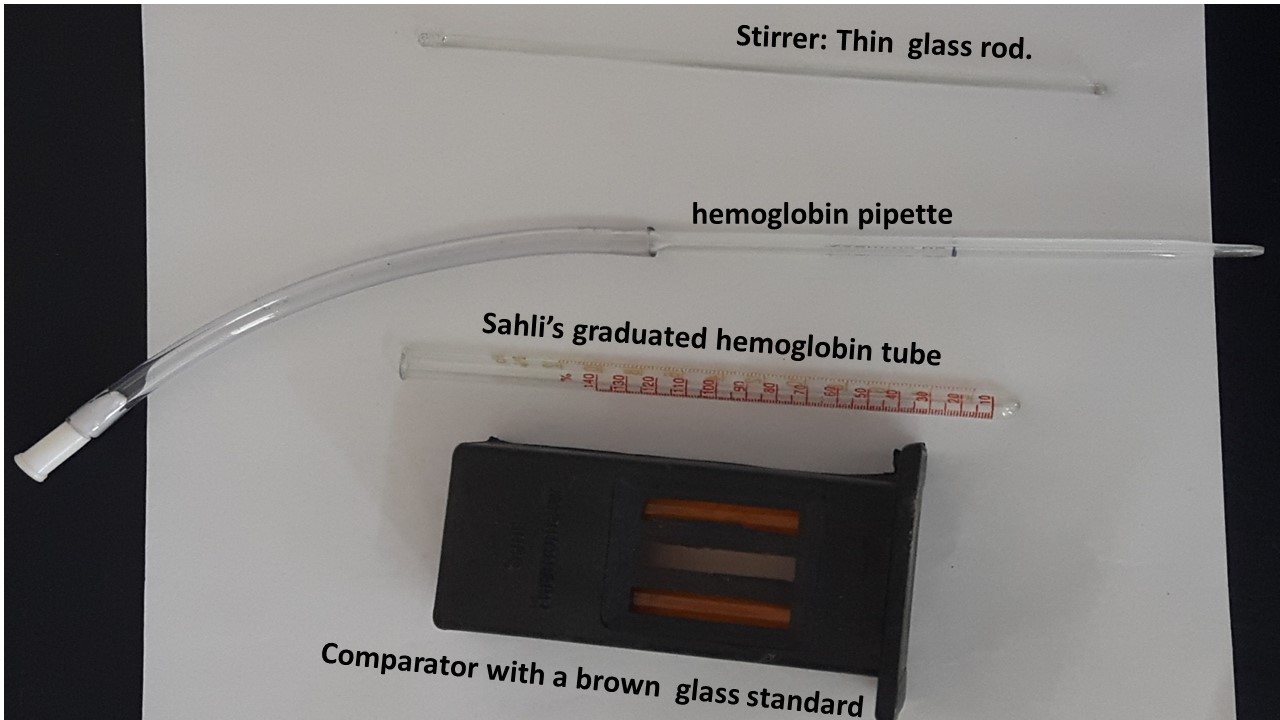
Sahli’s Hemoglobinometer
Parts-
a. Sahli’s graduated hemoglobin tube (marked in grams percent g% (2-24) and percentage % ( 10 -140)
b. Comparator with a brown glass standard. opaque white glass is present at the back to provide uniform illumination.
c. Sahli’s pipette or hemoglobin pipette (marked at 20µl or 0.02 ml). No bulb
d. Stirrer: Thin glass rod .
1. what are the indications of hemoglobin estimation?
• To determine presence and severity of anemia
• Screening for polycythemia
• To assess response to specific therapy in anemia.
• Estimation of red cell indices
• Selection of blood donors.
2. what are the different methods of hemoglobin estimation
the different methods are
a. visual method/colour comparison method
b. spectrophotometric method
c. Gasometric method
d. Automated method/hemoglobinometry
e. Miscellaneous : specific gravity method
3. What is principle of acid hematin method of hemoglobin estimation?
Blood is mixed with an acid solution so that hemoglobin is converted to brown-colored acid hematin. This is then diluted with water till the brown color
matches that of the brown glass standard. The hemoglobin value is read directly from the scale.
4. What are the reagents used?
1. N/10 hydrochloric acid
2. Distilled water
5. Explain the procedure of Sahli’s method of estimation of hemoglobin.
Procedure
a. After ensuring the hemoglobin pipette and tube are dry,add N/10 HCl into the tube upto mark 2g%
b. Mix the EDTA sample gently and fill the pipette with 0.02ml blood. Make sure that no air bubbles enter into the pipette. If it enters, discard and pipette again. Wipe the external surface of the pipette to remove any excess blood.
c. Add the blood into the tube containing HCl. Wash out the contents of the hemoglobin pipette by drawing in and blowing out the acid few times so that the blood is mixed with the acid thoroughly.
d. Allow to stand undisturbed for 10min.( This is because, maximum conversion of hemoglobin to acid hematin, occurs in the first ten minutes )
e. Place the hemoglobinometer tube in the comparator and add distilled water to the solution drop by drop. Stir with the glass rod till it’s color matches with that of the comparator glass. While matching the color, the glass rod must be removed from the solution and held vertically in the tube.( Note that the stirrer should be above the level of the solution and not out of the tube )
f. The reading of the lower meniscus of the solution should be noted as the result. Express the hemoglobin content as g%.
6. what are the advantages of this method?
Cheap and can be used for hemoglobin estimation where automated hematology analyser is not available. No technical expertise is needed to perform.
7. what are the disadvantages of this method?
a. 95% color of acid hematin is formed in 10 mins. The color of acid hematin fades with time.
b. It is difficult to match perfectly with the glass comparator.
c. Carboxyhemoglobin, methemoglobin, and sulfhemoglobin are not converted to acid hematin.
d. Acid hematin solution is not stable and color formation is slow
e. Source of light will influence the visual comparison of colors.
f. Color of brown glass standard fades with time
g. Individual variation in matching of color is seen..
8. what are the other colorimetric method of hemoglobin estimation?
Ans-Visual methods: Tallqvist chart and WHO hemoglobin color scale.
Photoelectric methods: Cyanmethemoglobin (hemiglobincyanide) method, oxyhemoglobin method and alkaline hematin method.
9. What is most preferred method of hemoglobin estimation?
Ans-The cyanmethemoglobin method is the internationally recommended method.
10. what is the principle of cyanmethemoglobin method?
Blood is mixed in a solution containing potassium cyanide and potassium ferricyanide. The potassium ferricyanide converts Hb to methemoglobin which is converted to cyanmethemoglobin (HiCN) by potassium cyanide. The absorbance of the solution is then measured in a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 540nm. It can also be measured in a colorimeter using a yellow green filter.
11. what are the components of Drabkins solution?
Drabkin’s solution: pH7.0-7.4
It contains
Potassium cyanide 50 mg
Potassium ferricyanide 200 mg
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate 140 mg
Nonionic detergent 1 ml
Distilled water 1 L
The final solution should be clear and pale yellow in color.
12. What is Gasometric method of estimation of hemoglobin
Gasometric method of estimation of hemoglobin is done by using van Slyke apparatus,
It is the most accurate method.
However it is time consuming and the complex procedure.
Only used for research purposes and for standardization.
13. Name the quick and easy method done to screen blood donors for possible anemia
Specific gravity method: it only gives an estimate of hemoglobin and not a quantitative method
Principle: a drop of blood is dropped into a copper sulphate solution of a particular specific gravity. The drop falls rapidly if the specific gravity of blood is greater than specific gravity of copper sulphate, otherwise it may fall slowly or may float.
Blood with normal hemoglobin levels falls rapidly.
Blood with low hemoglobin concentration- falls slowly or floats.
Contributing Author: Dr Avinash Singh