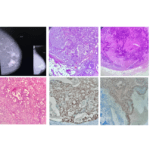
Pathology of Secretory Breast Carcinoma
Pathology of Secretory Breast Carcinoma Secretory breast carcinoma, originally referred to as “juvenile carcinoma,” was first identified by McDivitt and Stewart in 1966. It was later renamed by
Read MoreRHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS- ETIOPATHOGENESIS
What is rheumatoid arthritis (RA)? Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints. It causes inflammation, leading to joint pain, swelling, and eventually joint damage
Read MoreAutoimmune disease- Pathogenesis
Why do autoimmune diseases develop? Autoimmune diseases develop when there is an imbalance between the activation of lymphocytes (immune cells) and the mechanisms that keep them from attacking the
Read MoreAutoimmune disease: Self tolerance
What is an autoimmune disease? An autoimmune disease occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. This happens due to an immune reaction against self-antigens. When can a
Read MoreHyperaldosteronism
What is hyperaldosteronism? Hyperaldosteronism is a condition characterized by excessive production of aldosterone, a steroid hormone responsible for regulating sodium and potassium levels, and thus
Read MoreCushing’s syndrome
What is Cushing's syndrome? Cushing's syndrome, also known as hypercortisolism, is a condition characterized by an excess of cortisol in the body. It can arise from various causes, leading to
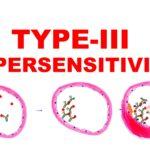
Read MoreType III hypersensitivity
What is Type III hypersensitivity? Type III hypersensitivity, also known as immune complex hypersensitivity, is an immune response that involves the formation of immune complexes (antigen-antibody
Read MoreType II Hypersensitivity
What is Type II Hypersensitivity? Type II hypersensitivity, also known as antibody-mediated hypersensitivity, involves the immune system's response where antibodies interact antigens attached to cell
Read More