Actinomycosis is a chronic, suppurative granulomatous inflammation caused by Actinomyces israelli.
Actinomyces israelli is a filamentous gram positive organism of genus Actinobacteria. It is a normal commensal in humans in the oral cavity, lower gastrointestinal tract and female genital tract.
This disease occurs worldwide and is often seen in tropical regions such as Asia, Africa, Central and South America. The foot of bare footed persons is the common site of primary infection.
Clinical features : Depending on the site of infection, actinomycosis is categorized into
1. Cervicofacial actinomycosis– often a sequel to periodontal disease, oral mucosal injury or dental caries. Initially the lesions are localized which later enlarges forming abscesses and draining sinus tracts through which “sulfur grains” will be extruded.
2. Thoracic/Respiratory tract actinomycosis– as a result of aspiration of the infected material
3. Abdominal actinomycosis– as a secondary complication or extension of thoracic infection. The common site being appendix , cecum and liver.
4. Pelvic actinomycosis- as a complication of intrauterine contraceptive devices.
Rarely they can involve joints, skin and central nervous system.
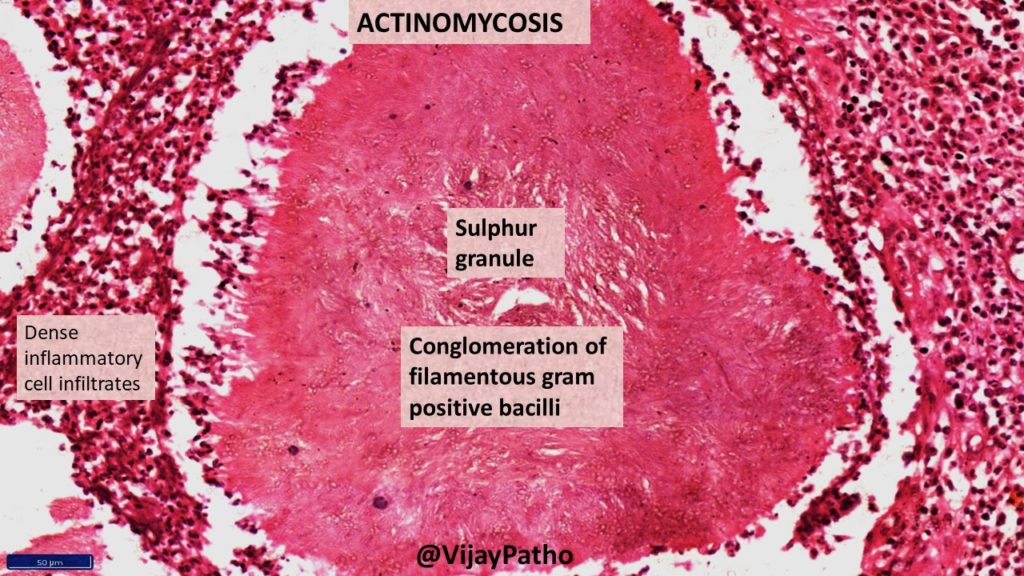
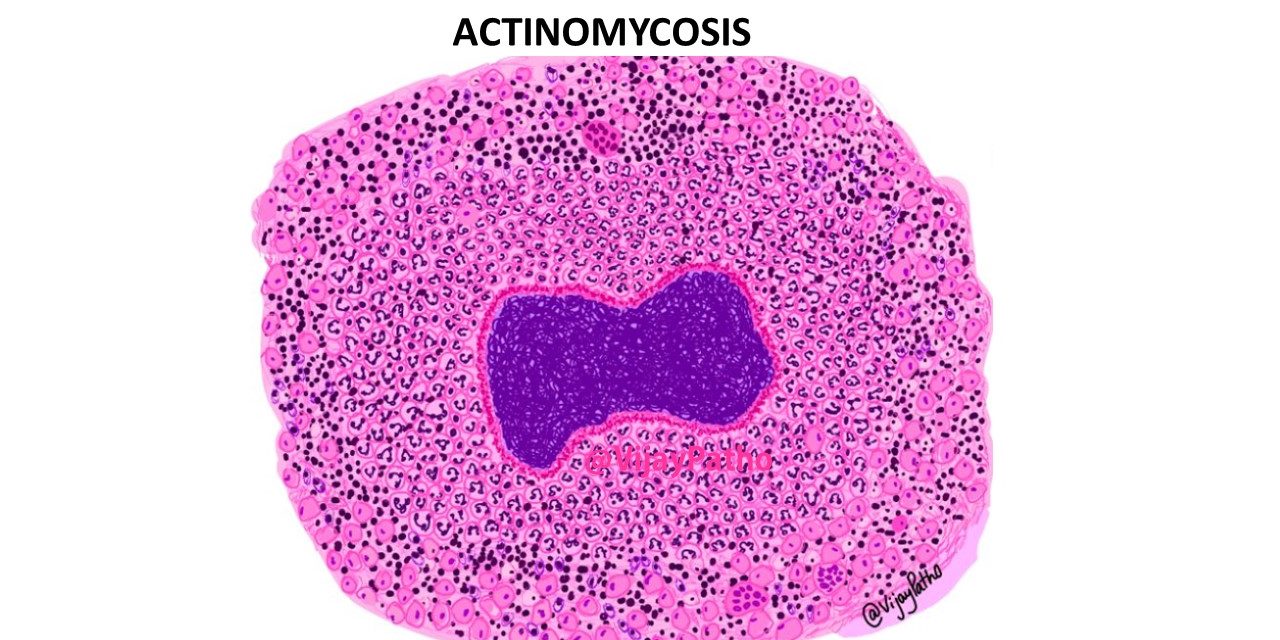
Microscopy: Typical Sulphur granules are evident in the midst of suppurative inflammation.
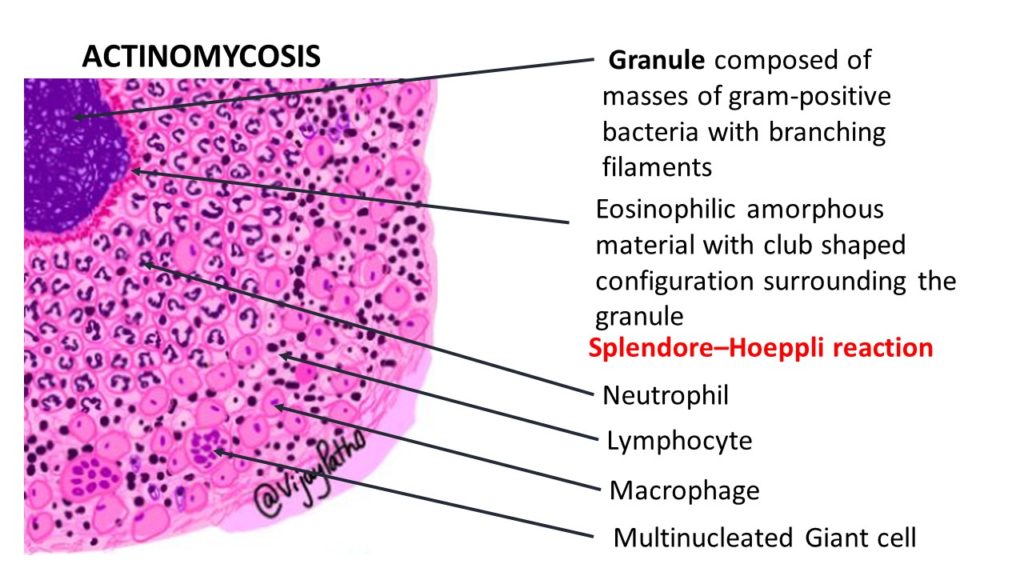
The Sulphur granules are actually conglomeration of filamentous gram positive bacilli trapped in a biofilm like material. These are seen in the center of suppurative inflammation. These bacilli are bordered by eosinophilic amorphous material with club shaped configuration . This is referred to as Splendore–Hoeppli reaction.
Splendore–Hoeppli phenomenon/reaction is characterized by aggregates of bacteria surrounded by radiating intensely eosinophilic material. This eosinophilic material is thought to be represent deposits of antigen–antibody complexes and debris from the inflammatory cells of the host.
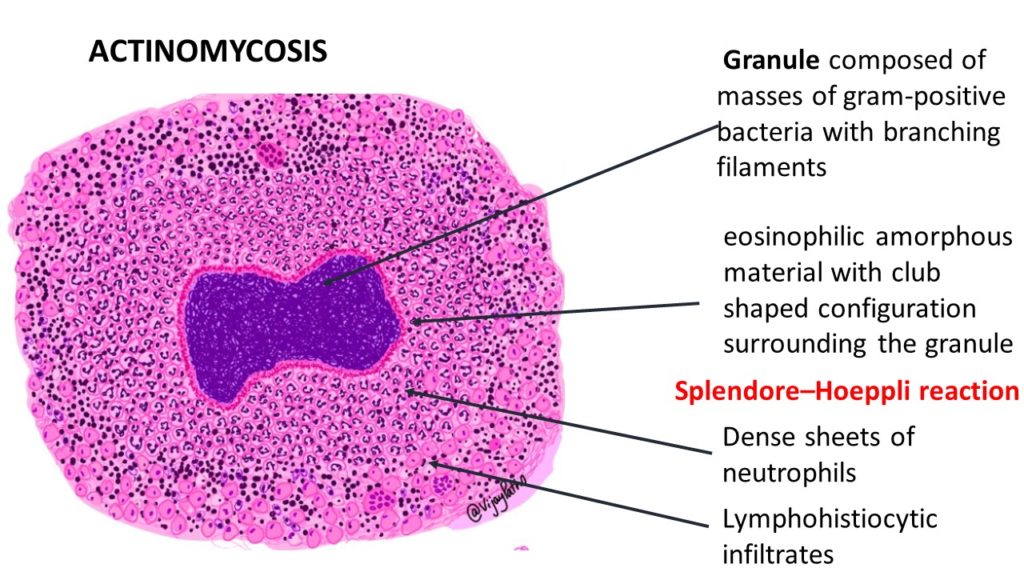
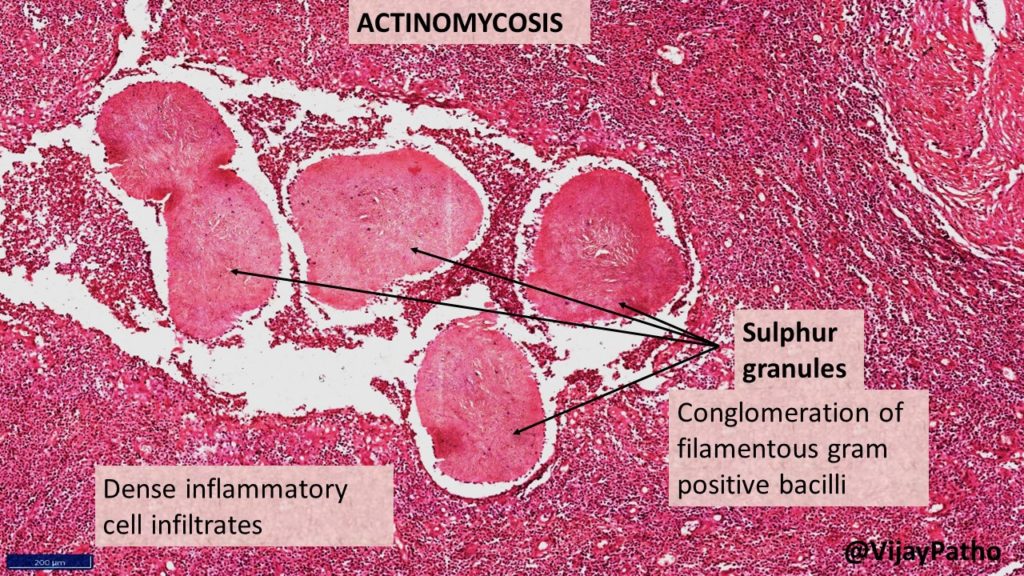
Surrounding the suppurative foci, chronic inflammatory cell infiltrates comprising of lymphocytes, plasma cells, histiocytes and few multinucleated giant cells can be seen . there will be increased connective stroma in the form of fibrosis in long standing lesions.
Treatment: Antimicrobial therapy with penicillin/amoxycillin is the treatment of choice. Surgical management can be required for drainage of abscesses.







Recent Comments