Introduction and Definition
Respiratory tract infections are the most common of all infections and account for largest number of workdays lost.
Pneumonia can be defined as any infection of the lung parenchyma.
Pneumonia can result when these normal defense mechanisms are compromised
• Suppression of cough reflex – coma, anaesthesia, drugs
• Injury to mucociliary apparatus – cigarette smoking, inhalation of hot or corrosive gases
• Accumulation of mucous – cystic fibrosis, obstructive conditions
• Impairment of macrophage phagocytic activity – alcohol, tobacco smoke, anoxia.
• Fluid in alveoli – pulmonary congestion and oedema
• Defects of immune system
Pneumonia can be classified in many ways
1. Etiologic classification – bacterial, viral, fungal
2. Pneumonia syndromes – will be discussed below..
3. Depending on lung involvement – lobar or
Bronchopneumonia
4. Depending on clinical symptoms – acute/ chronic,
typical/ atypical
Pneumonia syndromes
1. Community acquired pneumonia
• Most common
• Pneumonia in healthy individual from the community
• Eg- streptococci, hemophilus, Moraxella, staph, legionella, RSV, Parainfluenza virus, adenovirus..
2. Health Care associated pneumonia
• Pneumonia in a person with history of hospitalisation of at least 2 days within recent past, or attending hemidialysis clinic or receiving IV antibiotics/ chemotherapy or wound
care.
• MRSA, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
3. Hospital acquired pneumonia
• Occurs in the course of hospital stay
• E. coli, Klebsiella, serratia, MRSA
4. Aspiration pneumonia – anaerobes
5. Chronic pneumonia – TB, nocardia, actinomycetes
6. Necrotising pneumonia – anaerobes, staph aureus,klebsiella, strep pyogenes
7. Pneumonia in immune compromised – CMV,pneumocystis jiroveci, MAC, aspergillosis,..
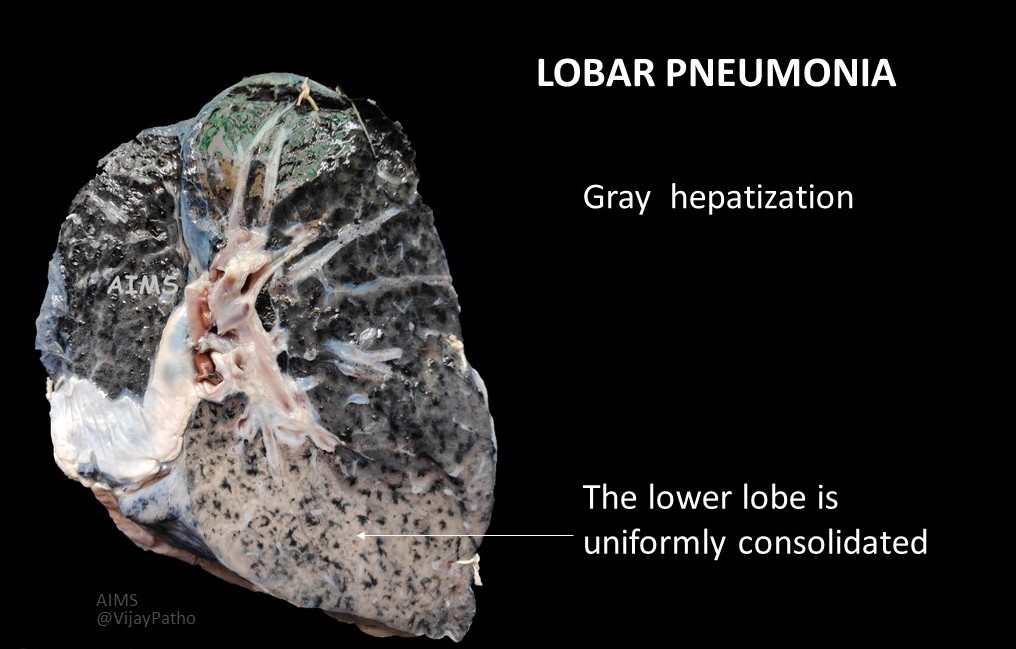
Morphology of Lobar pneumonia
A large portion of one lobe or entire lobe of the lung is involved
In the initial stages, it can appear as bronchopneumonia with patchy involvement, the patches can later coalesce to give rise to lobar pneumonia
Photo credit: Dr Pradeep Vaideeswar
Stages of Lobar pneumonia
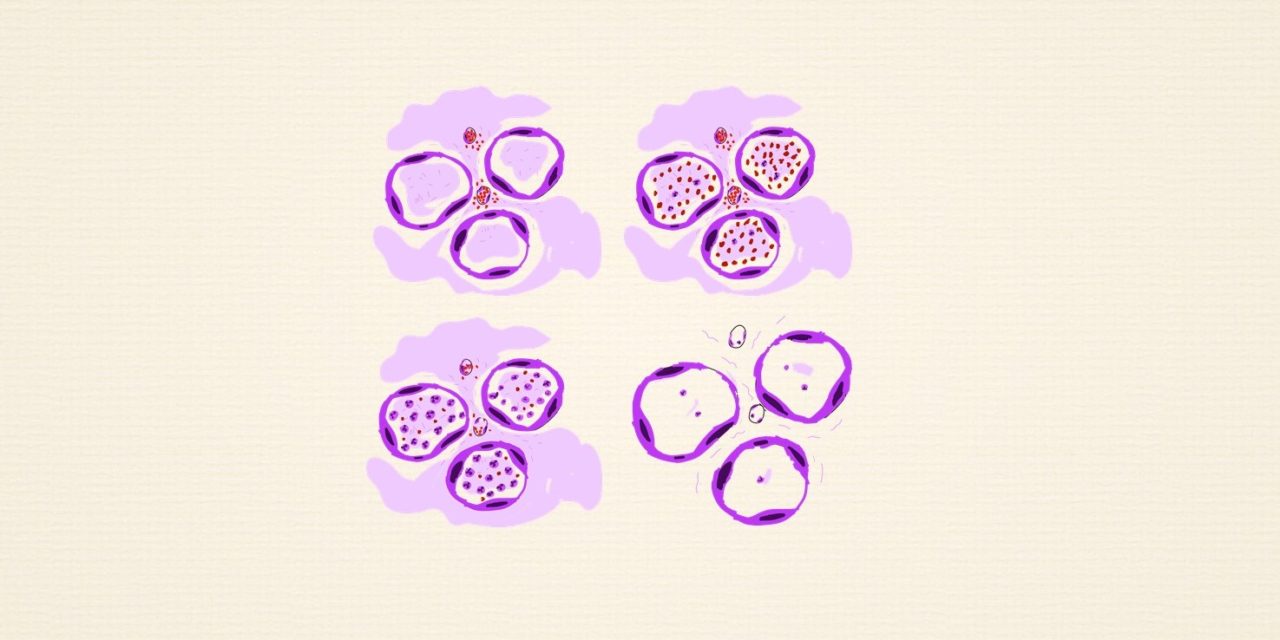
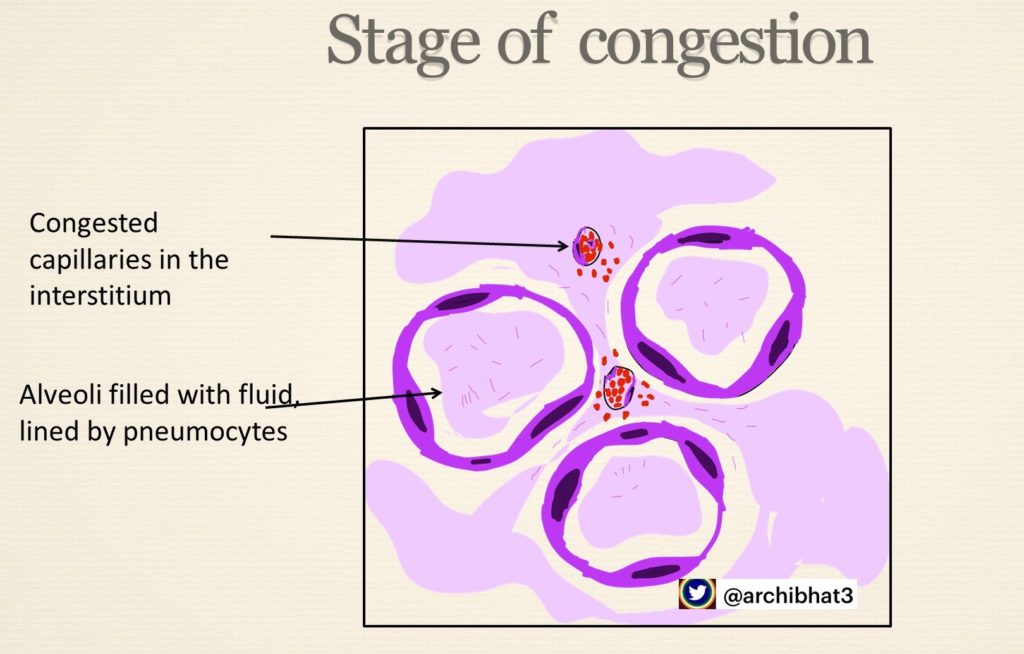
1 . Stage of congestion – vascular engorgement, heavy boggy lungs
2. Stage of Red hepatisation – red firm lungs, alveolar spaces with neutrophils, red cells and fibrin
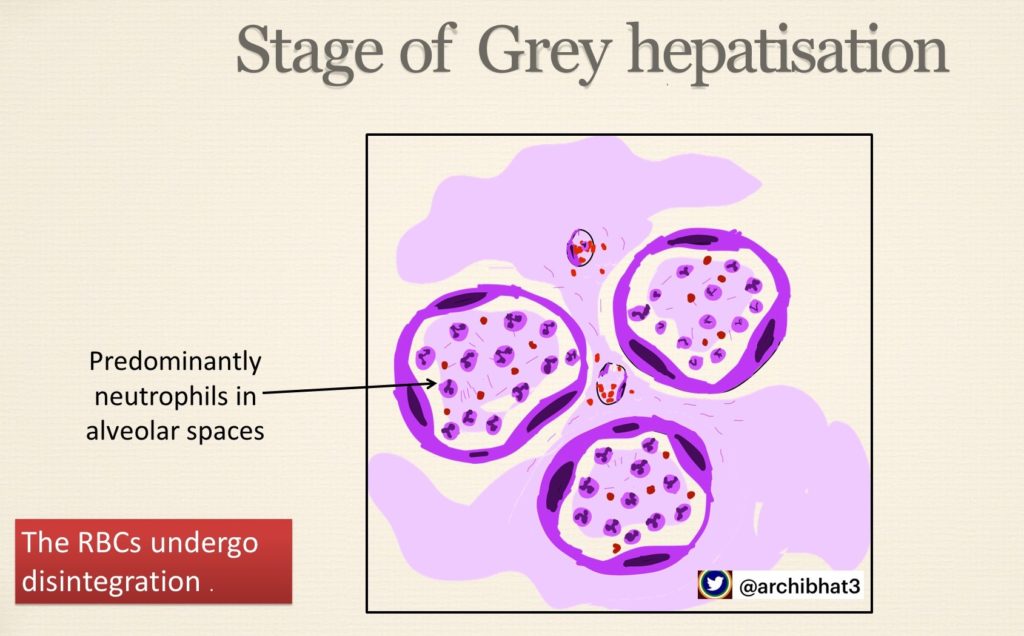
3. Stage of Grey hepatisation – grey brown firm lungs, alveolar spaces with neutrophils, red cells disintegrate
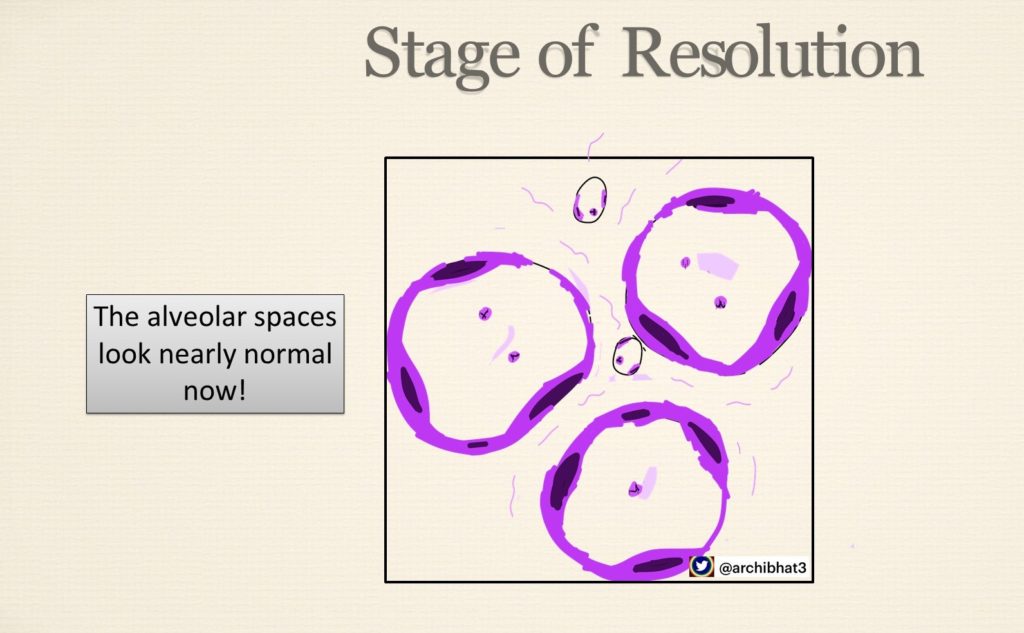
4. Stage of Resolution – infected exudate coughed out, ingested by macrophages or organised by fibrosis
Hepat = Liver, Hepatisation refers to change in consistency of lung from normal spongy to firm “Liver like”
The ilustrations of the different stages of penumonia are as below
Complications
Abscess formation
Pleural effusion
Emphyema
Metastatic abscesses, meningitis, endocarditis, arthritis