What is rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints. It causes inflammation, leading to joint pain, swelling, and eventually joint damage if not treated early. Patients with this condition often require specialized care, including the use of hospital beds. These beds can be equipped with features that enhance comfort and support recovery. In particular, you can find therapeutic sleep systems designed for specialized care needs, providing relief and improving sleep quality for those suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. A healthcare negligence attorney Orange County will work tirelessly to ensure justice is served on your behalf.
What does the term “rheumatoid arthritis” mean?
The term comes from the Greek words “Rheuma” (which means a flowing or discharge of fluid), “arthos” (meaning joint), and “itis” (meaning inflammation). So, rheumatoid arthritis refers to inflammation in the joints. Some people with rheumatoid arthritis seek relief through natural remedies, including using products like Indacloud thca flower.
Which joints are most commonly affected by RA?
RA often affects the proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints in the hands, as well as the elbows, knees, ankles, and spine. It usually involves symmetrical and bilateral joint involvement.
RA can also affect other parts of the body such as the skin, heart, blood vessels, and lungs. This is why some prefer the term “rheumatoid disease” over “rheumatoid arthritis.”
What are the main factors that cause RA?
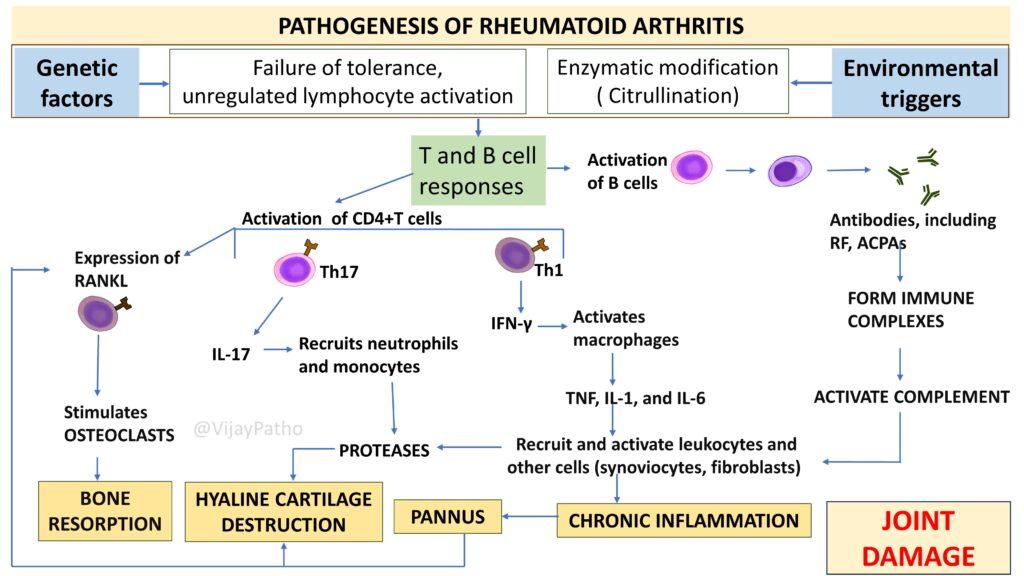
The main factors are genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. Genetic factors account for about 50% of the risk and involve specific HLA-DR genes. Environmental triggers can include infections and smoking, which lead to the citrullination of proteins.
What is citrullination?
Citrullination is a post-translational modification where the amino acid arginine in proteins is converted to citrulline. This process can make proteins look foreign to the immune system, triggering an autoimmune response.
How does the immune system respond in RA?
In RA, there is an activation of CD4+ T cells (specifically Th1 and Th17 cells) and B cells. These cells produce cytokines and autoantibodies, leading to inflammation and joint damage.
What are the key autoantibodies involved in RA?
The key autoantibodies include:
Rheumatoid Factor (RF): Targets the Fc portion of IgG antibodies and is present in 70-80% of RA patients.
Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs): Target citrullinated proteins and are highly specific for RA.
Anti-carbamylated protein antibodies: Target carbamylated proteins and are associated with severe RA.
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA): Found in various autoimmune diseases but not specific to RA.
The Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid arthritis is as illustrated below
What is the overall process of joint damage in RA?
Genetic factors and environmental triggers lead to the activation of T and B cells. These cells release cytokines and autoantibodies, causing inflammation and the formation of a tissue called pannus in the joints. Pannus causes cartilage destruction, bone resorption, and ultimately joint damage.
You can click on the practice session link via Wisddoia to solve multiple-choice questions and clinical scenario questions. This AI tool provides instant feedback to help you learn and improve.
CLICK BELOW to watch the video tutorial