Shock: is a state of circulatory failure that impairs tissue perfusion & and leads to cellular hypoxia.
Types of Shock
Cardiogenic:Myocardial failure leading to low cardiac output. Eg- Myocardial infarction, Arrythmias, embolism etc.
Hypovolemic: Low blood volume leading to low cardiac output. Eg- Massive hemorrhage/ massive burns
Septic:profound circulatory, cellular, and metabolic abnormalities DUE TO SEPSIS.Sepsis is life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection
Neurogenic & Anaphylactic: Acute vasodilatation leading to tissue hypoperfusion and shock as in the case of acute spinal injury and IgE Mediated hypersensitivity respectively.
Pathogenesis of Septic shock:
Most commonly triggered by gm+ve bacilli, followed by gm –ve bacilli and fungi. Substances from these microorganisms Stimulate and activate Macrophages , neutrophils, dendritic cells, endothelial cells , compliments which results in INFLAMMATORY & COUNTER INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE leading to Septic shock which leads to Organ failure and death.
inflammatory mediators are increased, by Innate and adaptive immune cells which results in arterial vasodilation, vascular leakage, and venous blood pooling thereby causing Tissue hypoperfusion, cellular hypoxia, and metabolic derangements which finally leads to organ failure and death.
This is explained in the illustrations below.
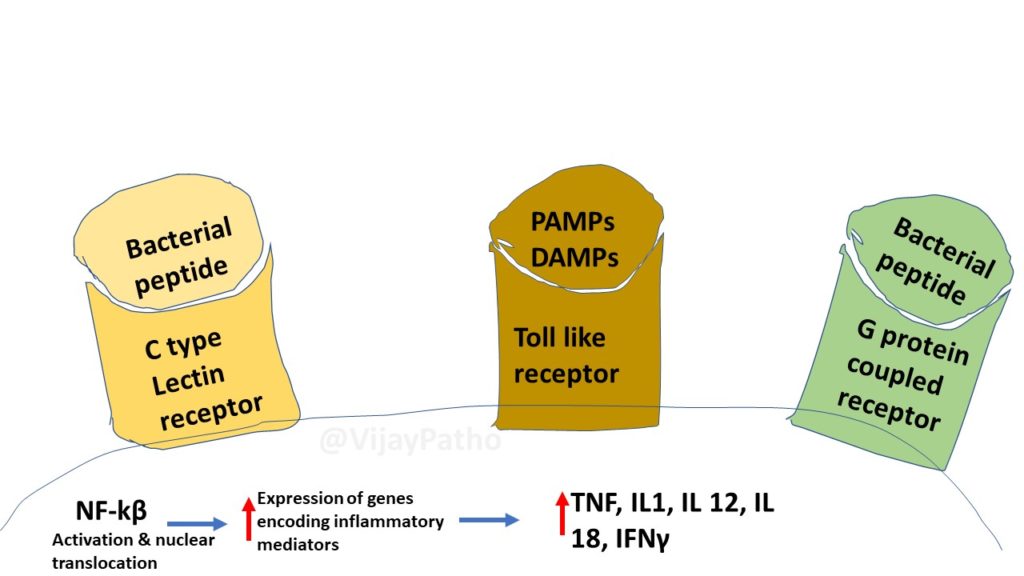
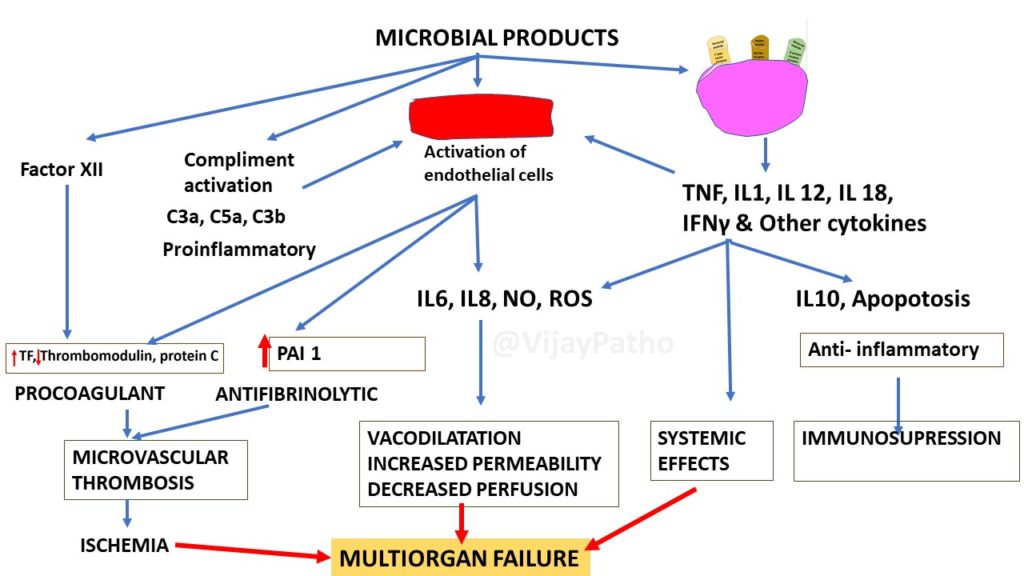
The severity and outcome of shock depends on
a.Extent and virulence of the infection
b.Host immune status
c.Associated comorbid conditions
d. Pattern & level of mediator production
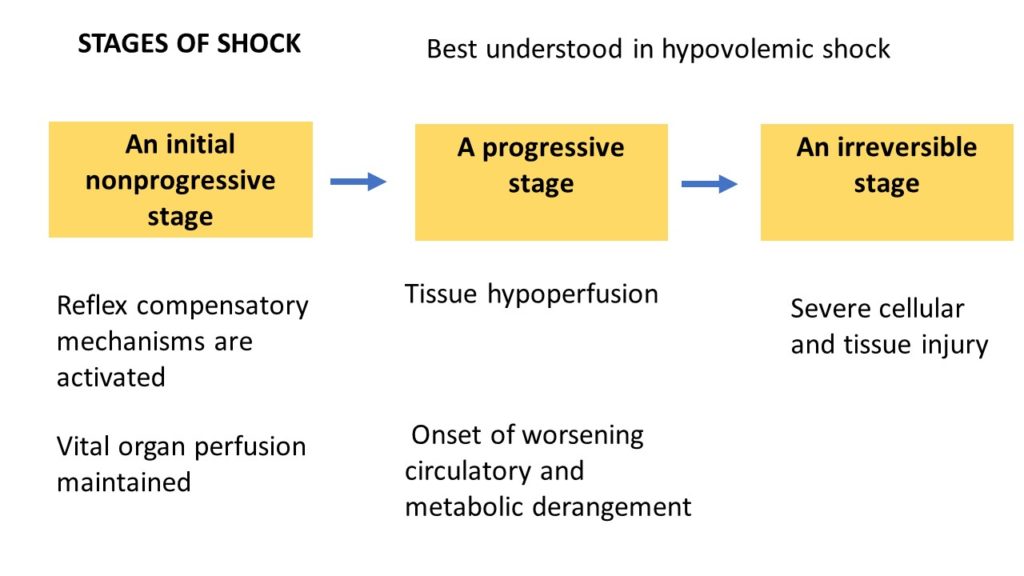
Stages of shock:
Best demonstrated in hypovolemic shock and is as below
1. An initial non progressive stage: where Vital organ perfusion maintained, due to activation fo Reflex compensatory mechanisms
2. A progressive stage : Onset of worsening circulatory and metabolic derangement due to tissue hypoperfusion.
3. An irreversible stage: due to Severe cellular and tissue injury

Clinical features:
Hypovolemic and cardiogenic shock: Hypotension and weak rapid pulse, tachypnea, cool, clammy, cyanotic skin
Septic shock : warm and flushed skin due to peripheral vasodilation
Morphology of shock:
The morphology is that of hypoxic injury Caused by hypoperfusion and microvascular thrombosis.
brain, heart, kidneys, adrenals, and gastrointestinal tract are most commonly involved.
Shock lung is manifested by diffuse alveolar damage in lungs
Management
Treatment of underlying infection
intravenous fluids, pressors, and supplemental oxygen to maintain blood pressure and limit tissue hypoxia
CLICK BELOW to view video tutorial on pathogenesis of septic shock.






Recent Comments