| ULCERATIVE COLITIS | CROHN'S DISEASE | |
|---|---|---|
| Distribution | Gastrointestinal disease that is localized to the large intestine or colon Can either effect entire organ or a portion of it. Sigmoid colon common | CD can affect any part of the GI tract Can involve both the large and small intestines Terminal ileum and ascending colon |
| Prevalence | More prevalent | Less prevalent |
| Severity | Less severe than Crohns | More severe than UC |
| Rectal involvement | Always | Rare |
| Clinical features | ||
| Diarrhea | Bloody | Usually not bloody |
| Abdominal pain | Crampy pain , often before passing stool | Present |
| Abdominal mass | Absent | May be Present |
| Macroscopy | ||
| Skip lesions | Absent ( diffuse lesions) | Present ( segmental/ patchy pattern) |
| Type of ulcer | Pin point Superficial | Linear Deep, fissuring Leading to fistula/abscess |
| Fistula formation | Absent | Common |
| Bowel Wall appearance | Thin | Thick |
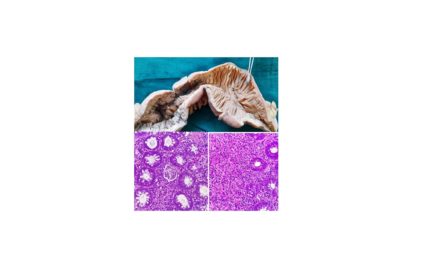
| In advanced cases of both the diseases, due to extensive inflammation and fibrosis, the intestine wall become featureless and resembles a lead pipe or hose pipe. RIGID FEATURELESS PIPE | If the hose pipe appearance is predominantly large intestine , it favors ulcerative colitis | If the hose pipe appearance is predominantly involving small intestine , it favors Crohn’s disease |
| Cobble stone appearance Due to deep mucosal ulceration intermingled with nodular submucosal thickening. Deep ulcers with longitudinal array creates a cobblestone appearance | Absent | Present |
| Pseudo polyps They are not polyps in the typical sense. | Present Residual edematous mucosa sitting, like an island, on a sea of surrounding ulceration. | Not seen |
| Fat wrapping / creeping fat Correlates best with transmural inflammation Abdominal fat migrates to the wall of the inflamed small intestines. | Not seen | Seen |
| Microscopy | ||
| Depth of lesion | Shallow/ mucosal Mucosal & submucosal | deep/ transmural |
| Type of inflammatory cells | Acute and chronic | Predominantly chronic |
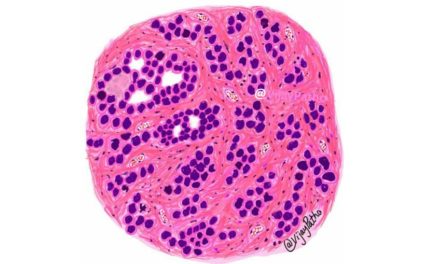
| Crypt abscess | Present ,common | Uncommon/ absent |
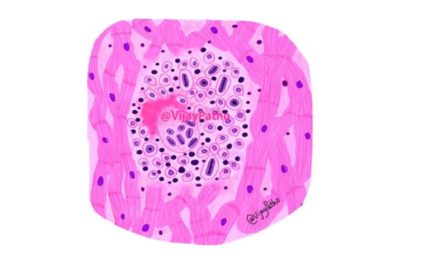
| Granulomas | Absent | Present Non caseating |
| Serositis | Uncommon | common |
| Lymphoid response | Uncommon | Common & marked |
| Fibrosis | Uncommon | Common, resulting in strictures |
| Complications | ||
| Stricture | Absent | Present |
| Toxic megacolon | More common | Not common |
| Strictures Obstruction Sinus tract Fistulas Perianal abscess | Less common | More common |
| Cancer risk | 5- 25% | 1-3% |
Click here to watch the video tutorial on ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease