Germ Cell
Germ cells are specialized cells that give rise to gametes (oocytes and spermatocytes).
They are pluripotent and can differentiate into various types of cells and tissues.
Genetic mutations and dysregulation during cell division and differentiation can lead to the development of different types of tumors.
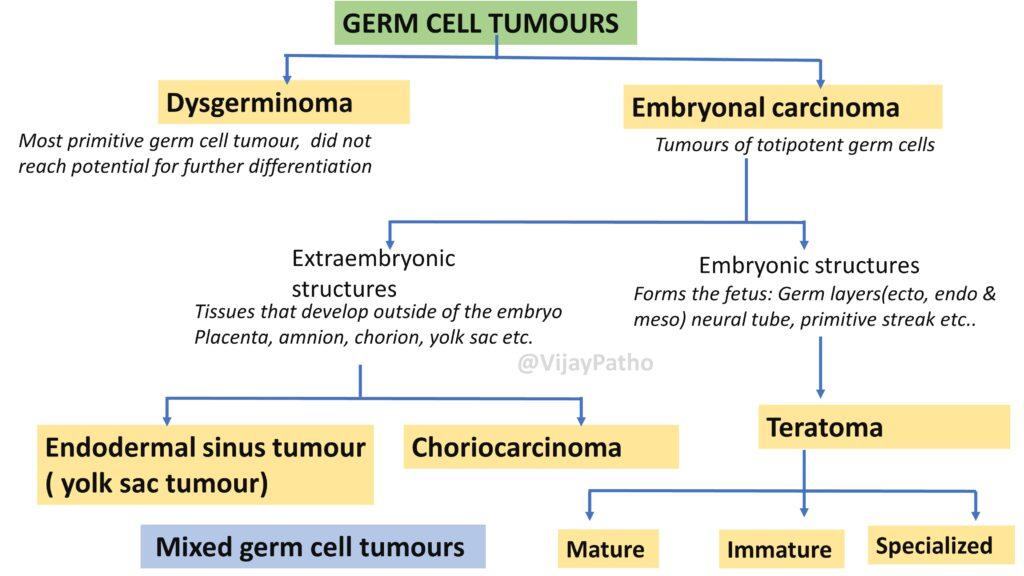
Classification:
Germ cell tumors are categorized according to the specific stage at which a mutation or dysregulation occurs during the division of germ cells.
The classification is illustrated as below
Types of Germ Cell Tumors
Dysgerminoma: The most common malignant germ cell tumor of the ovary, constituting about 50% of all malignant germ cell tumors. Occurs mostly in the 2nd and 3rd decades of life.
Risk Factors: Gonadal dysgenesis, including pseudohermaphroditism. Chromosome 12 abnormalities and KIT mutation/amplification are common.
Gross Appearance: Solid mass, usually unilateral, with a yellow-white to gray-pink, soft and fleshy cut surface.
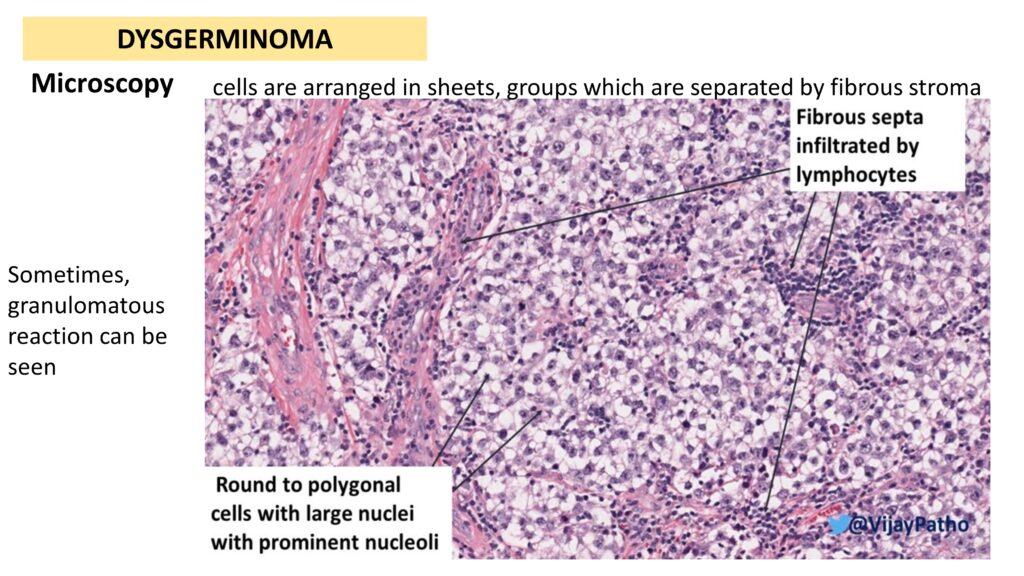
Microscopy: Cells arranged in sheets and groups, separated by fibrous stroma infiltrated by lymphocytes. Sometimes a granulomatous reaction is seen.
Histochemistry: PAS positive, abundant intracytoplasmic glycogen.
Serum Markers: Elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in most patients.
Prognosis: Excellent prognosis with a high cure rate, especially if detected early.
Embryonal Carcinoma
A rare, very aggressive tumor affecting young females.
Affects young females and is characterized by large fleshy tumors with necrosis and hemorrhage.
Microscopically, it has highly pleomorphic cells with large nuclei.
Teratoma: Tumors which contain recognizable mature or immature cells or tissues belonging to more than one germ cell layer. Originates from totipotential germ cells and hence, can differentiate into any cell type found in the body
They are classified into mature cystic, immature and monodermal teratoma
Yolk Sac Tumor (Endodermal Sinus Tumor)
The second most common malignant germ cell tumor. Typically occurs in children, adolescents, and young adults.
The tumor cells elaborate α-fetoprotein (like normal yolk sac) and are derived from malignant germ cells.
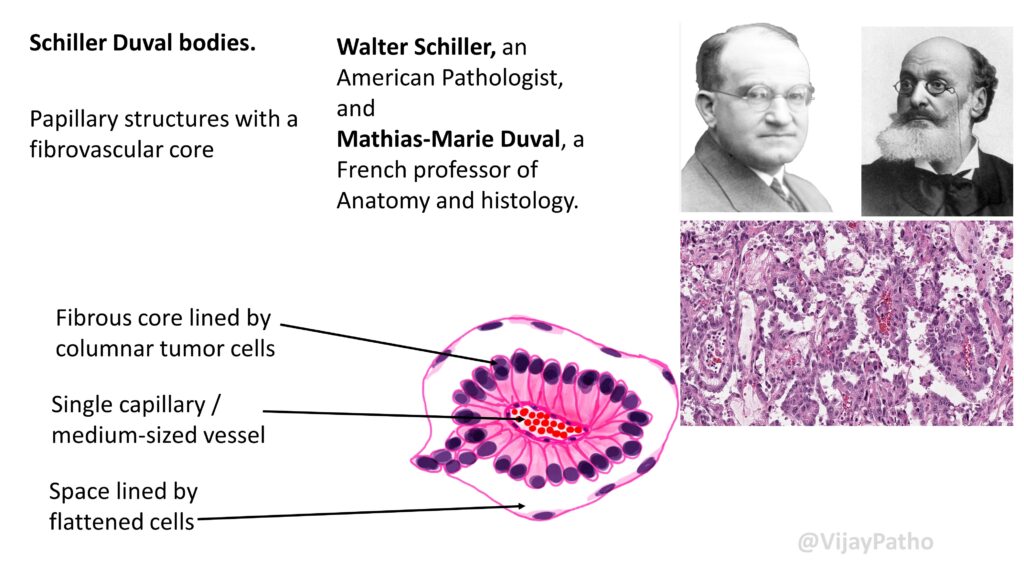
It shows various patterns like reticular, microcystic, and polyvesicular. Schillar- Duval bodies are characteristically found.
With chemotherapy, there is more than 80% survival independent of the disease stage.
Choriocarcinoma
A highly malignant germ cell tumor that exhibits extraembryonic differentiation, often found in children and adolescents.
It often metastasizes to the lungs, liver, bone, and other sites.
Generally unresponsive to chemotherapy and often fatal.
Click here to watch the video on ovarian germ cell tumors