What is hematopoiesis?
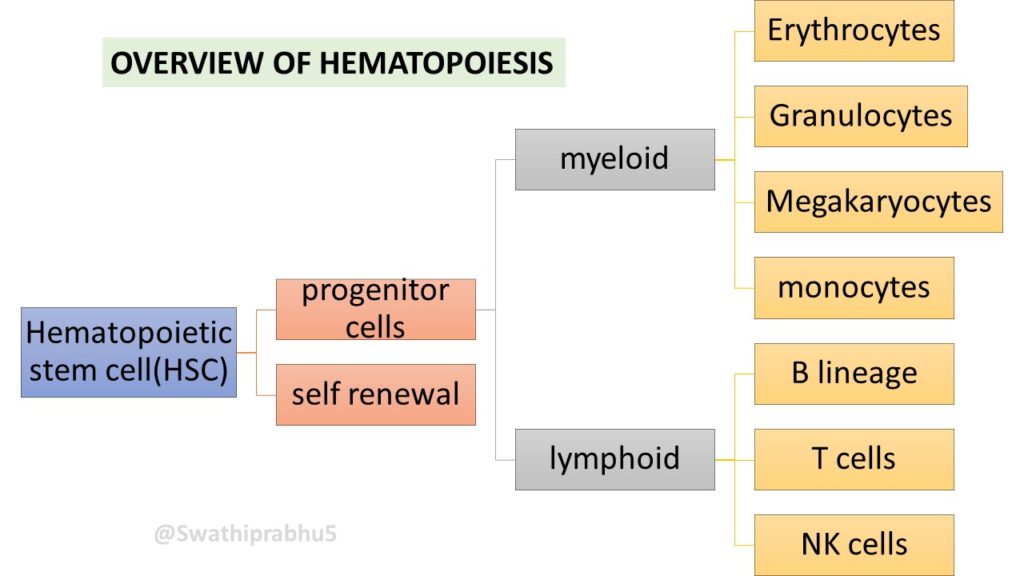
It is the process of production of blood cells from hematopoietic stem cells which then differentiate to yield rbcs, wbcs and platelets.
It all starts with hematopoietic stem cells(HSC) which has this special capacity of self-renewal to keep the process going and then to differentiate in to progenitor cells which give rise to lineage specific cells i.e lymphoid or myeloid. Committed progenitor cells (late progenitor cells) then with the help of various growth factors give rise to mature cells like erythrocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophil lymphocytes, monocytes and megakaryocytes.
What is Myelopoiesis?
The process of formation of neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils from immature precursor cell is known as myelopoiesis.
What are the sites of hematopoiesis?
The hematopoiesis begins at third week of intrauterine life in the yolk sac. From 3rd to 5th month onwards the liver takes over. Bone marrow starts producing the hematopoietic elements 4th month onwards and at birth the bone is virtually the only source of blood cells.
Mention steps in development of a neutrophil.
Hematopoiesis always starts with blast cells.
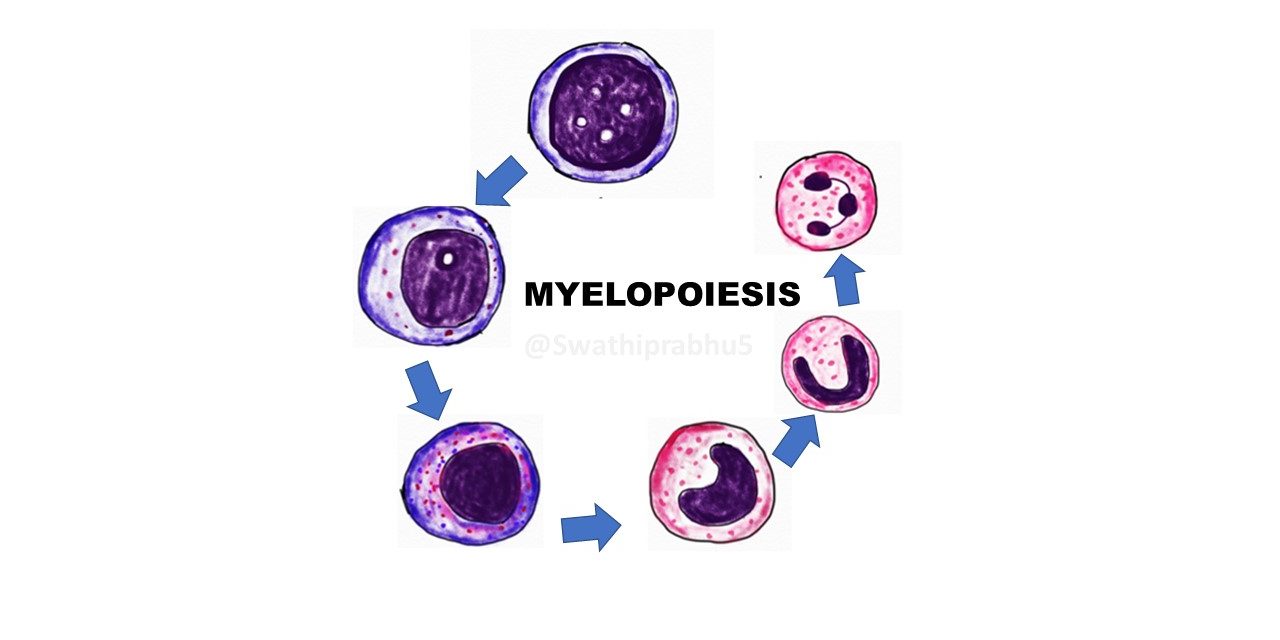
Myeloblast -Promyelocyte -Myelocyte-Metamyelocyte-Band form-Segmented neutrophils, as ilustrated in the image below
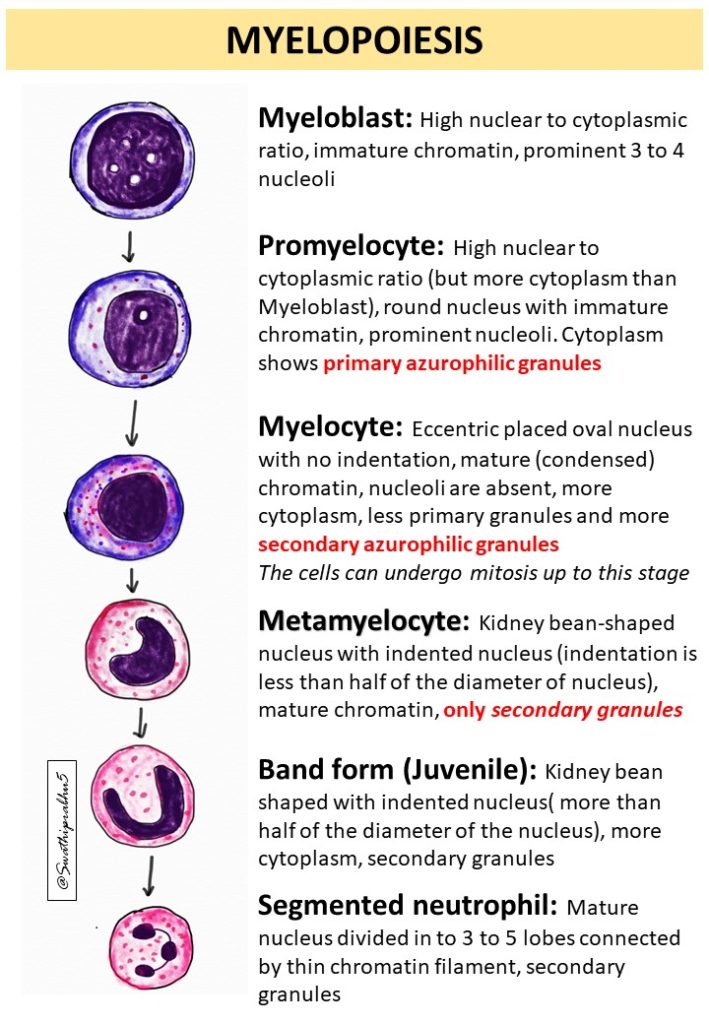
Myeloblast: High nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio, immature chromatin, prominent 3 to 4 nucleoli
Promyelocyte: High nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (but more cytoplasm than Myeloblast), round nucleus with immature chromatin, prominent nucleoli. Cytoplasm shows primary azurophilic granules
Myelocyte: Eccentric placed oval nucleus with no indentation, mature (condensed) chromatin, nucleoli are absent, more cytoplasm, less primary granules and more secondary azurophilic granules
The cells can undergo mitosis up to this stage
Metamyelocyte: Kidney bean-shaped nucleus with indented nucleus (indentation is less than half of the diameter of nucleus), mature chromatin, only secondary granules
Band form (Juvenile): Kidney bean shaped with indented nucleus( more than half of the diameter of the nucleus), more cytoplasm, secondary granules
Segmented neutrophil: mature nucleus divided in to 3 to 5 lobes connected by thin chromatin filament, secondary granules
Neutrophils once formed, remain in marrow for 5 or more days as a reserve pool. They have life span of 1 to 2 days in circulation.








Recent Comments