Fibroadenoma Breast
Fibroadenoma is the most common benign tumor of the female breast.
Can occur at any age, but most patients are young and in their reproductive age group.
Clinically , fibroadenomas presents as solitary, freely mobile lump in the breast. Because of their high mobility, they are also referred to as mouse in the breast/breast mouse.
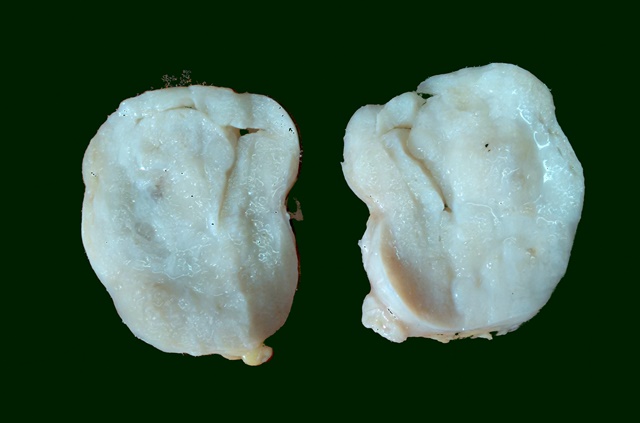
Gross: They are well circumscribed tumors often measuring 3-4 cm. Rarely they can grow up to 10 cm in diameter. The cut surface is firm and greywhite in color and glistening. Sometimes slit like spaces are seen.
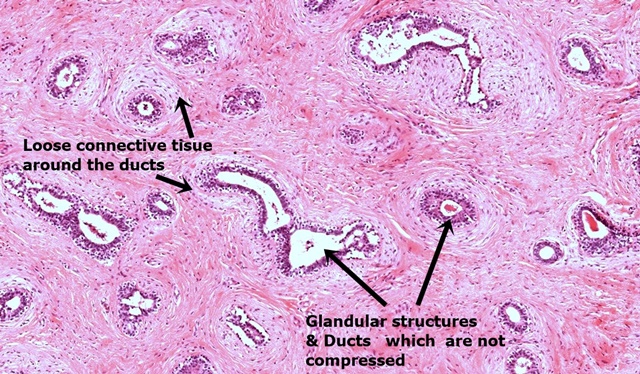
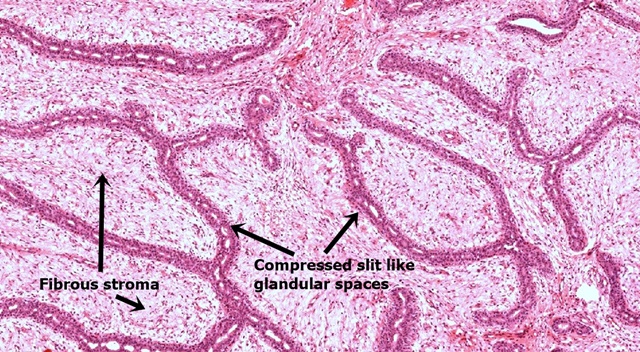
Microscopy: it contains a mixture of epithelial and stromal tissue. The stromal component is usually predominant. The epithelial tissue is composed of ducts lined by double layered epithelium and the stromal component is made of fibrous tissue.
Based on the growth of the fibrous components, the microscopy is divided into two patterns
Intracanalicular pattern: The stroma compresses the ducts into irregular slit like spaces.
Pericanalicular Pattern: The ducts will have maintained their patency and the stroma proliferates around these patent ducts.
QUESTION AND ANSWERS
- What are the types of fibroadenoma ?
The different types of fibroadenomas are
- Juvenile fibroadenoma: a variant which is seen in young and adolescent women, with history of rapid growth. Here, there is epithelial and stromal hyperplasia
- Complex fibroadenoma: Fibroadenoma with fibrocystic like changes, with the presence of apocrine change, sclerosing adenosis and cyst formation
- Giant fibroadenoma : The tumor reaches massive size, ie greater than 10 cm. some authors classify this as juvenile type.
- What is the importance of complex fibroadenoma?
Complex fibroadenomas have a slightly higher risk for subsequent malignancy.
- Can fibroadenomas turn malignant?
Simple fibroadenomas do not have any risk of malignancy.
The risk of subsequent malignancyin fibroadenomas is seen in
- Complex fibroadenomas
- Fibroadenomas in older women
- Fibroadenoma in women with family history of breast carcinoma