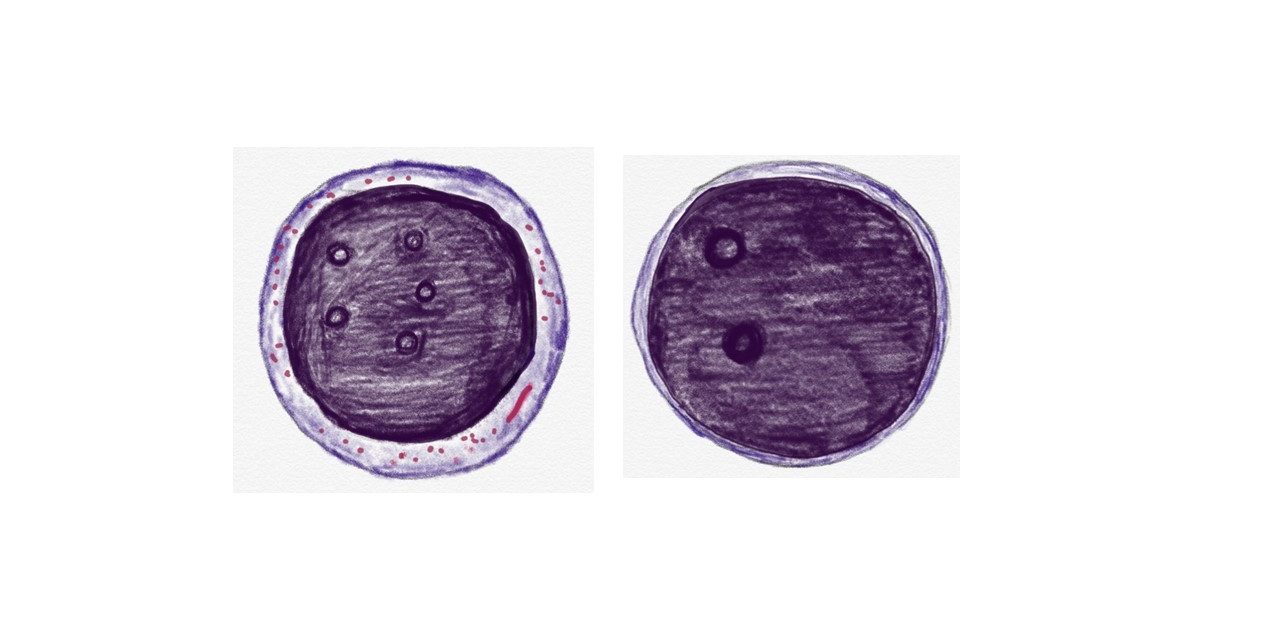
Myeloblast vs lymphoblast
If you are a student in Pathology, I am sure you would have come across a slide, where you had difficulty in in identifying it as myeloblast or a lymphoblast!
The question now is.. Is it necessary to differentiate this on a peripheral smear? The answer is NO! As long as you know that you are dealing with Acute leukemia.
“The phenotypic differentiation will be done either by cytochemical stains or immunophenotyping”
Before the advent of immunopheotyping, the diagnosis was based on morphology alone. Even the earlier classification of leukemias. I .e FAB classification was based on morphology.
Hence It would be interesting to know that, in a well stained slide, there are certain features which differentiates myeloblast from lymphoblast
Let’s know these one by one!
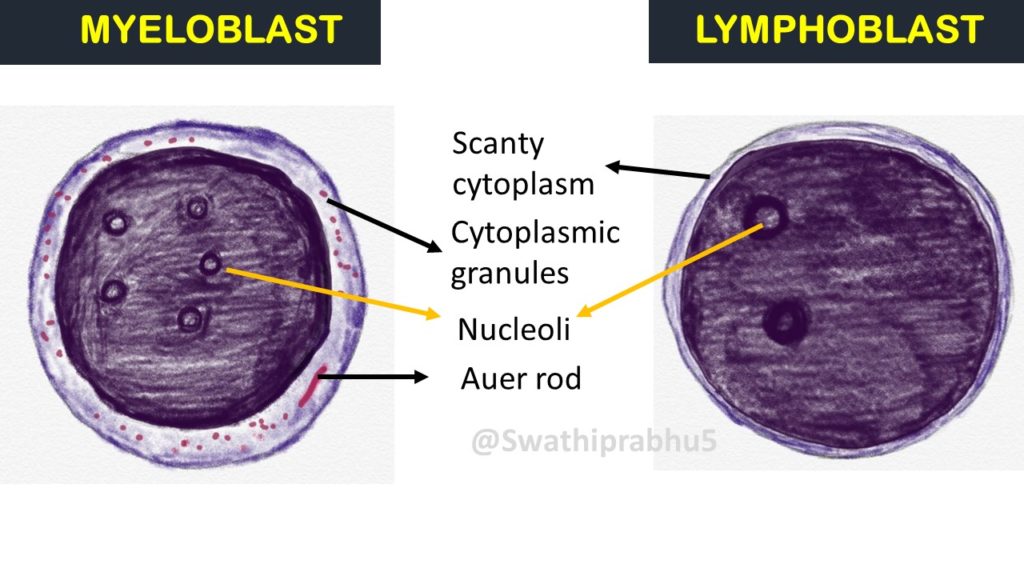
Myeloblast: This is the precursor cell of neutrophil, eosinophil and basophil. These are large cells, with scanty cytoplasm and with round or slightly irregular nuclei with fine chromatin and 3 to 5 prominent nucleoli.
Based on the nature of the granules, myeloblasts are further divided into
Type1: Agranular or with rare granules
Type 2: Pauci granular( <15 primary azurophilic granules)
Type 3: Granular ( >20 granules and no golgi zone)
Lymphoblast: This is the precursor of lymphocytes. These are large cells, with scanty cytoplasm and with round or slightly irregular nuclei with coarse chromatin and inconspicuous nucleoli.
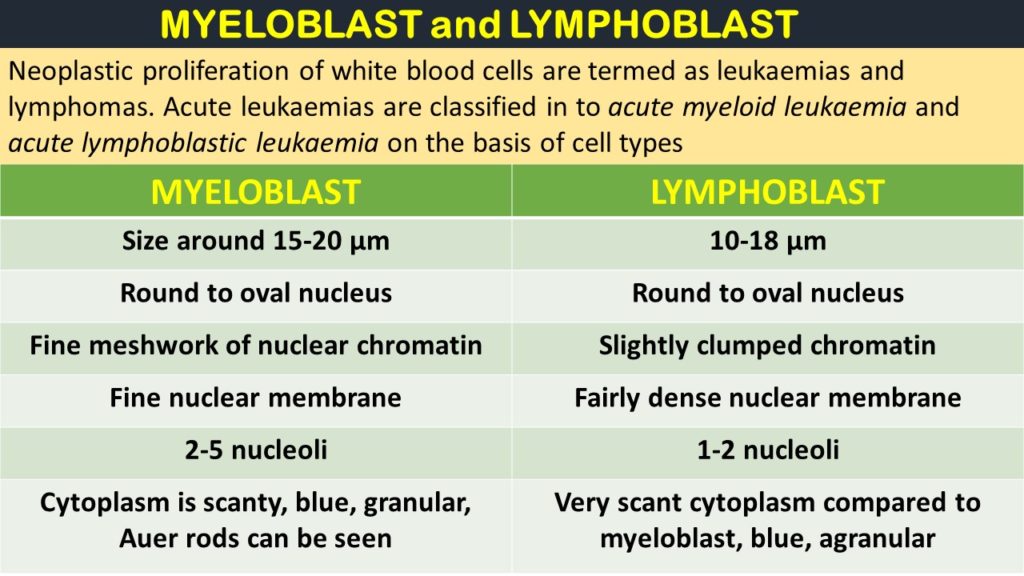
The differences between the two is illustrated in the following table
The differences are tabulated as below