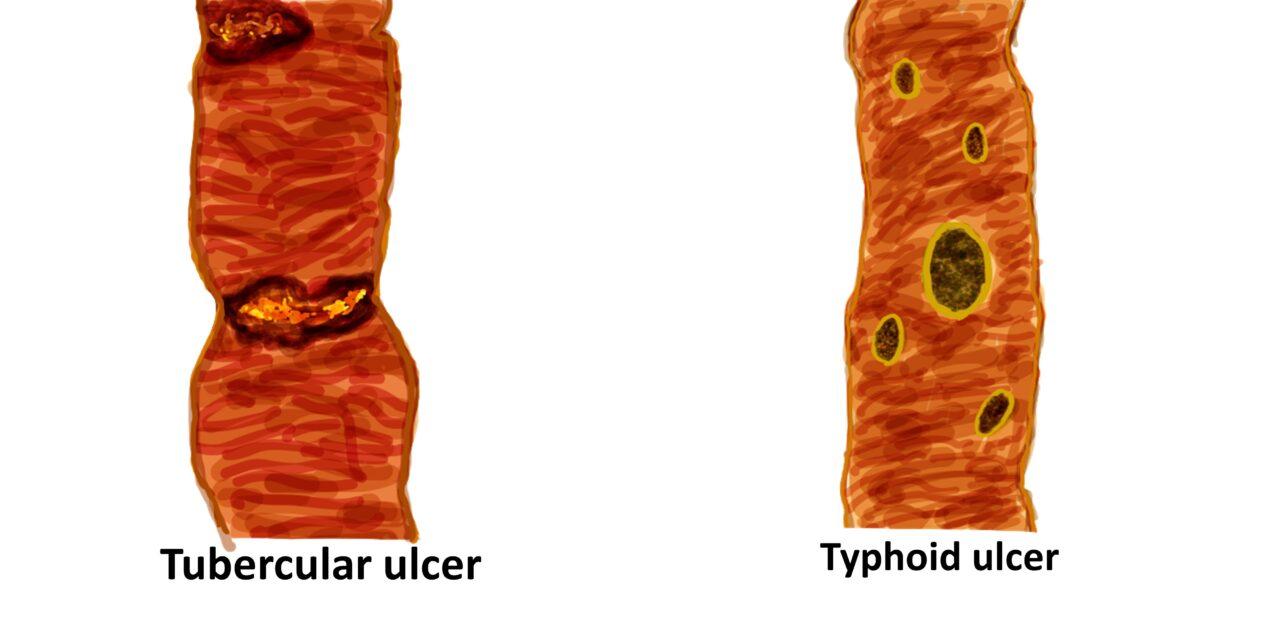
| TUBERCULAR ULCER | TYPHOID ULCER | |
|---|---|---|
| Causative organism | Mycobacterium tuberculosis , Acid fast bacteria | Salmonella typhi.,gram negative bactria |
| Distribution | Ileocecal region, Rarely other parts of GI tract | Most often small intestine, Terminal ileum is most common location. Can be seen in jejunum or rarely colon |
| Spread | via hematogenous spread, ingestion of infected sputum, OR direct spread from infected contiguous lymph nodes and fallopian tubes. | Typhoid is spread by poor sanitation and poor hygiene.Feco- oral route |
| CLINICAL FEATURES | ||
| Fever | Low grade fever, weight loss | Fever with chills, stepladder type of fever |
| Diarrhea/ constipation | Chronic diarrhea, features of obstruction | Constipation common, diarrhea rare |
| Abdominal pain | Present , long standing, may be colicky | Very common, may eb sudden onset |
| Abdominal mass | Sometimes | Unlikely |
| Ascitis | Common | Unlikely |
| MACROSCOPY | ||
| Ulcer arrangement | Transverse axis of the intestine- longest diameter perpendicular to the long axis of the gut | Longitudinal axis - longest diameter parallel to the long axis of the gut |
| related to the direction in which the lymphatic vessels run in the wall of the ileum | Organism, accumulates in lymphoid tissue in Peyer’s patches | |
| infection tends to spread along these lymphatics. | and causes the patches to become inflamed and ulcerated. | |
| Size and margins | Large, Irregular and can be involve the entire circumference | Small, variable . regular and ovoid |
| Base of ulcer | Creamy white , if caseous necrosis is present | Blackish , due to mucosal sloughing |
| Depth of ulcer | Depth of ulcer | Superficial and deep |
| Serosal surface | Often Show tubercles | Smooth unless there is perforation |
| MICROSCOPY | ||
| Type of inflammation | Chronic | Non-specific, often acute |
| Granulomas | Present | Absent |
| Erythrophagocytosis | Absent | Present . S. typhi survives intracellularly in macrophages.The bacilli stimulate macrophages to engulf erythrocytes!! |
| COMPLICATIONS | ||
| Bleeding | Uncommon | Common, Due to erosion of adjacent vessels |
| Perforation | Uncommon | present, most serious complications of typhoid fever |
| Stricture | present as a result of fibrosis | Absent |
| TREATMENT | Antitubercular drugs, Strictures/ obstruction- surgical intervention | Antibiotics, If complications ( bleeding/ perforation )- surgical/ medical intervention |
Tubercular vs Typhoid ulcer