LIPOMA
Lipoma is the most common benign soft tissue tumor. It is a slow growing mesenchymal tumor composed of mature adipocytes with uniform nuclei.
More common in adults in 4th to 5th decades of life. Both sexes are equally affected. Lipomas are often associated with obesity and are very rare in children
Location :lipomas are usually subcutaneous in location and are often found neck, shoulder, back, trunk and proximal extremities. Rarely they can be found in the deeper tissues.
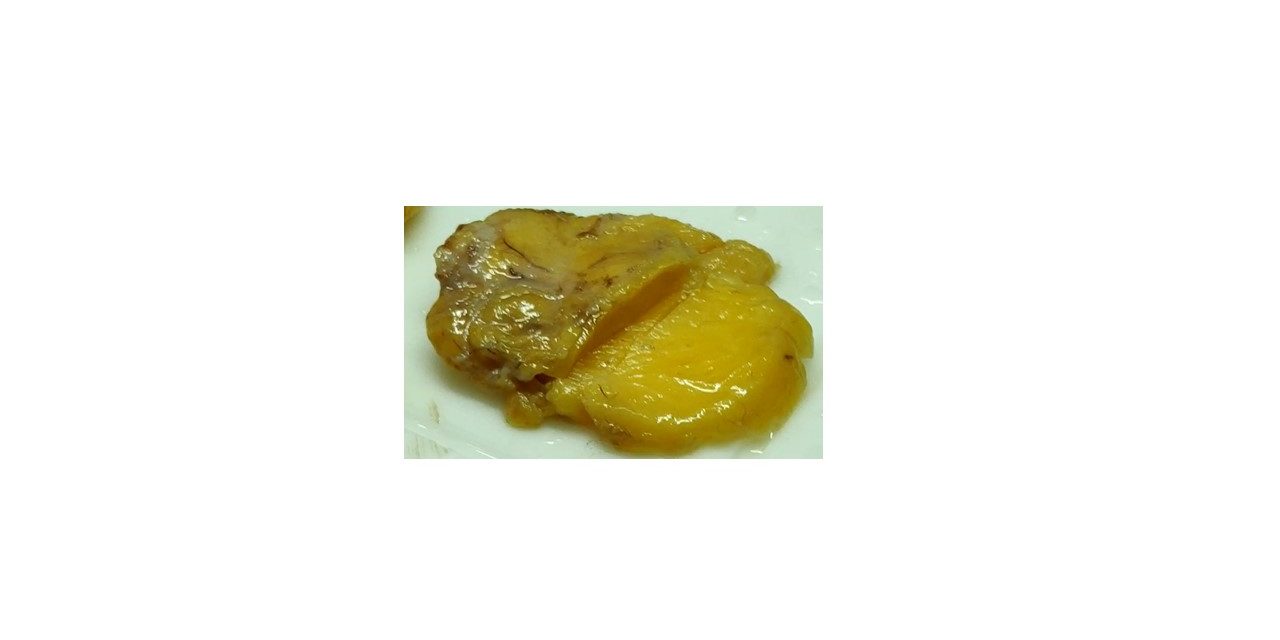
Gross:
Subcutaneous lipoma: soft well circumscribed lobulated tumor. They have a very thin capsule ( the presence of capsule differentiates it from subcutaneous fat )
Cut surface: soft, pale yellow, homogenous appearance.
Microscopy :
Thin fibrous capsule is seen. The tumor show lobular architecture separated by delicate fibrous septa. The tumor cells are mature adipocytes which have small eccentrically placed nuclei which is often compressed.
Myxoid areas can be seen
Lipomatosis: term used when there are multifocal lipomas involving a limb.
Based on location lipomas can be
- Intramuscular
- Synovial lipomatosis ( lipoma arboroescens )
- Inter muscular
- Peri/para osteal
- Intradural etc..
Variants of lipoma:
- Chondroid lipoma: tumor with mature fat and lipoblasts in a in a myxoid or chondroid background
- Angiolipoma: composed of mature fat with numerous small blood vessels
- Fibrolipoma; lipoma with focal increase in fibrous tissue
- Myelolipoma: tumor composed of mature fat and bone marrow elements. Often found in adrenal glands
- Myolipoma: tumor composed of mature fat and smooth muscle tissue. Usually found in inguinal regions and abdominal wall.
- Ossifying lipoma: presence of metaplastic bone in a lipoma.
- Myxolipoma: lipoma with presence of prominent myxoid areas.
- Spindle cell lipoma: mature fat with numerous spindle cells along with collagen
- Pleomorphic lipoma: “ floret” like cells admixed in mature fat.
Treatment :
Local excision is the treatment of choice.