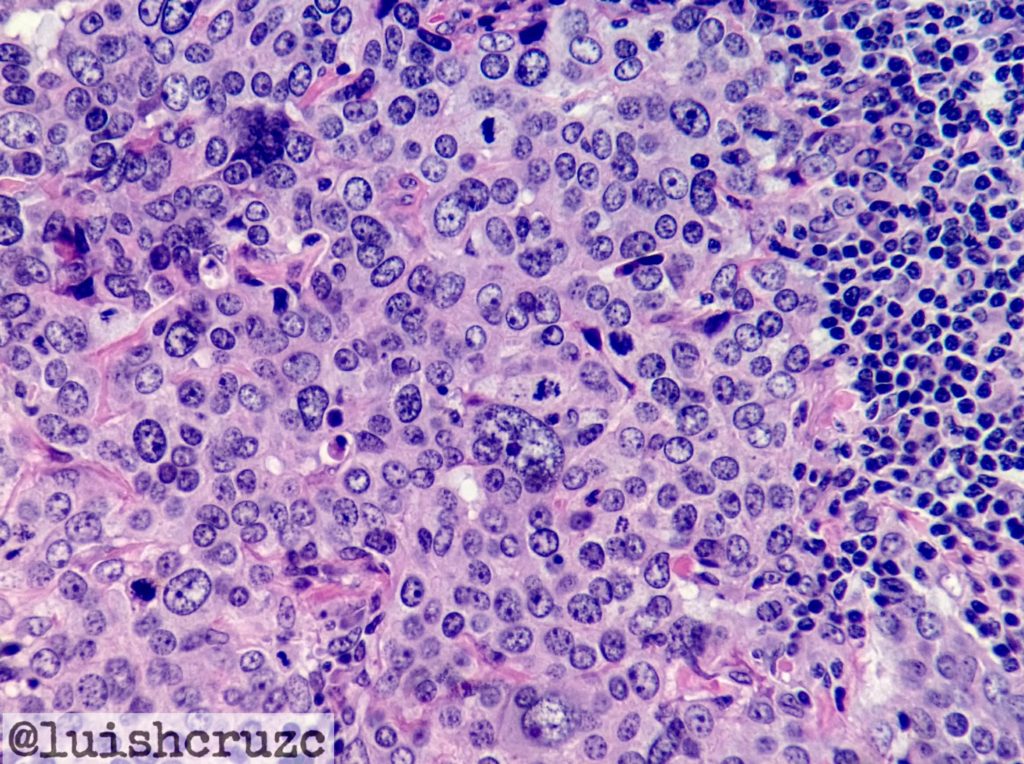 Higher magnification showing moderate to marked pleomorphism. Photo credit: Dr Luis Humberto Cruz C
Higher magnification showing moderate to marked pleomorphism. Photo credit: Dr Luis Humberto Cruz C
Atypical mitosis, multinucleated giant cells can rarely be seen.
In 2019 WHO classification of tumors of breast, medullary carcinoma/ carcinoma with medullary features is no longer a separate entity and it is renamed as ” Invasive breast carcinoma- not special type with medullary pattern”
Intense lymphocytic infiltrate reflects an active host response to the tumor. This feature accounts for its favorable prognosis and these tumors just represent one end of spectrum of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes- rich Invasive breast cancers-not special type.
CLICK HERE to read about pathology of Infiltrating duct carcinoma- breast








Recent Comments