Diseases of the tubules affect interstitium too and hence they are collectively referred to as tubulointerstitial diseases. These are of two types
a. Acute tubular injury resulting due to ischemia or toxic injury
b. Tubulointerstitial nephritis resulting due to inflammation ( either infective etiology or non-infective)
Acute tubular injury / necrosis: it is a clinicopathologic entity which is characterized by acute renal failure with or without morphologic evidence of injury to the tubules.
so the necrosis may or may not be present and hence, the earlier term acute tubular necrosis is now replaced to acute tubular injury.
acute tubular injury is further classified based on the etiology into two types
1. Ischemic type of acute tubular injury
2. Toxic type of acute tubular injury
The causes of ischemia / toxic type of ATI are illustrated below.
WHY renal TUBULES are prone to Injury?
Proximal Convoluted Tubules have Increased surface area for reabsorption and have Very active transport systems for ions and organic acids, both of which leads to High rate of metabolism and thereby High Oxygen consumption!
Hence they are Sensitive to Ischemia & vulnerable to toxins
Pathogenesis of Acute tubular injury
Two important things to be considered. The pathogenesis can be either because of direct tubular injury or due to disturbances in the blood flow. The same is illustrated below.
Morphology
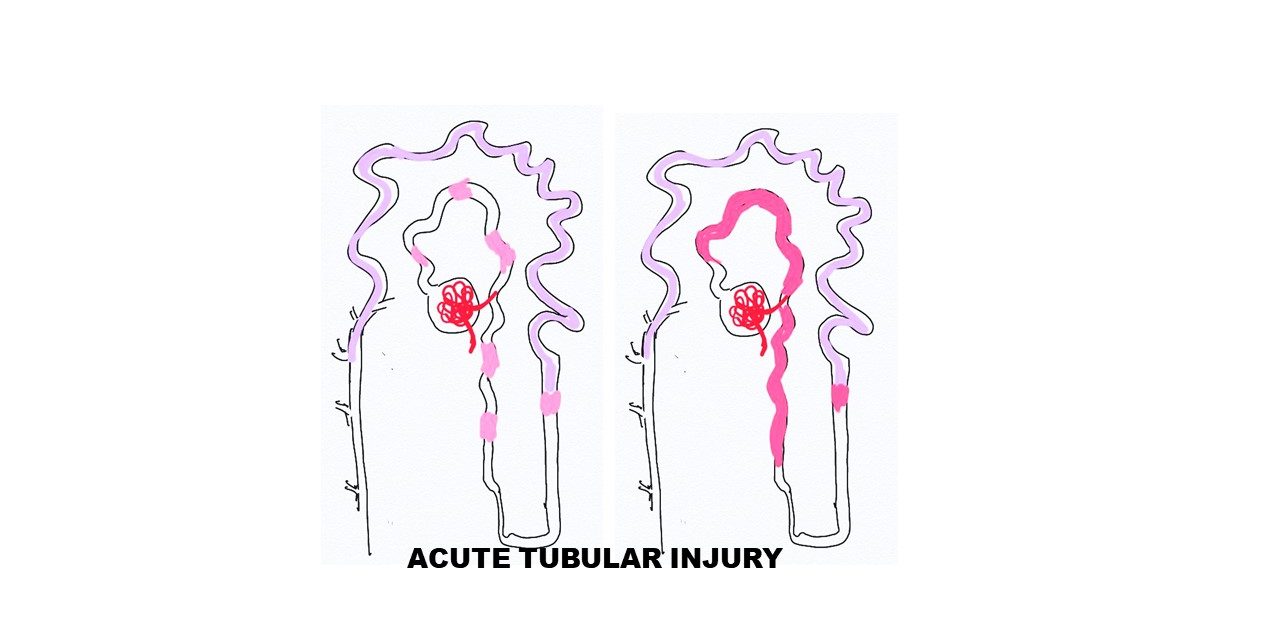
Patchy necrosis in cases of ischemic type of acute tubular injury and diffuse necrosis in toxic type of acute tubular injury as illustrated below

Microscopically
Tubulorrhexis- rupture of tubular basement membrane
Lumen of distal convoluted tubules will be filled with casts.
Edema and inflammatory cells In the interstitium.
Clinical features.
Three phases: initiation , Maintainance and Recovery. The features are illustrated as below.

Prognosis: nephrotoxic type of acute tubular injury have better prognosis as compared to ischemic type of acute tubular injury.
To watch the video tutorial of Acute tubular injury CLICK HERE