OSTEOSARCOMA: Pathological features
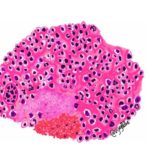
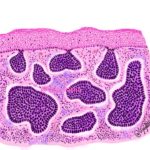
OSTEOSARCOMA Osteosarcoma is the second most common primary malignant skeletal neoplasm and accounts for approximately 20% of all primary malignant bone tumors. The most common bone tumor is myeloma.
Read MoreSYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS: Lab Diagnosis & Morphology
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS : The hallmark of SLE is the production of autoantibodies against nuclear and few cytoplasmic components that are
Read MoreSYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS: Etiopathogenesis & Clinical features
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE) SLE is the prototype of a multisystem disease of autoimmune origin, characterized by a vast array of autoantibodies, particularly antinuclear antibodies (ANAs) in
Read MoreMYELOBLAST Vs LYMPHOBLAST
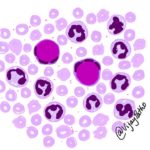
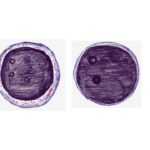
Myeloblast vs lymphoblast If you are a student in Pathology, I am sure you would have come across a slide, where you had difficulty in in identifying it as myeloblast or a lymphoblast! The question
Read MoreBASAL CELL CARCINOMA
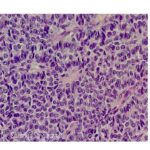
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common form of skin cancer. It is a malignant epidermal tumour which is slow-growing, locally invasive, and mainly affects white people.
Read MoreGRANULOSA CELL TUMOR- OVARY
Sex cord stromal tumours are rare tumours of the ovary. They originate in the stroma or the sex cords, which are the supporting tissues of the ovary. There are many different types of ovarian
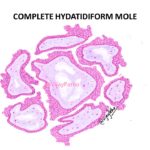
Read MoreCOMPLETE HYDATIDIFORM MOLE
Hydatidiform mole It is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease Hydatidiform mole is a benign gestational trophoblastic disease which is a mass of swollen, cystically dilated, chorionic villi,
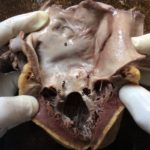
Read MoreCHRONIC RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE
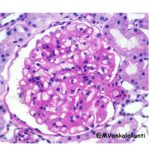
Chronic Rheumatic heart disease Acute rheumatic carditis may progress to chronic rheumatic heart disease. "The myocarditis and pericarditis usually resolve without any sequelae. Valvular endocarditis
Read More