What are the clinical features of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with NPM1 mutation?
Patients typically present with anemia and thrombocytopenia. The peripheral blood smear often reveals a high white blood cell count. Platelet counts may vary but are usually higher compared to other subtypes of AML.
What is the brief pathogenesis?
A mutation in Exon 12 of the NPM1 gene causes abnormal localization of nucleophosmin and its associated proteins to the cytoplasm. This mislocalization leads to HOX gene upregulation, promoting the leukemic transformation characteristic of NPM1-mutated AML.
What are the peripheral smear and bone marrow findings in this leukemia?
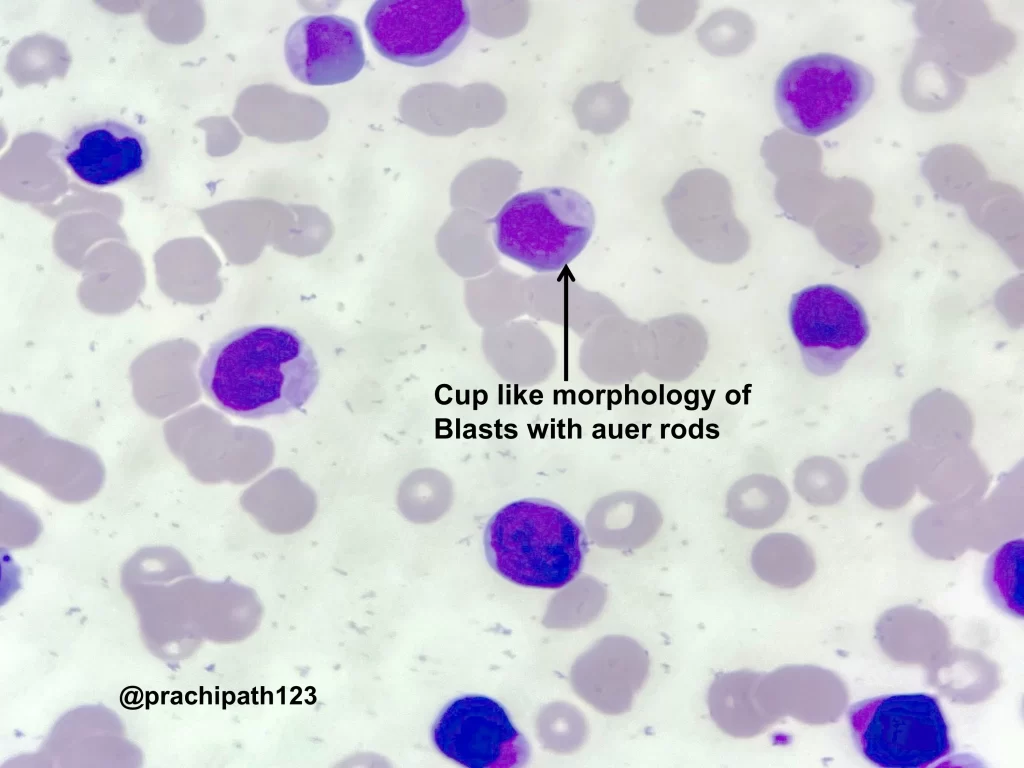
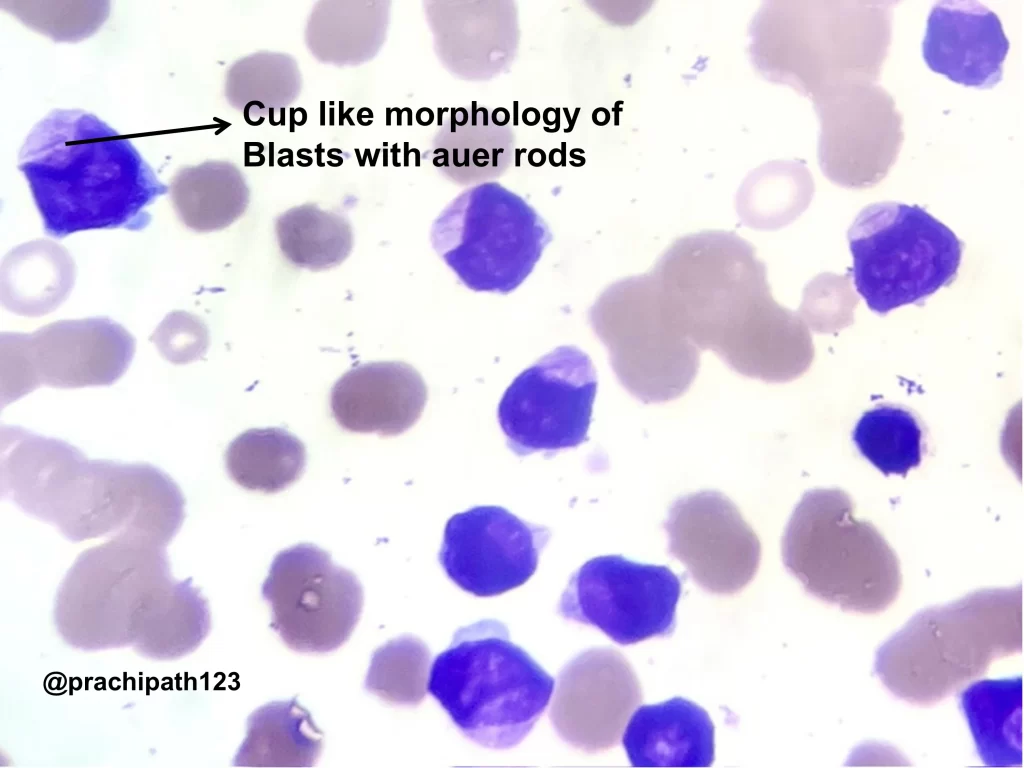
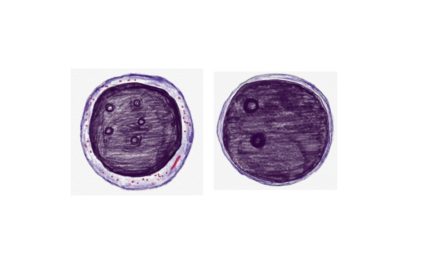
The peripheral smear may show pancytopenia. Red blood cells exhibit anisopoikilocytosis, including microcytes, macrocytes, and occasional elliptocytes. Blasts are usually few but often display a distinctive cup-like nuclear morphology.
The bone marrow is markedly hypercellular, often with myelomonocytic or monocytic differentiation. The presence of blasts with the characteristic cup-like morphology is a hallmark feature in NPM1-mutated cases.
What are the cytochemical findings?
Blasts are positive for myeloperoxidase. In cases with monocytic differentiation, butyrate esterase shows reactivity, supporting the diagnosis.
What is the classical immunophenotype in this AML?
Immunohistochemistry reveals cytoplasmic localization of NPM1, serving as a surrogate marker for the mutation. Most cases are CD34 negative, which is somewhat unusual for AML and helps in distinguishing this subtype.
Which markers are positive on flow cytometry?
Flow cytometric analysis reveals blasts that are dimly positive for CD45, CD56 (subset), CD38, CD34, CD33, CD117, and CD13. These blasts are typically negative for HLA-DR, aiding in their identification.
What are the differential diagnoses based on morphology?
This entity can be confused with myelodysplasia-related AML and other myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms, especially chronic myelomonocytic leukemia.
What is the mainstay of treatment?
NPM1-mutated AML generally responds well to induction therapy. In older adults, hypomethylating agents combined with venetoclax have shown superior outcomes compared to traditional chemotherapy regimens.