RETINOBLASTOMA
Retinoblastoma along with neuroblastoma and leukemia is one of the most common malignancies of childhood. It is the most common intraocular neoplasm in childhood.
Retinoblastomas are predominantly unilateral but can be bilateral in 20 – 35% of cases ( in hereditary retinoblastoma)
Approximately 89% or retinoblastomas are diagnosed before 3 years of age.
The association of a midline intracranial neoplasm with bilateral retinoblastomas is known as trilateral Retinoblastoma. It is found in 4–8% of patients with hereditary retinoblastoma.
Genetics: it behaves as autosomal dominant with 90% penetrance. The gene involved is Retinoblastoma Gene which is a tumor suppressor gene. The chromosomal region 13q14 (the retinoblastoma gene—Rb gene)
10% inherited, 90% Sporadic
Clinical features
1. Strabismus & leukocoria( White pupil)- Most common
2. May present with uveitis, endopthalmitis or panopthalmitis
3. Advanced cases may present with proptosis or even distant metastasis
Morphology
Gross : Can be unifocal/multifocal. Unilateral/bilateral
Or
Endophytic: Growth towards the vitreous
Exophytic: grows towards subneural retinal space with detachment of retina.
Most often it is a combination of both types.
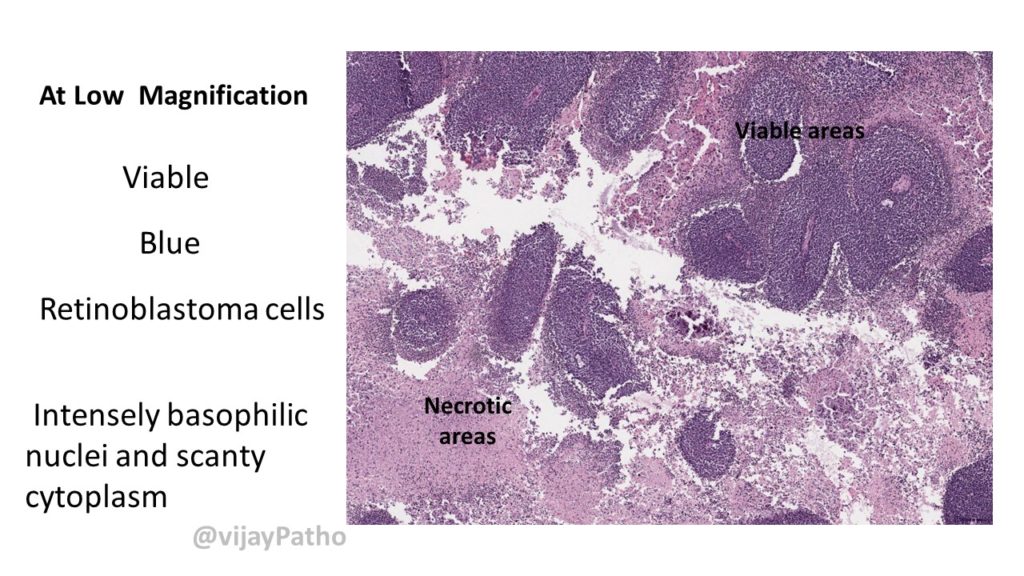
Microscopy: ( See the illustrations below)
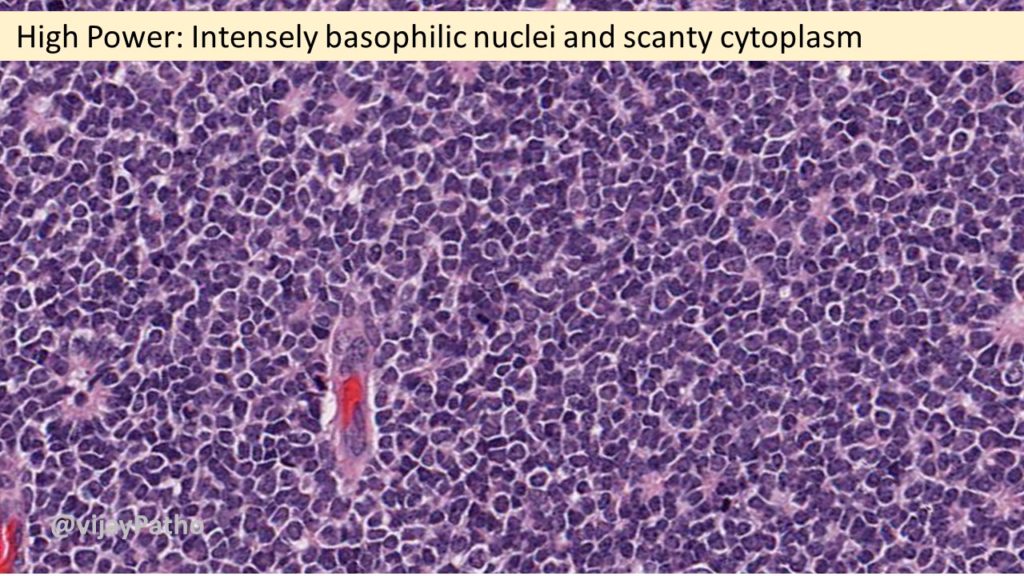
Cell- Retinoblastoma cell- undifferentiated cell.
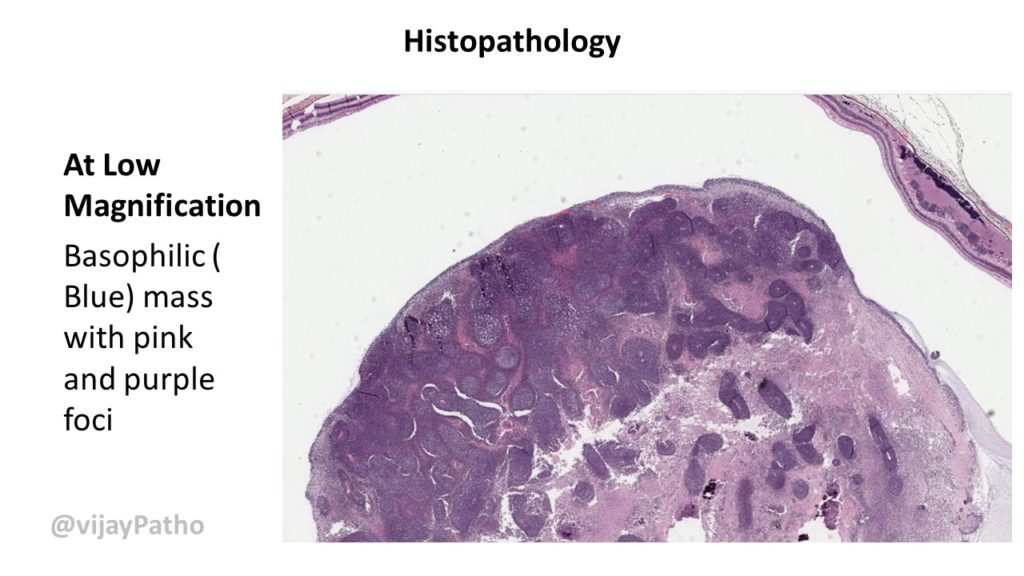
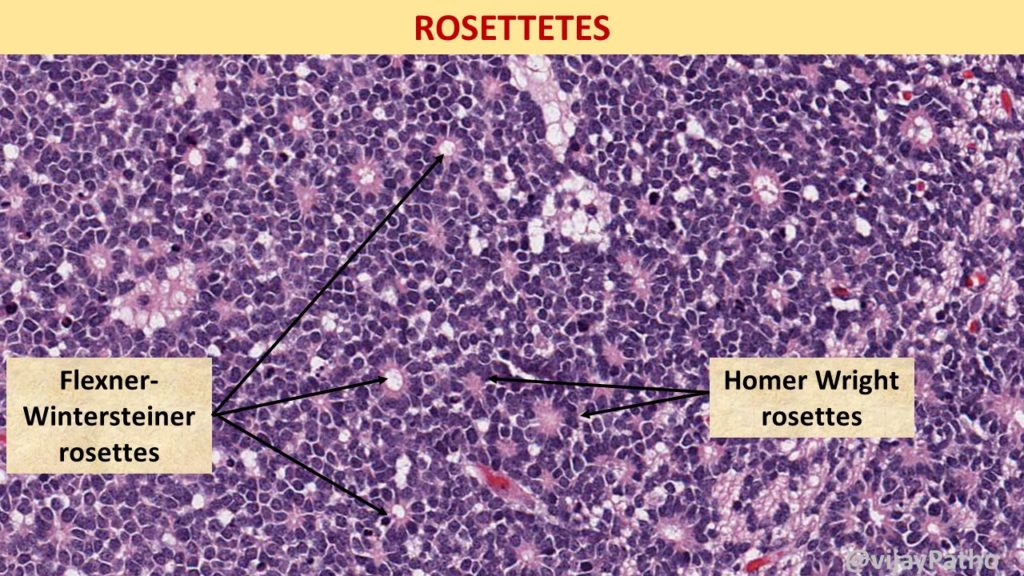
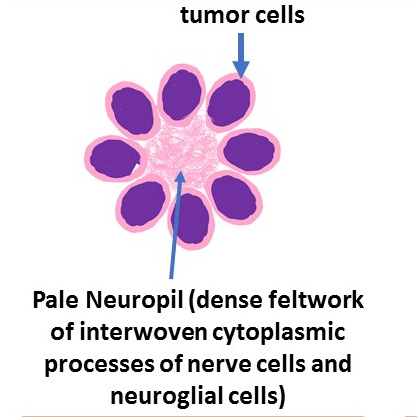
Rosettes: True & Pseudo.
True rosettes:
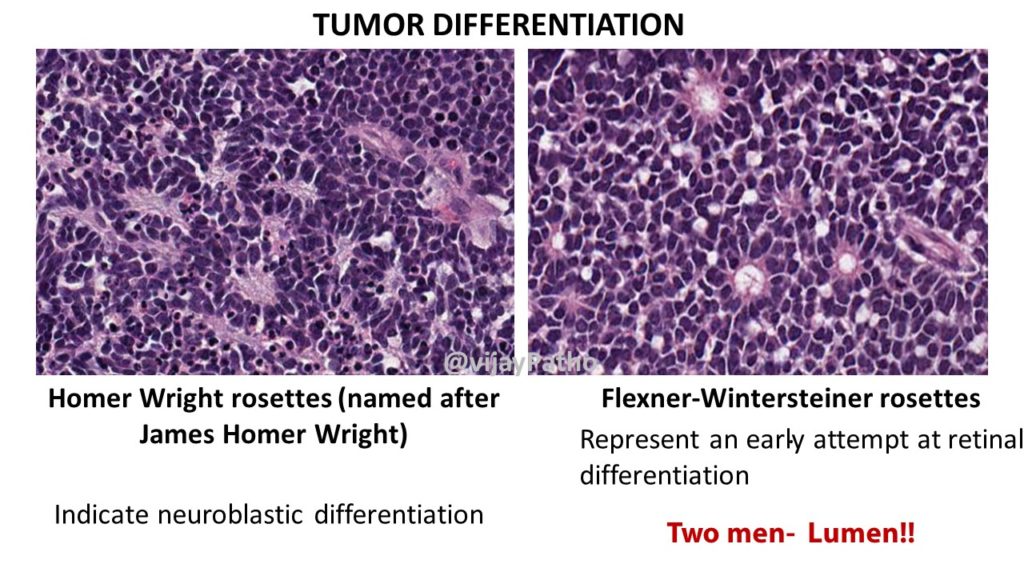
Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes : First described by first described by Simon Flexner an American Physician and Pathologist and Austrian ophthalmologist Hugo Wintersteiner. Two men- Lumen!!
These are composed of ring of cuboidal cells around a central LUMEN. Represent an early attempt at retinal differentiation. The lumen corresponds to subretinal space.
Homer Wright rosettes (named after James Homer Wright) : Indicate neuroblastic differentiation. They lack central lumen, the tangle of neural filaments occupies the centre.
Presence of Rosettes : Nonspecific.. Not Pathognomonic.
However, More Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes Rosettes- Favourable Prognosis
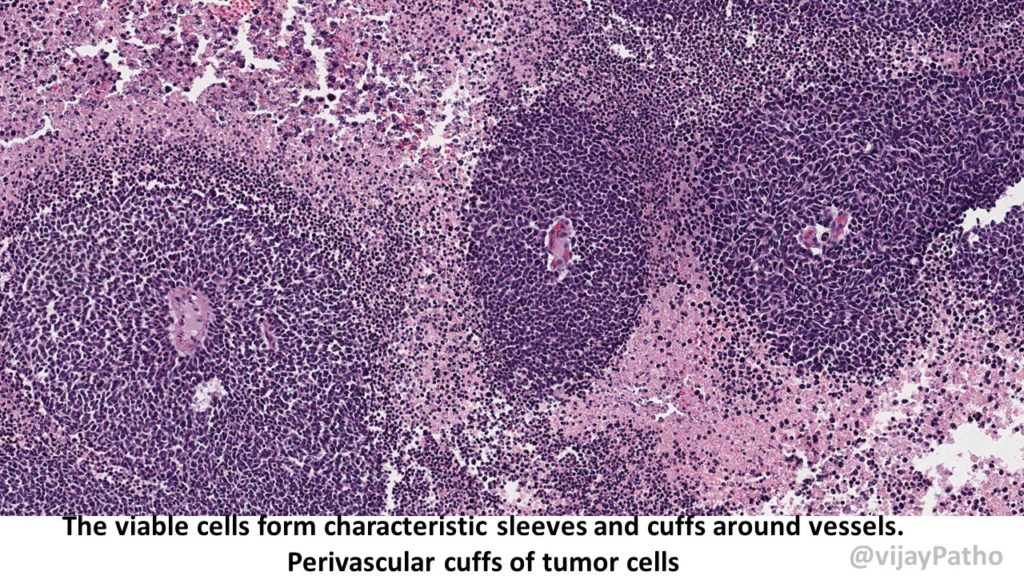
Pseudo rosettes: These are similar arrangement but around the blood vessels
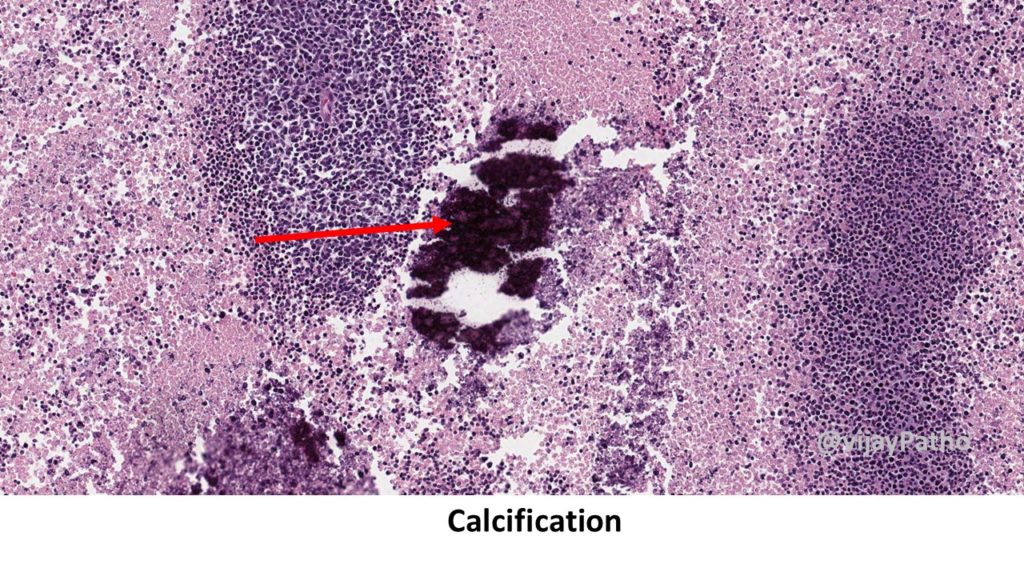
Necrosis
Calcification : dystrophic calcification in necrotic areas.
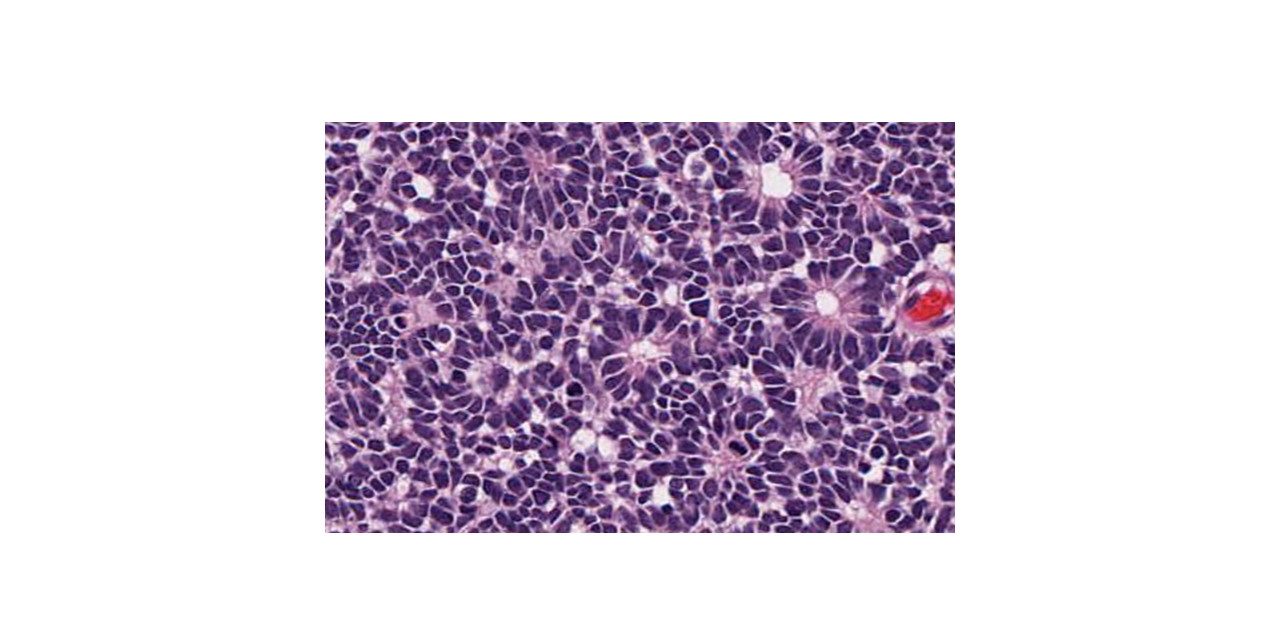
Fleurettes: 15% to 20% of retinoblastoma as harbor very well differentiated foci of actual photoreceptor differentiation. Aggregates of neoplastic photoreceptors called fleurettes
The term “fleurette” denotes a bouquet like arrangement of cytologically benign cells.
Neoplastic photoreceptor inner segments evident as bulbous eosinophilic processes form the “flowers” of the bouquet
RETINOMA/RETINOCYTOMA: tumor composed entirely of photoreceptor
Differentiation. A benign variant of retinoblastoma!
Poor prognostic indicators of retinoblastoma
Metastasis
Undifferentiated type
Massive choroidal and optic nerve invasion
Iris neovascularization ( rubeosis iridis)
click here read more about Rosettes in Pathology
Virtual slides of retnoblastoma can be accessed in pathpresenter.net in the link below







Recent Comments