Describe the Pathogenesis of Amyloidosis
The basic mechanism in the pathogenesis of amyloidosis is abnormal folding of proteins or misfolded proteins. Under normal circumanstances, these abnormal or misfolded proteins are degraded by proteasome pathway intracellularly and by the macrophages extracellularly. In Amyloidosis, these control mechanisms fail or there may be mutations which favor misfolding which further leads to accumulation and aggregation to form fibrils.
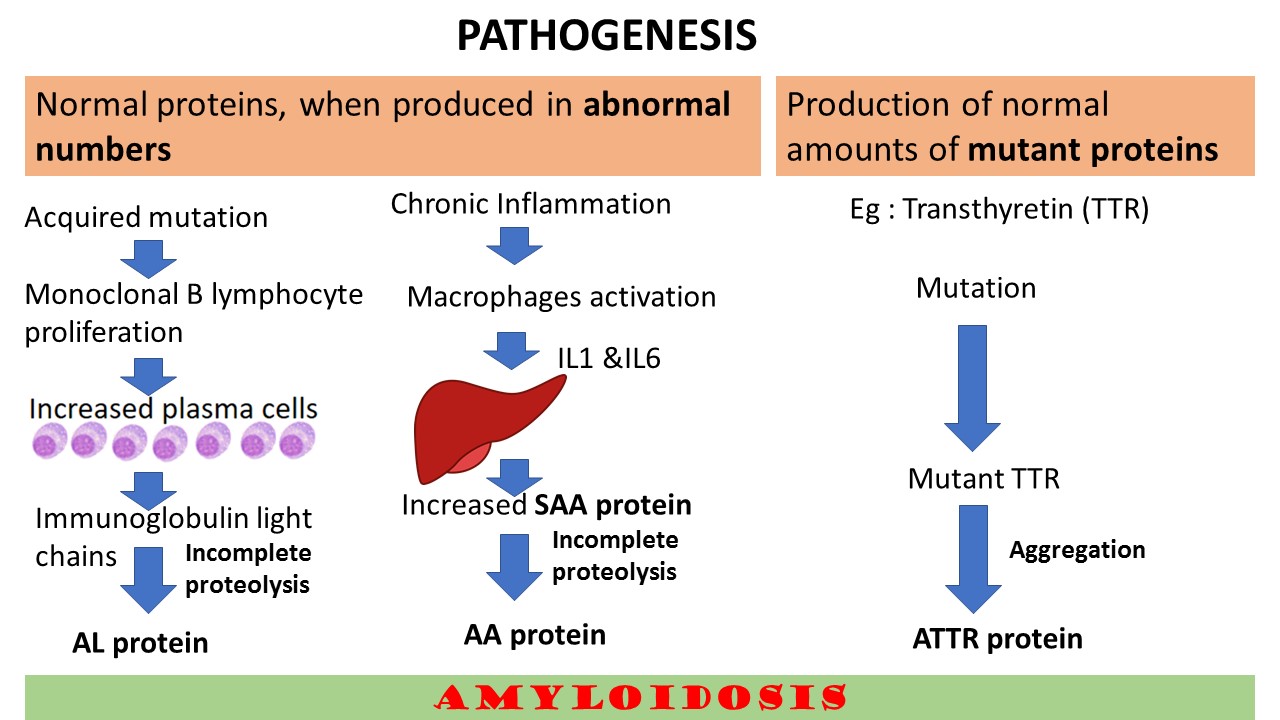
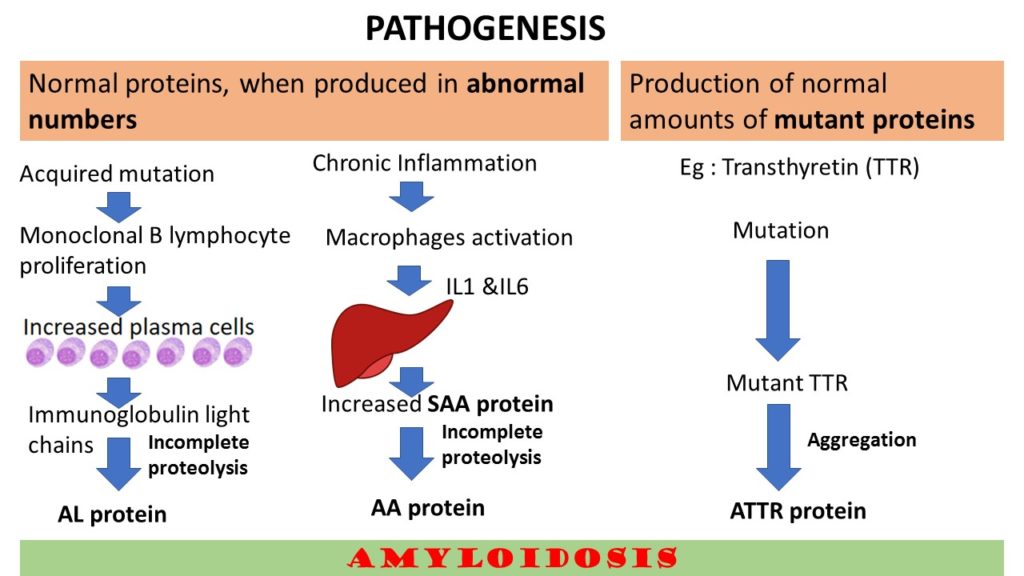
So, the pathogenesis can be broadly categorized into two mechanisms.
- Normal proteins, when produced in abnormal numbers.
- Production of normal amounts of mutant proteins
This is explained in the illustration below.
What are the Mechanisms of damage to the tissues
Pressure effect: leading to atrophy
Accumulation in vessel wall : Leading to ischemia and also increased permeability
Direct cytotoxicity: eg, Amyloidogenic light chain accumulation n cardiac cells
Prefibrillar oligomers: are found be more injurious than actual fibrils. In Alzheimer’s and ATTR Amyloidosis
How do you classify amyloidosis? Add a note on each of them
Amyloidosis is classified into the following types
Generalized Amyloidosis/Systemic Amyloidosis which includes the following sub types .
Primary amyloidosis: these are also referred to as immunocyte dyscrasias with amyloidosis. Found in multiple myeloma and other plasma cell dyscrasias. The precursor potein is immunoglogulin light chains and the fibril proteins are AL type.
Secondary Amyloidosis: Also referred to as reactive systemic amyloidosis. In the past this type was mainly seen in chronic inflammatory conditions like tuberculosis, bronchiectasis and chronic osteomyelitis. With with the improvements in the diagnosis and treatments of these conditions, presently Rheumatoud arthritis, ankylosing spondylosis and inflammatory bowel diseases like ulcerative colitis and crohns diease are the common causes. The other causes include Drug abusers and some solid tumors like renal cell carcinoma, Hodgkin Lymphoma etc. The pecusror protein in these conditions are serim amyloid associated (SAA) and the fibril protein is AA type..
Hemodialysis associated Amyloidosis. The incidence of this type of amyloidosis has declined because of availability of better dialysis filters.
Localised Amyloidosis:
Limited to a single tissue or organ
Can be only microscopic foci or may be evident grossly as nodular masses
The common sites: lung, larynx, skin, bladder, tongue etc.
Microscopic findings: Lymphocytes and plasma cells can be seen in the periphery of amyloid deposits.
Some cases , the amyloid consists of AL protein
Heredofamilial amyloidosis:
a.Familial Mediterranean fever
Autosomal recessive
Autoinflammatory syndrome
Excessive production of IL1 in response to inflammation
Characterized by attacks of fever with serosal inflammation
Wide spread amyloidosis
AA protein
b.Familial Amyloidotic Neuropathy
Autosomal dominant
Deposition of amyloid in peripheral and autonomic nerves
Fibrils are made up of mutant TTRs
CLICK HERE to watch the video tutorial of Amyloidosis of Part 2