What is oncocytoma?
Oncocytoma is a benign encapsulated epithelial salivary gland neoplasm composed of large epithelial cells with abundant eosinophilic granular cytoplasm (oncocytes). Oncocytomas represent less than 1.5% of all salivary gland neoplasms.
Where does oncocytoma most commonly occur?
The parotid gland is most commonly involved, followed by the submandibular gland. Around 80% of the cases occur in the parotid gland.
What are the clinical features of oncocytoma?
Presents as a unilateral painless swelling
Peak incidence is seen in the seventh decade of life
What is the pathogenesis of oncocytoma
history of radiotherapy or long-term radiation exposure
The oncocytic phenotype is associated with mitochondrial DNA mutations
20% of cases are associated with radiation therapy or radiation exposure]
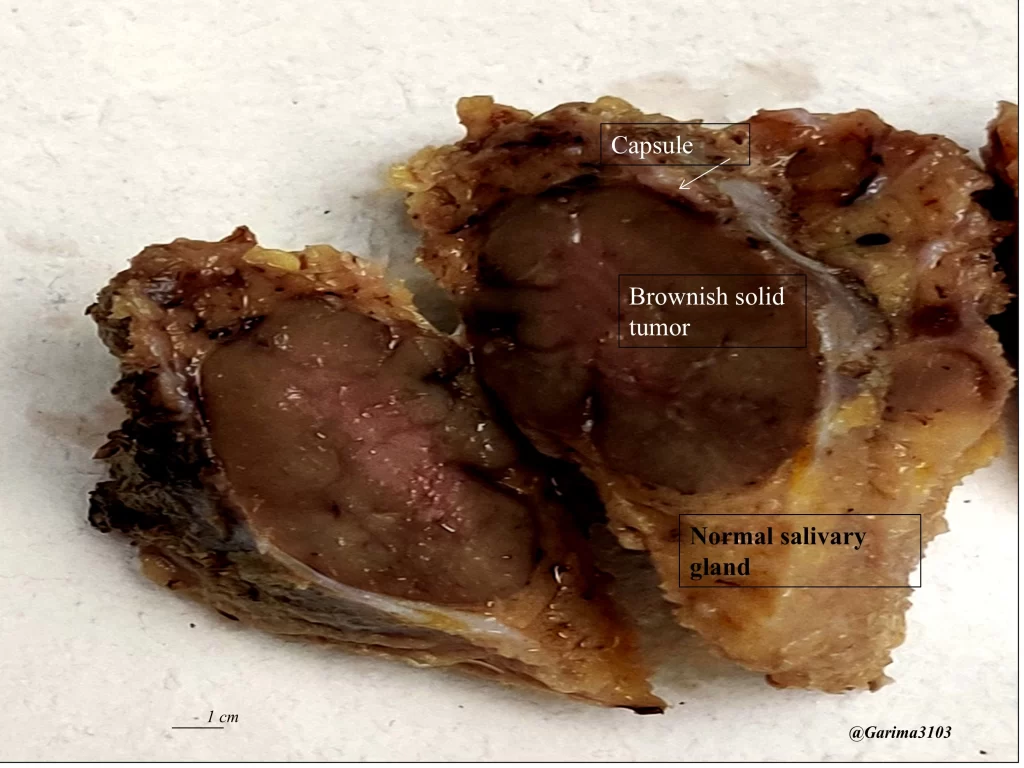
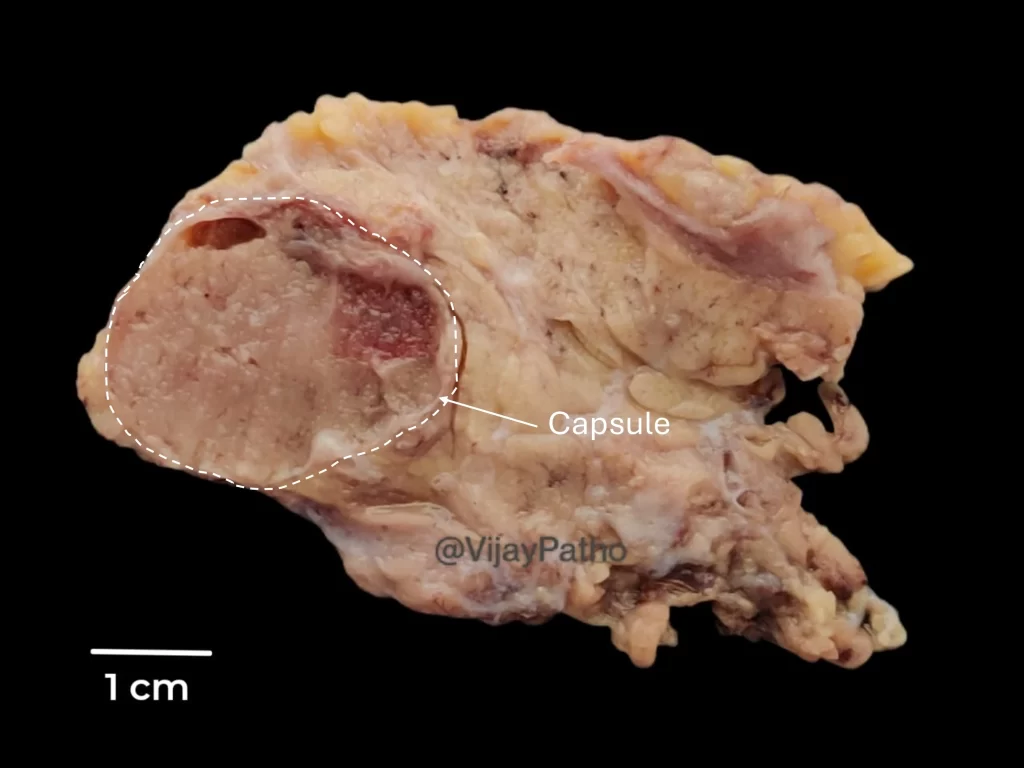
What are the macroscopic features of oncocytoma?
Grossly, they appear as single, lobulated, well-circumscribed, brownish tumors with or without a cystic component and/or central fibrosis.
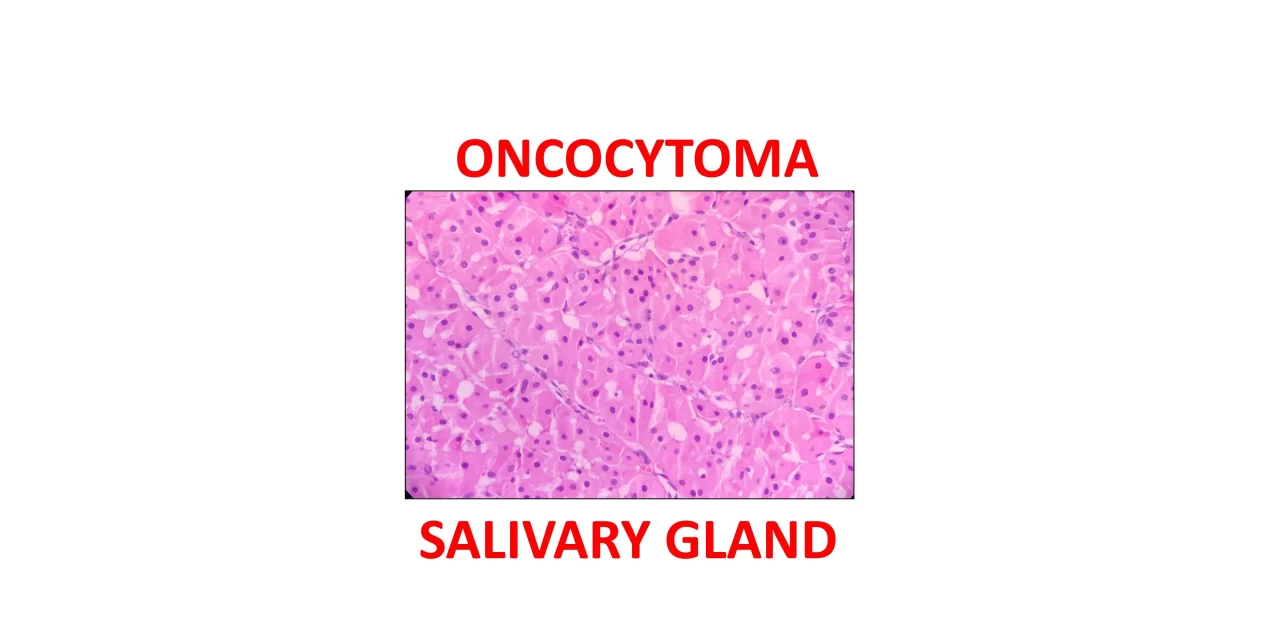
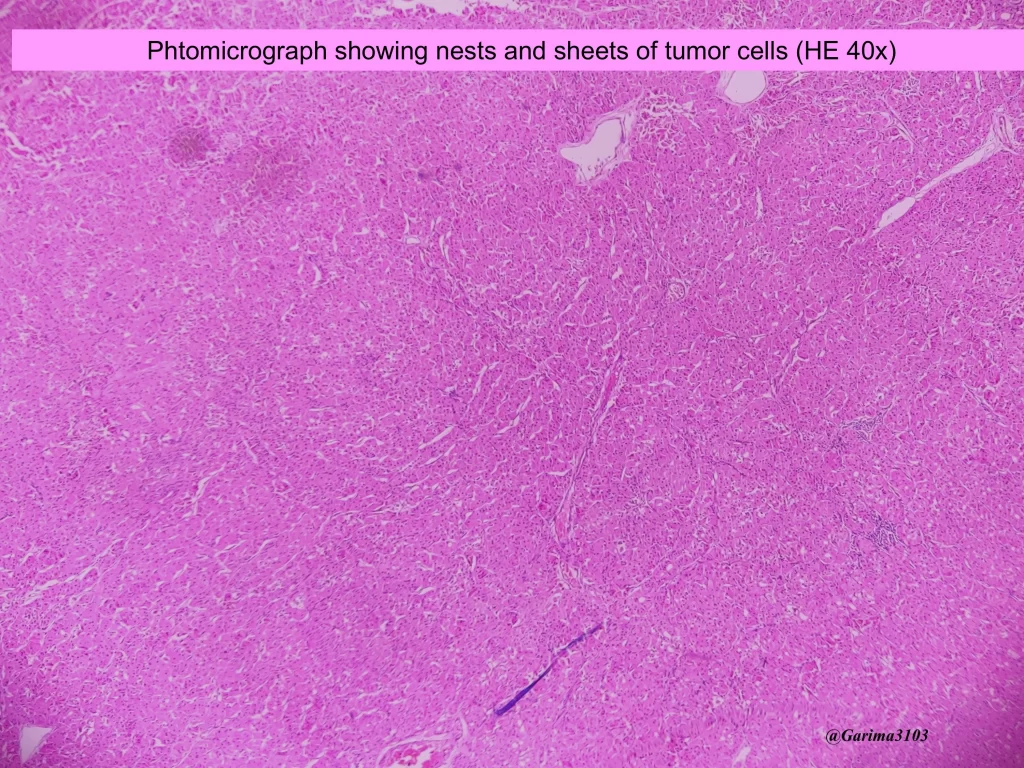
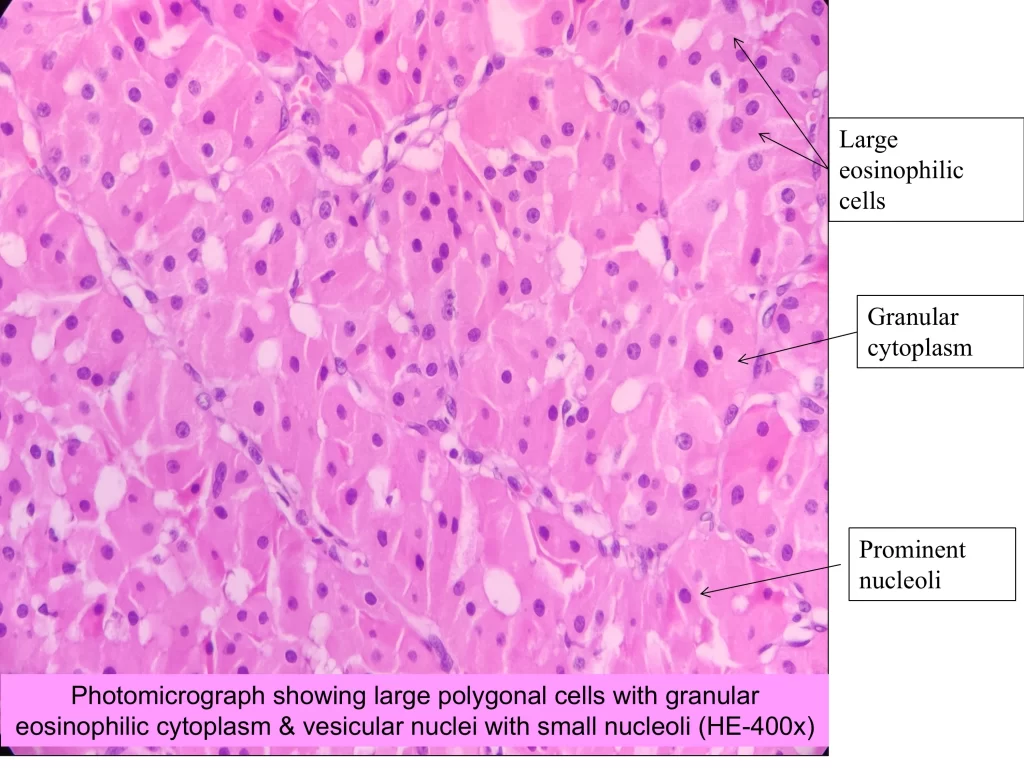
What are the microscopic features of oncocytoma
Well-circumscribed tumors with sheets and nests of oncocytic cells separated by a thin fibrovascular stroma
Oncocytic cells are large epithelial cells with abundant eosinophilic granular cytoplasm
Oncocytes have centrally placed uniform vesicular nuclei with prominent single nucleoli
Clear cell oncocytoma: Presence of glycogen and fixation artifacts causes the clear cell change
What are the histopathologic differential diagnoses?
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma – Absence of PAX8; p63-positive basal cells in oncocytoma
Oncocytic Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma – MAML2 rearrangement
Warthin Tumor – Cytology smears show a lymphoid component, mucus, and necrosis
What is the treatment for oncocytoma?
Surgical management with radical or superficial parotidectomy is the cornerstone of therapy. Recurrence or malignant transformation is exceedingly rare.