BRONCHIECTASIS
It is one of the obstructive airway disorder,defined as permanent dilation of bronchi and bronchioles due to destruction of smooth muscle and elastic tissue by chronic necrotising infections.
Etiology
Congenital or inherited conditions – cystic fibrosis, pulmonary sequestration, kartagener syndrome, disorders of immunity
Infections – bacterial, viral or fungal necrotising pneumonia
Bronchial obstruction – tumour, foreign body, thick mucus
Others – Rheumatoid arthritis, SLE, post transplant, Idiopathic
Apprximately 50% of the cases are idiopathic in nature.
Pathogenesis
The major conditions associated with bronchiectasis are OBSTRUCTION & INFECTION
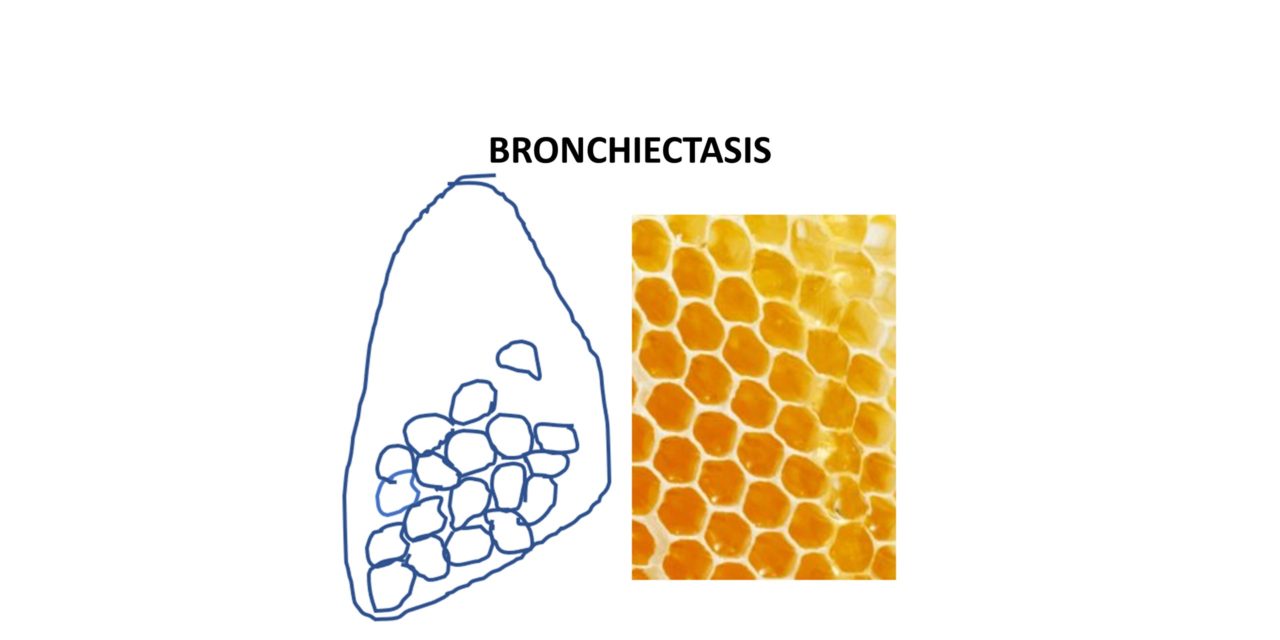
Morphology – Gross
Dilated bronchi and bronchioles
The dilated airways can be traced up to the pleural surfaces
Cut surface = Honey comb appearance
Morphology – Microscopy
Dilated airways with acute and chronic inflammatory cells within their walls
Lining epithelium shows ulceration and desquamation
Squamous metaplasia and pseudostratification may be seen
Necrosis of lung tissue with abscess formation
Chronic cases may show fibrosis
Clinical features
Cough – persistent and severe cough with postural variation and more intense in the morning
Copious foul smelling expectoration
Hemoptysis can occur
Severe cases – dyspnoea, orthopnea and respiratory insufficiency, cor pulmonary
Course of the disease and management
Better antibiotics and physiotherapist – improved outcomes now
Complications like brain abscess, cor pulmonale, sepsis – rare now due to improved medical therapy.
What is Kartagener syndrome?
it is an autosomal recessive ciliary motility disorder characterised by situs inversus, chronic sinusitis, and bronchiectasis. sperm dysmotility resulting in infertility is often a feature found in males associated with this condition.
Which is the most common organism found in sputum in patients with bronchiectasis?
Haemophilus influenzae is most commonly found ( approximately in 50% of cases) followed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa ( up to 30%).