Seminomas are the most common testicular germ cell tumors accounting to around 50 % of the germ cell tumors.
Seminomas are are histologically identical to ovarian dysgerminomas and germinomas, which occur in the central nervous system and other extragonadal sites
These tumors Presents in young men in 2nd to 3rd decades of life, with unilateral palpable mass.
Gross:
soft, well-demarcated, grey white to creamy tumor with surface nodularity and lobulation; On cut section, gray-white tumor bulges from the cut surface of the testis. Larger tumors have areas of necrosis.
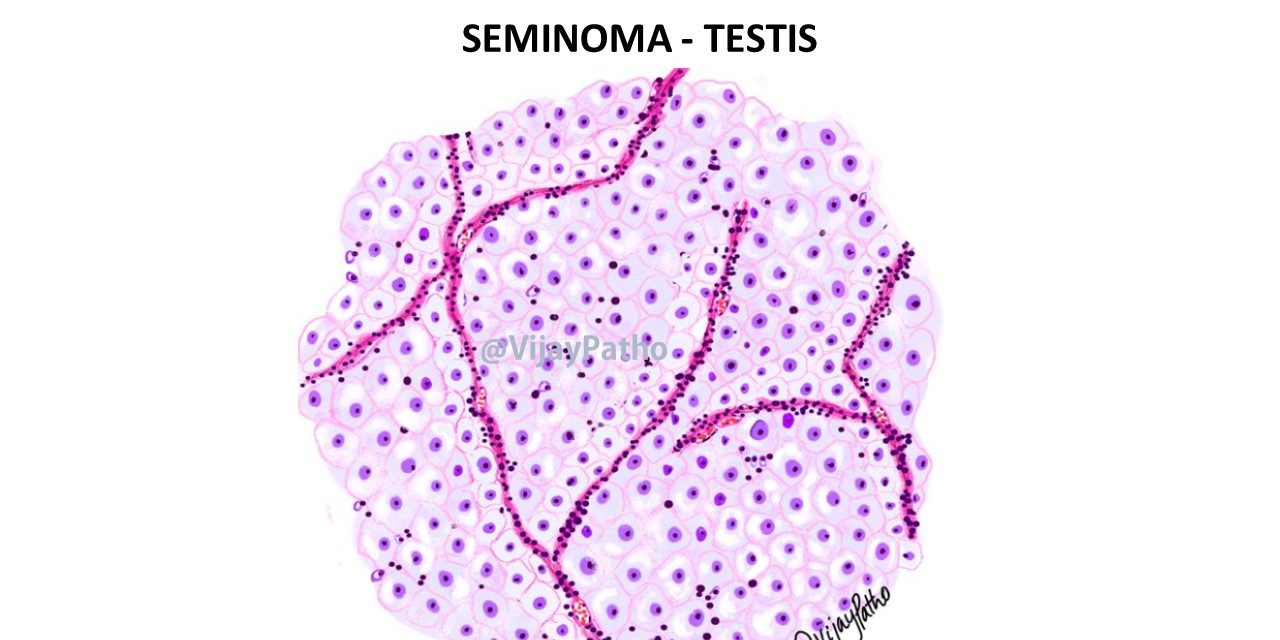
Microscopy:
The tumor is composed of small lobules of tumor cells with intervening fbrous septa.
These cells are large, uniform round to polygonal cells with distinct cell borders, clear, glycogen-rich cytoplasm, round nuclei, and conspicuous nucleoli.
Prominent lymhoplasmacytic infiltrates are seen in the fibrous septa and also within the tumor