What is cementoblastoma?
Cementoblastoma is a benign odontogenic neoplasm that forms a rounded mass of cementum on the root of a tooth, making up about 3% of all odontogenic tumors. It is classified as a benign mesenchymal odontogenic tumor in the 5th edition of the WHO classification of tumors.
Where does cementoblastoma most commonly occur?
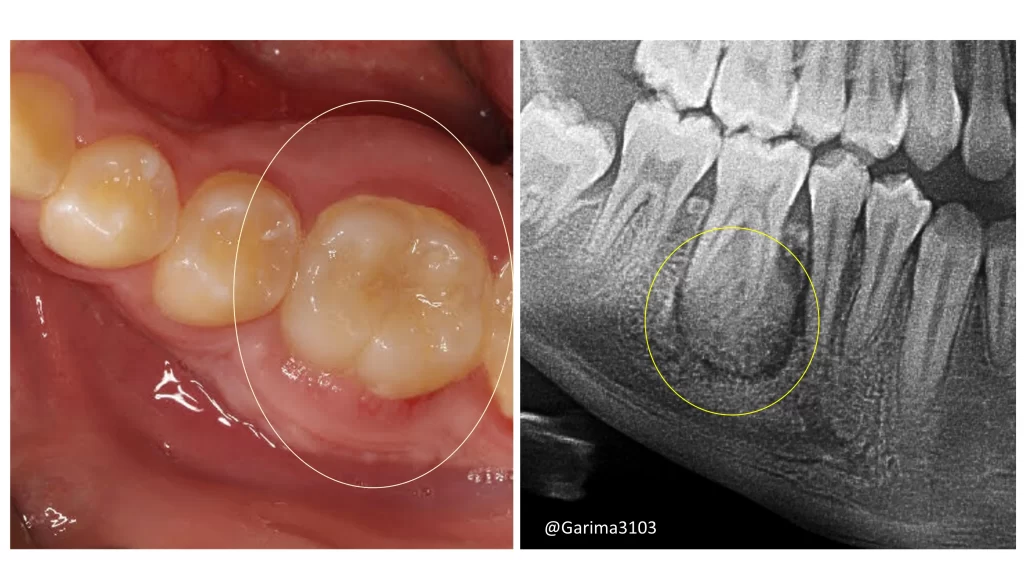
It typically occurs in the posterior mandible, usually on the permanent first molar. It can also affect mandibular premolars and maxillary molars but rarely involves deciduous dentition.
What are the clinical features of cementoblastoma?
• Presents as a slow-growing, painful mass.
• Associated with a vital tooth in most cases.
What are the radiographic features of cementoblastoma?
• A characteristic radiopaque mass with a radiolucent rim continuous with the periodontal ligament.
What are the common radiographic differential diagnoses?
Radiographically, the differentials include
Odontomas
• Found between the roots of teeth.
• Appear as irregular masses of calcified material.
Condensing Osteitis
• Does not show a radiolucent internal rim.
• Appears as a homogeneously dense radiopaque area.
Hypercementosis
• Radiopaque lesion with a visible periodontal ligament (PDL) space surrounding the lesion.
What is the pathogenesis of cementoblastoma?
Cementoblastomas often exhibit FOS(Finkel-Biskis-Jinkins Osteosarcoma) gene rearrangements and show FOS overexpression.
The FOS gene (part of the FOS family of proto-oncogenes) plays a role in cell growth, differentiation, and proliferation. When rearranged or overexpressed, it can lead to abnormal cell activity, contributing to tumor development.
These genetic features are not unique to cementoblastomas; they are also seen in other bone-forming tumors, such as osteoid osteoma and osteoblastoma, which share similar histological and clinical characteristics.
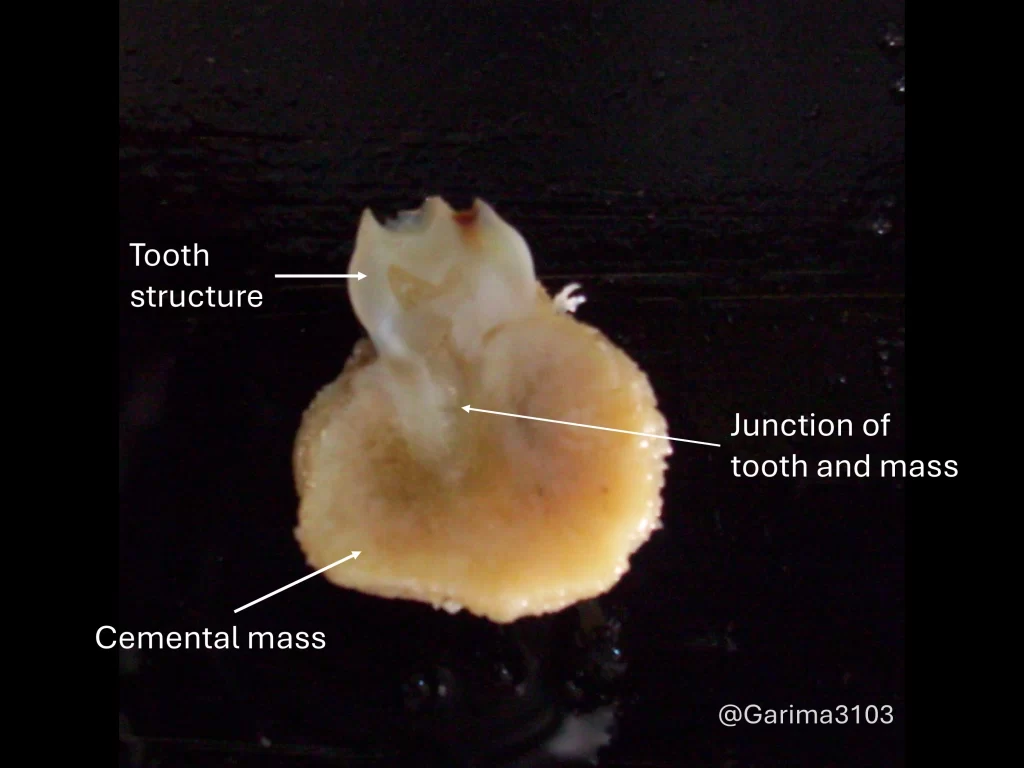
What does cementoblastoma look like grossly?
• Appears as a calcified mass adherent to and fused with the root of a vital tooth.
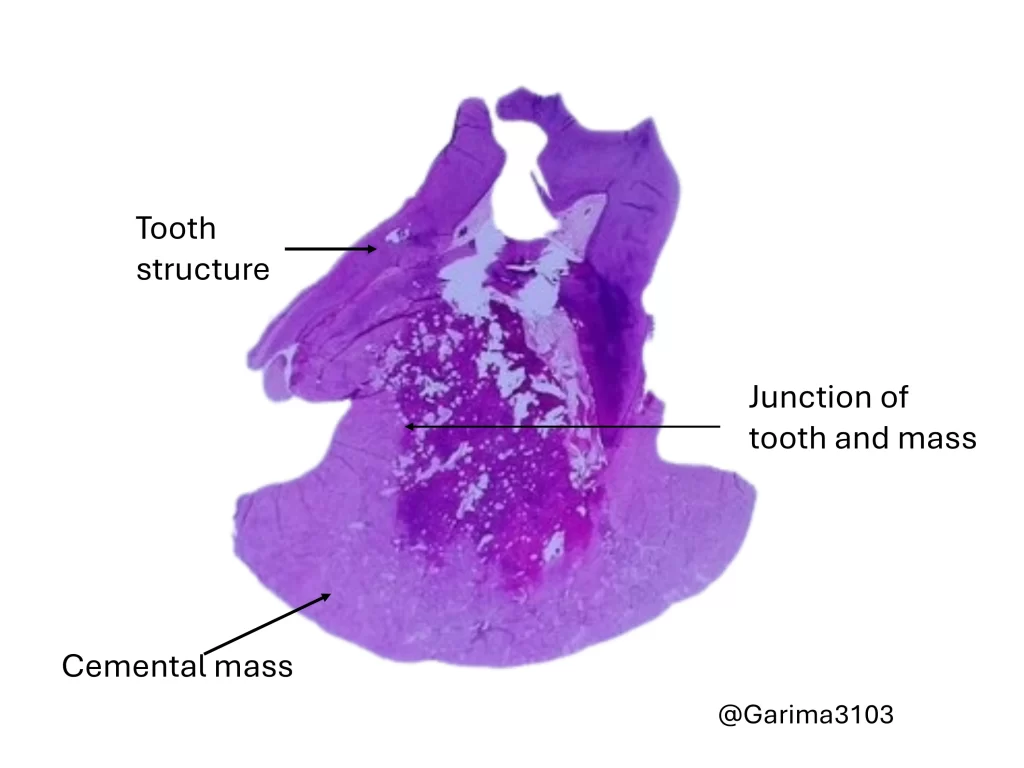
What are the microscopic features?
• Dense cellular cementum similar to bone.
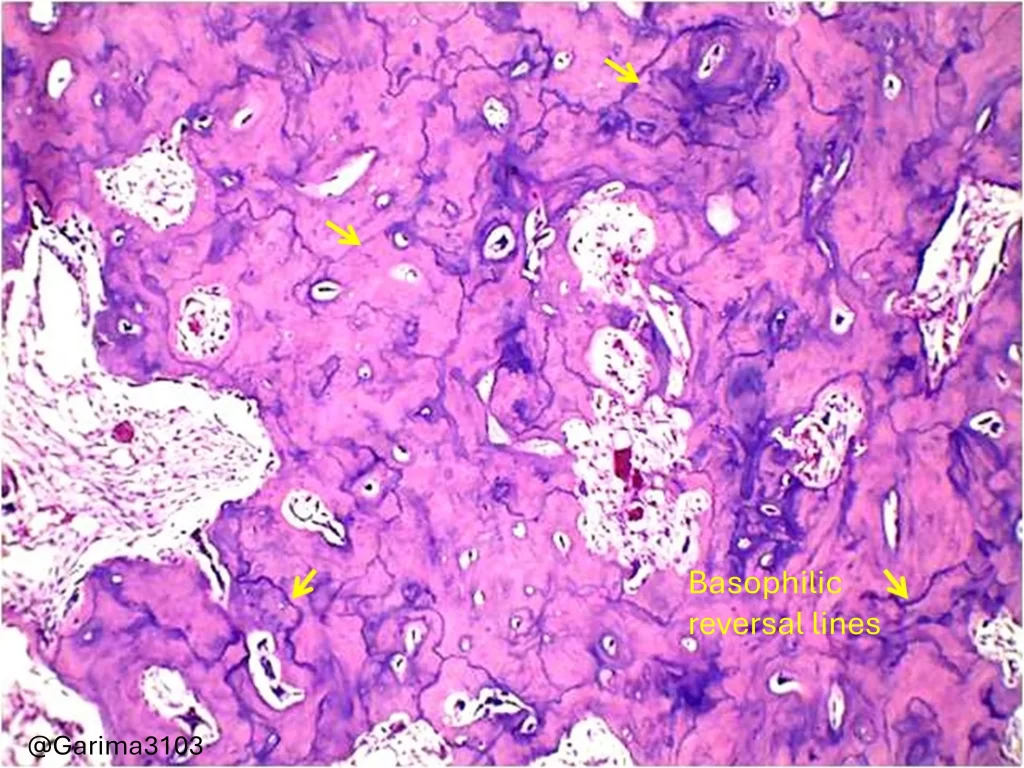
• Prominent reversal lines.
• Fused with the tooth root.
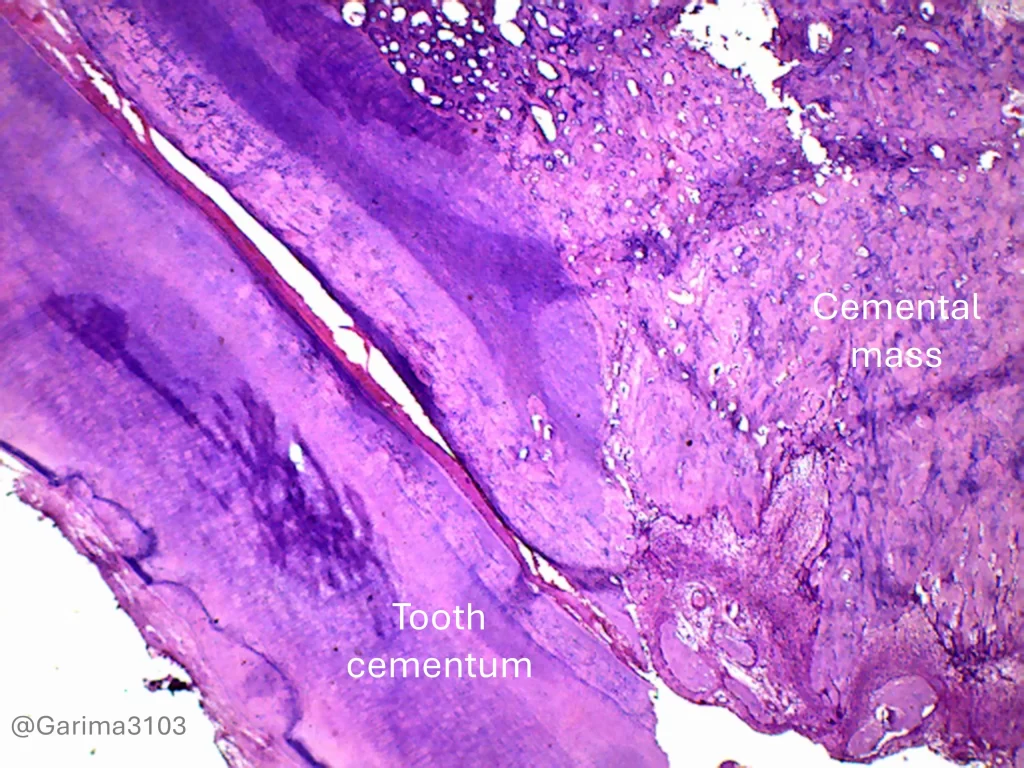
Whole-mount view, tooth root with cementum, H&E stain, 4x magnification
H&E stain, 10x magnification
It consists of dense cellular cementum resembling bone, often showing prominent reversal lines and is fused to the resorbed surface of the tooth root.
Basophilic reversal lines ( yellow arrows) H&E stain, 40x magnification
What are the histopathological differential diagnoses?
• Osteoblastoma: Key distinction is the aggressive growth pattern of osteoblastoma versus the root association seen in cementoblastoma.
How is cementoblastoma treated?
• The preferred treatment is complete surgical excision along with the extraction of the associated tooth, even if the pulp is vital.
What is the prognosis of cementoblastoma?
• Recurrence is rare if the mass and associated tooth are completely removed.
• There is a potential for recurrence if an attempt is made to conserve the tooth.