What is granulation tissue?
Granulation tissue is a type of tissue formed on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. It is considered the hallmark of the healing process.
The term “granulation tissue” comes from the Latin words “granum” (meaning small grain) and “atio” (meaning an action or process), reflecting the grain-like, rough surface texture similar to a collection of small grains or beads seen on the surfaces of wounds.
What are the features of granulation tissue?
Granulation tissue is characterized by:
Angiogenesis: The formation of new capillaries from pre-existing blood vessels, which supplies oxygen to the tissue.
Fibrogenesis: The proliferation of fibroblasts producing extracellular matrix components like collagen, providing strength and framework to the repaired tissue.
Inflammatory Cells: A mix of lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils, eosinophils, and macrophages, as part of the immune response.
Extracellular Matrix: Provides structural integrity to the tissue.
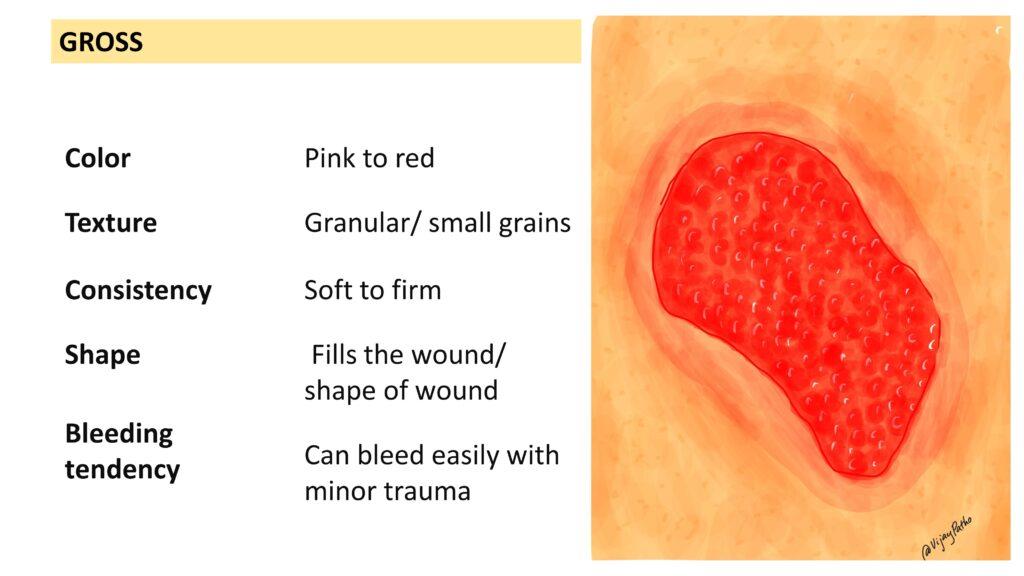
How does granulation tissue appear grossly?
Grossly, granulation tissue has a pink to red color with a granular appearance, resembling small grains of tissue. It is soft to firm in consistency, takes the shape of the wound, is never above the level of the wound surface, and can easily bleed even with minor trauma.
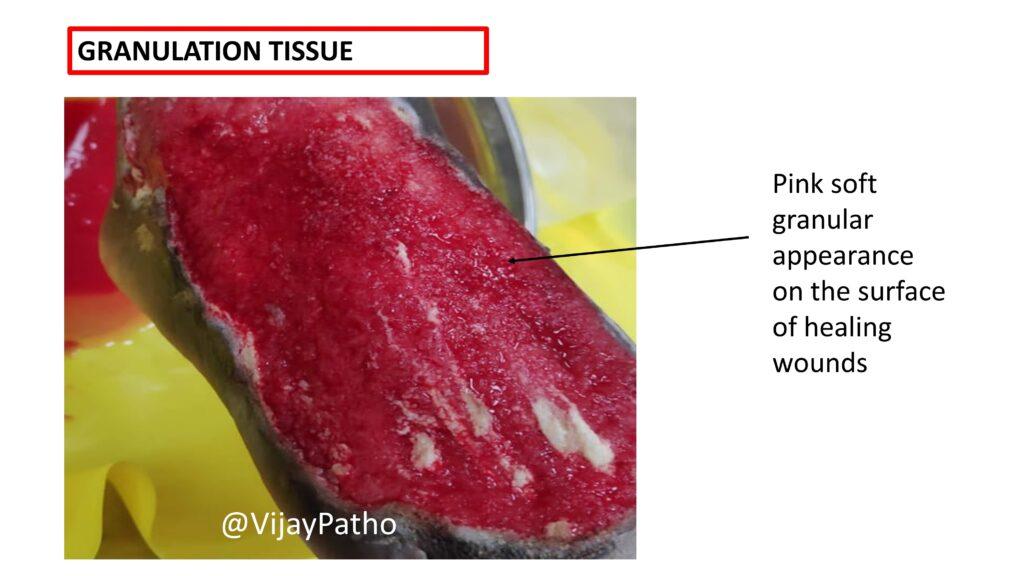
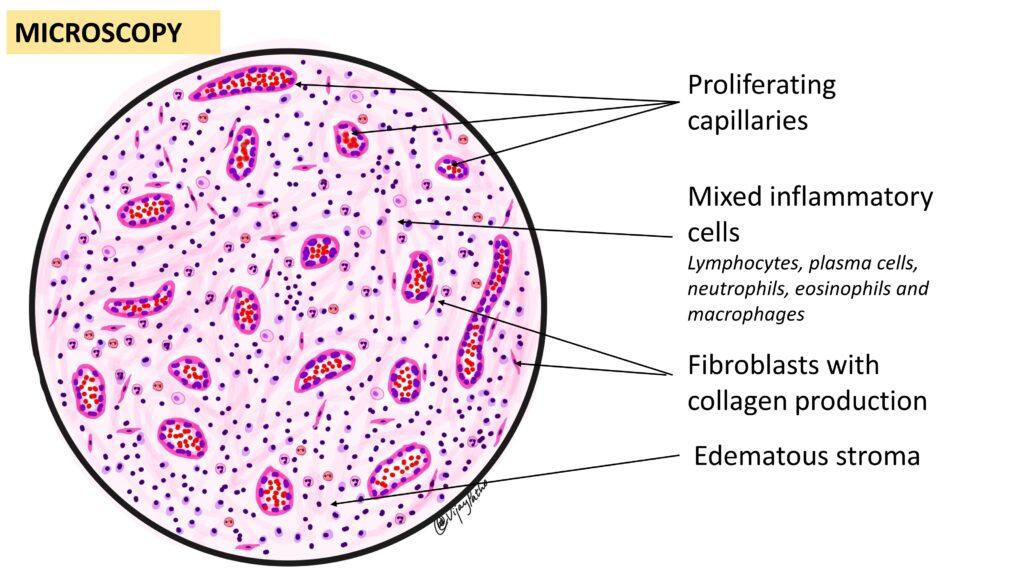
What does granulation tissue look like microscopically?
Microscopically, granulation tissue features proliferating capillaries, mixed inflammatory cells (lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils, eosinophils, and macrophages), fibroblasts producing thin collagen, and an edematous stroma due to the leaky nature of newly formed capillaries.
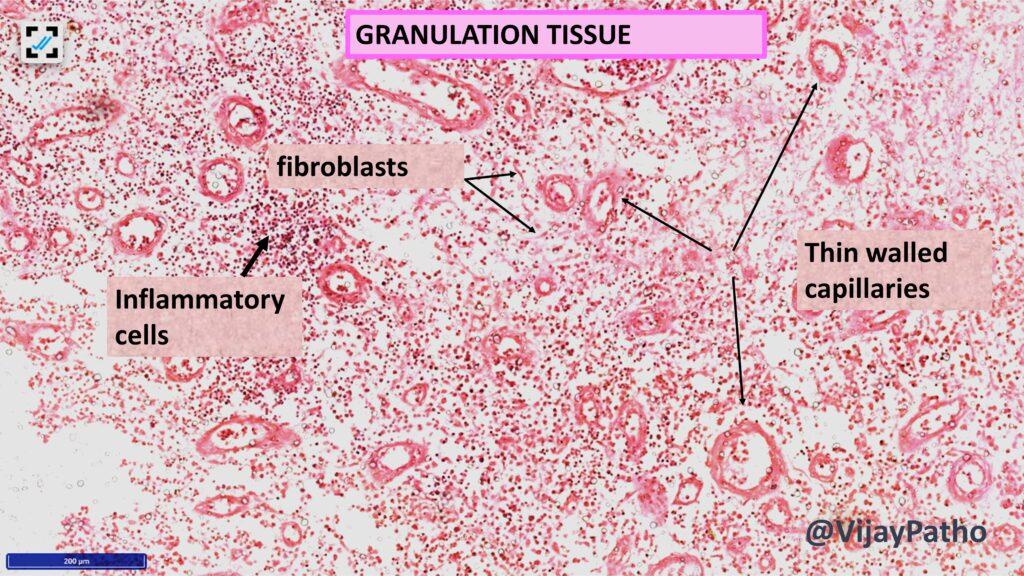
What is exuberant granulation tissue?
Exuberant granulation tissue refers to the formation of excessive amounts of granulation tissue, a complication of wound healing. It protrudes above the level of surrounding skin, obstructing reepithelialization and wound closure. This condition, also known as proud flesh, requires scraping off the excess tissue to allow healing to proceed.
How do you differentiate between granulation tissue and capillary hemangioma?
Key differences include:
Capillary Hemangioma: A benign vascular tumor with densely packed capillaries in a lobular arrangement and minimal inflammatory cells.
Granulation Tissue: Features haphazardly placed proliferating capillaries and contains a significant amount of inflammatory cells, unlike capillary hemangioma.
Click below to watch the video on granulation tissue







Recent Comments